激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57 (7): 071602, 网络出版: 2020-03-31
钙钛矿微纳激光器研究进展  下载: 4356次特邀综述封底文章
下载: 4356次特邀综述封底文章
Review of Perovskite Micro -and Nano-Lasers
图 & 表
图 1. 钙钛矿晶体结构[22]。(a)钙钛矿晶胞单元结构图;(b)通式ABX3钙钛矿三维晶体结构图
Fig. 1. Perovskite crystal structure[22]. (a) Perovskite cell structure; (b) general ABX3 perovskite 3D crystal structure
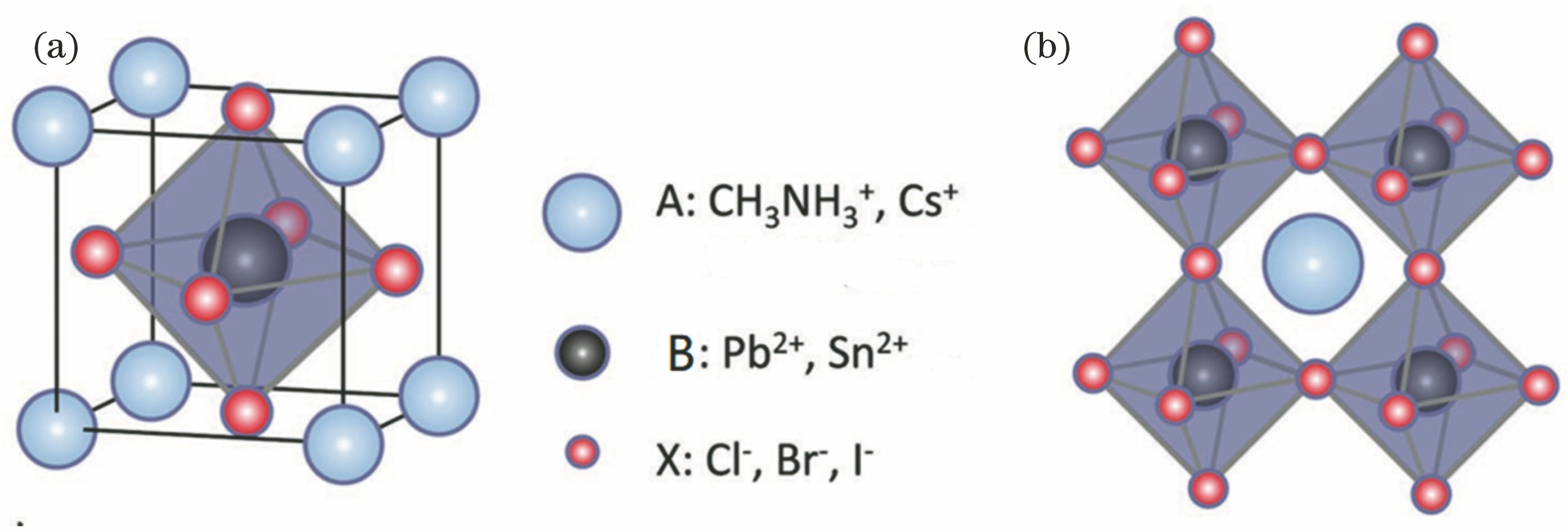
图 2. 钙钛矿纳米材料的波长可调谐。(a)改变MAPb(I1-xBrx)3中碘和溴的比例,可以实现786 nm到544 nm的调谐。上图是吸收光谱,下图是纳米复合物的图像[40];(b) MAPbX3(X=Cl、Br、I)改变卤化物的比例,可以实现390到790 nm可见红外的发射波长调谐[26];(c)(d)改变卤素原子,对无机钙钛矿CsPbX3的波长调谐[41-42];(e)对A位原子的调谐。改变FA和MA
Fig. 2. Wavelength tunability of perovskite nanomaterials. (a) By changing the ratio of iodine to bromine in MAPb(I1-xBrx)3, tuning of 786 to 544 nm can be achieved. Above is the absorption spectrum, below is an image of the nanocomposite[40]; (b) MAPbX3(X=Cl, Br, I) can be tuned to the emission wavelength from 390 to 790 nm in visible infrared by changing the ratio of hal

