High-speed underwater wireless optical communications: from a perspective of advanced modulation formats [Invited]  Download: 969次
Download: 969次
Chao Fei 1,2Xiaojian Hong 1,2Ji Du 1,2Guowu Zhang 1,2Yuan Wang 1,2Xiaoman Shen 1,2Yuefeng Lu 1,2Yang Guo 1,2Sailing He 1,2,*
1 Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, National Engineering Research Center for Optical Instruments, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
2 Ningbo Research Institute, Zhejiang University, Ningbo 315100, China
Figures & Tables
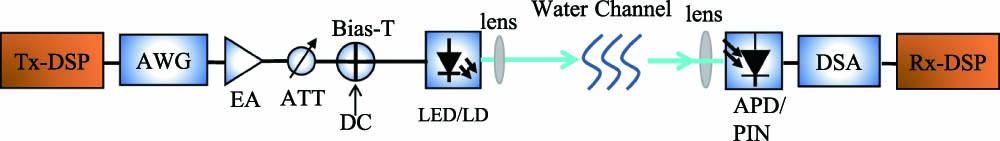
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the general UWOC setup in a lab experiment. AWG: arbitrary waveform generator; EA: electrical amplifier; ATT: adjustable attenuator; DC: direct current; LD: laser diode; APD: avalanche photodiode; DSA: digital serial analyzer; Tx-DSP: digital signal processing at the transmitter; Rx-DSP: digital signal processing at the receiver.
下载图片 查看原文
Fig. 2. Received optical power (ROP) and SNR versus transmission distance under tap water. w/: with; w/o: without; NLE: nonlinear equalization[39].
下载图片 查看原文
Fig. 3. (a) Received SNR versus the volume of added Maalox suspension after a 1 m underwater transmission. (b) Attenuation coefficient versus volume of the added Maalox suspension. (c)–(f) The snapshots of the optical beam passing through water of different turbidities which represent (c) “tap water”, (d) “clear ocean”, (e) “coastal ocean”, and (f) “harbor water”[39].
下载图片 查看原文
Fig. 4. (a) Shannon capacity limit under different underwater transmission distances. (b) Entropy of different subcarriers for 25 m and 35 m underwater transmission distances. (c) Graphical illustrations for bit-power loading and the PCS-256/1024QAM-DMT scheme of three different entropies. Note that the bars denote the probability of each modulation symbol[42].
下载图片 查看原文
Fig. 5. Received constellation diagrams of (a) bit-power loading, (b) PCS-256QAM-DMT for 35 m, and (c) PCS-1024QAM-DMT for 25 m underwater transmissions[36].
下载图片 查看原文
Table1. Summary of Recent Works in UWOC
| Authors | Transmitter type | Light output power | Photodetector | Modulation formats | Data rate | Distance (m) | Distance-data rate product (Gbps·m) | Real time |
|---|
| Xu et al.[30] | Blue LED | N/A | PIN | 16-QAM-OFDM | 161 Mb/s | 2 | 0.32 | N | | Tian et al.[10] | 440 nm micro-LED | N/A | PIN/APD | OOK | 800/200 Mb/s | 0.6/5.4 | 1.08 | N | | Wang et al.[33] | 521 nm LED | 160 mW | 2 PINs | 64-QAM-DMT, MRC | 2.175 Gb/s | 1.2 | 2.61 | N | | Zhou et al.[72] | RGBYC LED | | PIN | Bit-power loading DMT | 15.17 Gb/s | 1.2 | 18.2 | N | | Wang et al.[59] | 448 nm LED | N/A | APD | OOK | 25 Mb/s | 10 | 0.25 | Y | | Wang et al.[32] | 520 nm LD | 15 mW | MPPC | 32-QAM-OFDM | 312.03 Mb/s | 21 | 6.55 | N | | Oubei et al.[35] | 450 nm LD | 15 mW | APD | 16-QAM-OFDM | 4.8 Gb/s | 5.4 | 25.92 | N | | Chen et al.[36] | 520 nm LD | 15 mW | APD | 32-QAM-OFDM | 5.5 Gb/s | 5/21 | 115.5 | N | | Liu et al.[73] | 520 nm LD | 19.4 mW | PIN/APD | OOK | 2.7 Gb/s | 34.5 | 93.15 | N | | Fei et al.[39] | 450 nm LD | 20 mW | APD | Bit-power loading DMT, NE | 7.3 Gb/s | 15 | 109.95 | N | | Fei et al.[41] | 450 nm LD | 12.8 mW | APD | MB-DFT-S-DMT | 5.6 Gb/s | 55 | 308 | N | | Fei et al.[40] | 450 nm LD | 120 mW | PIN | Bit-power loading DMT, NE | 16.6/6.6 Gb/s | 5/55 | 462@35 m | N | | Li et al.[37] | Two 488 nm LDs | 20 mW | PIN | PAM4, injection locking | 16 Gb/s | 10 | 160 | N | | Li et al.[14] | Three 680 nm LDs | 3 mW | PIN | Injection locking, OOK | 25 Gb/s | 10 | 250 | N | | Huang et al.[38] | 450 nm LD | 120 mW | PIN/APD | 16-QAM-OFDM | 14.8/10.8 Gb/s | 1.7/10.2 | 25.16/110 | N | | Hong et al.[42] | 450 nm LD | 120 mW | PIN | PCS-DMT | 18.09/12.6 Gb/s | 5/35 | 441@35 m | N | | Wang et al.[44] | 520 nm LD | 15 mW | APD | OOK, NE | 500 Mb/s | 100 | 50 | N | | Hu et al.[43] | 532 nm LD | N/A | SPD | 256-PPM & RS, LDPC | ∼MHz | 120 | N/A | N | | JAMSTEC[52] | 450 nm LD | | PMT | N/A | 20 Mb/s | 120 | 2.4 | Y |
|
查看原文
Chao Fei, Xiaojian Hong, Ji Du, Guowu Zhang, Yuan Wang, Xiaoman Shen, Yuefeng Lu, Yang Guo, Sailing He. High-speed underwater wireless optical communications: from a perspective of advanced modulation formats [Invited][J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2019, 17(10): 100012.
 Download: 969次
Download: 969次