图 3. 有机无机杂化钙钛矿WGM 激光。(a)六边形和三角形钙钛矿MAPbI3-aXa纳米片的近红外WGM模式激光[59];(b)四边形钙钛矿MAPbBr3纳米片随着泵浦强度的增大,WGM激光模式的出现以及在阈值上下的纳米片光学激发图像[60];(c)三角形钙钛矿纳米片MAPbI3形成的WGM腔[61];(d)随着泵浦能量增加,三角形钙钛矿纳米片MAPbI3中出现WGM激光[61];(e)近似环形腔的WGM激光发射[59] ; (b) quadrilateral perovskite MAPbBr3 nanoplatelet with the increase of pump strength, the appearance of WGM laser and the optical excitation image of nanoplatelet above and below the threshold[60]; (c) WGM

图 4. 不同方案实现的WGM激光。(a)利用两个交叉的钙钛矿MAPbBr3纳米棒的横切面形成的WGM微腔[64];(b)可调谐尺寸的无机钙钛矿CsPbX3纳米球WGM微腔[65];(c)通过硅球作为谐振腔,实现WGM模式激光[35];(d)在可尺寸调谐的无机钙钛矿CsPbBr3微米线阵列中实现WGM激光[67]; (e)激光打印实现的钙钛矿MAPbBrxIy微盘,以及宽谱调谐的WGM激光的发射[Fig. 4. Different schemes of WGM mode laser. (a) WGM microcavity was formed by cross section of two crossed perovskite MAPbBr3 nanorods[64]; (b) tunable size of the perovskite CsPbX3 nano inorganic spheres WGM microcavity[65]; (c) WGM laser is realized by using silicon sphere as resonator[35]; (d) WGM mode laser is implemented

Fig. 4. Different schemes of WGM mode laser. (a) WGM microcavity was formed by cross section of two crossed perovskite MAPbBr3 nanorods[64]; (b) tunable size of the perovskite CsPbX3 nano inorganic spheres WGM microcavity[65]; (c) WGM laser is realized by using silicon sphere as resonator[35]; (d) WGM mode laser is implemented

图 5. 不同方案实现的WGM模式激光。(a)将无机钙钛矿CsPbBr3量子点嵌入二氧化硅球以及发光原理[72]; (b)将CsPbBr3-SiO2微米球放进直径40 μm的圆柱形微管中的发光图像以及WGM模式激光的原理[72];(c)CdS/CsPbBr3壳核结构[74]; (d) CsPbBr3/CdS核/壳结构放入圆柱形微管中产生WGM激光以及内嵌图为发光原理的图片[74]; (e)无机钙钛矿Cs4PbBr6微盘,随着激发光强增大,出现WGM激光
Fig. 5. Different schemes of WGM mode laser. (a) Schemes of inorganic perovskite CsPbBr3 quantum dots embedded silica sphere[72]; (b) CsPbBr3-SiO2 micro sphere into a diameter of 40 μm cylindrical tubes of luminous images, and the principle of laser WGM mode[72]; (c) CdS/CsPbBr3 shell/core structure[74]; (d) CsPb

图 6. 钙钛矿纳米线激光。 (a)纳米线结构发光原理图[76-77]; (b) MAPbX3钙钛矿纳米线随着泵浦光强的增加的光学图像[44]; (c)钙钛矿MAPbIxCl3-x纳米线随着泵浦强度的增加,F-P模式激光的强度分布[78]; (d)钙钛矿MAPbBr3、MAPbIxCl3-x和MAPbI3的F-P模式激光图以及激发阈值[Fig. 6. Perovskite nanowire laser. (a) Scheme of nanowire structure lasers[76-77]; (b) optical image of MAPbX3 perovskite nanowires with increased pump light intensity[44]; (c) with the increase of pumping intensity, intensity distribution of F-P mode perovskite MAPbIxCl3-x nanowires laser[
Fig. 6. Perovskite nanowire laser. (a) Scheme of nanowire structure lasers[76-77]; (b) optical image of MAPbX3 perovskite nanowires with increased pump light intensity[44]; (c) with the increase of pumping intensity, intensity distribution of F-P mode perovskite MAPbIxCl3-x nanowires laser[

图 7. 无机钙钛矿CsPbX3纳米线。 (a)不同泵浦强度下的纳米线发光图像[79]; (b)随着激发强度的升高,钙钛矿CsPbBr3纳米线出现F-P模式激光[79]; (c)在固定的脉冲能量激发下,纳米线激光可以维持超过1 h(相当于109个激发循环)[79];(d)钙钛矿MAPbX3纳米线阵列[84];(e)全无机钙钛矿CsPbX3纳米线阵列[85]
Fig. 7. All inorganic perovskite CsPbX3 nanowires. (a) Nanowire lasing image with different pump density[79]; (b) with the increase of excitation intensity, F-P mode laser appears on perovskite CsPbBr3 nanowires[79]; (c) nanowire laser can last for more than an hour (equivalent to 109 excitation cycles) with a fixed pulsed energy[

图 8. 不同方案的F-P模式激光。(a)全无机钙钛矿CsPbBr3微米立方块中实现F-P模式激光[86];(b)使用改良的低温溶液处理方法合成高品质钙钛矿CsPbBr3纳米立方块SEM图像[87];(c)F-P腔的晶体结构和驻波示意图[87];(d)无机钙钛矿CsPbBr3纳米立方块随着激发强度的增加实现单模激光[87];(e)立方金字塔形状的杂化钙钛矿MAPbBr3实现F-P模式的激光发射[88];(f) 立方金字
Fig. 8. Different schemes of F-P mode lasers. (a) F-P mode laser in all inorganic perovskite CsPbBr3 micron cube[86]; (b) SEM image of high-quality perovskite CsPbBr3 nano cubes using an improved low-temperature solution treatment method[87]; (c) schematic of the crystal structure and standing wave of the F-P cavity[87]; (d) inorganic

图 9. 外加辅助腔实现F-P模式激光。(a)钙钛矿MAPbI3-xClx垂直腔F-P模式激光光谱[90]; (b) 全无机钙钛矿CsPbBr3垂直发射激光器的结构[93];(c)F-P模式激光光谱图[93];(d)钙钛矿激光器的DFB光栅的结构[94];(e)F-P模式激光[94];(f)全无机钙钛矿DFB激光器结构[Fig. 9. F-P mode laser with auxiliary cavity. (a) Perovskite MAPbI3-xClx vertical cavity F-P mode laser spectrum[90]; (b) structure of all-inorganic perovskite CsPbBr3 VCSEL[93]; (c) FP mode laser spectrogram[93]; (d) perovskite laser with DFB structure[94

Fig. 9. F-P mode laser with auxiliary cavity. (a) Perovskite MAPbI3-xClx vertical cavity F-P mode laser spectrum[90]; (b) structure of all-inorganic perovskite CsPbBr3 VCSEL[93]; (c) FP mode laser spectrogram[93]; (d) perovskite laser with DFB structure[94

图 10. 随机激光。(a)利用无序介质的多重散射实现随机激光[96]。 (b)荧光图像显示出泵浦强度下,钙钛矿MAPbI3做成平面的微晶网络实现随机激光的空间分布[97];(c)低于泵浦阈值、泵浦阈值相近、高于泵浦阈值的发射光谱图[97];(d)单晶钙钛矿CsPbBr3薄膜的TEM图像[35];(e) 单晶CsPb(Br/Cl)3薄膜中的随机激光光谱图[35];(f) 一步法合成的CsPbBr3量子点用胺基介质钉扎在硅
Fig. 10. Random lasers. (a) Random lasers using multiple scattering from a disordered medium[96]; (b) fluorescent images showing the pumping intensity, spatial distribution of perovskite MAPbI3 random lasers[97]; (c) emission spectrum diagrams below the pump threshold, close to the pump threshold, and above the pump threshold[97]; (d) TEM image o

黄斯豪, 刘征征, 杜鹃, 冷雨欣. 钙钛矿微纳激光器研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(7): 071602. Sihao Huang, Zhengzheng Liu, Juan Du, Yuxin Leng. Review of Perovskite Micro -and Nano-Lasers[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(7): 071602.





