空气激光:强场新效应和远程探测新技术  下载: 2979次内封面文章特邀综述
下载: 2979次内封面文章特邀综述
姚金平, 程亚. 空气激光:强场新效应和远程探测新技术[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47(5): 0500005.
Jinping Yao, Ya Cheng. Air Lasing: Novel Effects in Strong Laser Fields and New Technology in Remote Sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(5): 0500005.
[1] Maiman T H. Stimulated optical radiation in ruby[J]. Nature, 1960, 187(4736): 493-494.
[2] Cohen-Tannoudji C N. Nobel lecture: manipulating atoms with photons[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1998, 70(3): 707-719.
[3] Ashkin A, Dziedzic J. Optical trapping and manipulation of viruses and bacteria[J]. Science, 1987, 235(4795): 1517-1520.
[4] Cao X, Jahazi M, Immarigeon J P, et al. A review of laser welding techniques for magnesium alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2006, 171(2): 188-204.
[5] Mourou G A, Tajima T, Bulanov S V. Optics in the relativistic regime[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2006, 78(2): 309-371.
[6] Mourou G, Tajima T. The extreme light infrastructure: optics’ next horizon[J]. Optics and Photonics News, 2011, 22(7): 47-51.
[7] Agostini P, Fabre F, Mainfray G, et al. Free-free transitions following six-photon ionization of xenon atoms[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1979, 42(17): 1127-1130.
[8] Fittinghoff D N, Bolton P R, Chang B, et al. Observation of nonsequential double ionization of helium with optical tunneling[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1992, 69(18): 2642-2645.
[9] L'Huillier A. Balcou P. High-order harmonic generation in rare gases with a 1-ps 1053-nm laser[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1993, 70(6): 774-777.
[10] Krause J L, Schafer K J, Kulander K C. High-order harmonic generation from atoms and ions in the high intensity regime[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1992, 68(24): 3535-3538.
[11] Krausz F, Ivanov M. Attosecond physics[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2009, 81(1): 163-234.
[12] Esarey E, Schroeder C B, Leemans W P. Physics of laser-driven plasma-based electron accelerators[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2009, 81(3): 1229-1285.
[13] Henig A, Kiefer D, Markey K, et al. Enhanced laser-driven ion acceleration in the relativistic transparency regime[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(4): 045002.
[14] Sugioka K, Cheng Y. Ultrafast lasers: reliable tools for advanced materials processing[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2014, 3(4): e149.
[15] Wang C, Fomovsky M, Miao G X, et al. Femtosecond laser crosslinking of the cornea for non-invasive vision correction[J]. Nature Photonics, 2018, 12(7): 416-422.
[16] Kasparian J. White-light filaments for atmospheric analysis[J]. Science, 2003, 301(5629): 61-64.
[17] Xu H L, Cheng Y, Chin S L, et al. Femtosecond laser ionization and fragmentation of molecules for environmental sensing[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2015, 9(3): 275-293.
[18] Vaulin V A, Slinko V N, Sulakshin S S. Air ultraviolet laser excited by high-power microwave pulses[J]. Soviet Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1988, 18(11): 1457-1458.
[19] Strickland D, Mourou G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses[J]. Optics Communications, 1985, 56(3): 219-221.
[20] Braun A, Korn G, Liu X, et al. Self-channeling of high-peak-power femtosecond laser pulses in air[J]. Optics Letters, 1995, 20(1): 73-75.
[21] Luo Q, Liu W W, Chin S L. Lasing action in air induced by ultra-fast laser filamentation[J]. Applied Physics B: Lasers and Optics, 2003, 76(3): 337-340.
[23] Yao J P, Zeng B, Xu H L, et al. High-brightness switchable multiwavelength remote laser in air[J]. Physical Review A, 2011, 84(5): 051802.
[24] PolynkinP, ChengY. Air lasing[M]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018.
[25] Yuan L Q, Liu Y, Yao J P, et al. Recent advances in air lasing: a perspective from quantum coherence[J]. Advanced Quantum Technologies, 2019, 2(11): 1900080.
[26] Li H L, Yao D W, Wang S Q, et al. Air lasing: phenomena and mechanisms[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2019, 28(11): 114204.
[27] DogariuA, Miles RB. Nitrogen lasing in air[C]// Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics. San Jose, California, United States: Optical Society of America, 2013: QW1E. 1.
[28] Laurain A, Scheller M, Polynkin P. Low-threshold bidirectional air lasing[J]. Pysical Review Letters, 2014, 113(25): 253901.
[29] Kartashov D, Ališauskas S, Andriukaitis G, et al. Free-space nitrogen gas laser driven by a femtosecond filament[J]. Physical Review A, 2012, 86(3): 033831.
[31] Kartashov D, Ališauskas S, Baltuška A, et al. Remotely pumped stimulated emission at 337 nm in atmospheric nitrogen[J]. Physical Review A, 2013, 88(4): 041805.
[32] Yao J P, Li G H, Jing C R, et al. Remote creation of coherent emissions in air with two-color ultrafast laser pulses[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2013, 15(2): 023046.
[33] Dogariu A, Miles R B. Three-photon femtosecond pumped backwards lasing in argon[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(6): A544-A552.
[34] Chu W, Zeng B, Yao J P, et al. Multiwavelength amplified harmonic emissions from carbon dioxide pumped by mid-infrared femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Europhysics Letters, 2012, 97(6): 64004.
[35] Yuan S, Wang T J, Teranishi Y, et al. Lasing action in water vapor induced by ultrashort laser filamentation[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102(22): 224102.
[36] DogariuA, Chng TL, Miles RB. Remote backward-propagating water lasing in atmospheric air[C]//Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics. San Jose, California. Washington, D.C.: OSA, 2016: AW4K. 5.
[39] Malevich P N, Maurer R, Kartashov D, et al. Stimulated Raman gas sensing by backward UV lasing from a femtosecond filament[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(11): 2469-2472.
[40] DogariuA. Remote trace detection of hazardous substances using nonlinear optics[C]//Light, Energy and the Environment. Canberra. Washington, D.C.: OSA, 2014: EF4A. 4.
[42] Liu Z X, Yao J P, Zhang H S, et al. Extreme nonlinear Raman interaction of an ultrashort nitrogen ion laser with an impulsively excited molecular wavepacket[J]. Physical Review A, 2020, 101(4): 043404.
[43] Yao J P, Chu W, Liu Z X, et al. An anatomy of strong-field ionization-induced air lasing[J]. Applied Physics B, 2018, 124(5): 73.
[45] Mitryukovskiy S, Liu Y, Ding P J, et al. Plasma luminescence from femtosecond filaments in air: evidence for impact excitation with circularly polarized light pulses[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2015, 114(6): 063003.
[46] Zhang H S, Jing C R, Yao J P, et al. Rotational coherence encoded in an “air-laser” spectrum of nitrogen molecular ions in an intense laser field[J]. Physical Review X, 2013, 3(4): 041009.
[47] Liu Y, Ding P J, Lambert G, et al. Recollision-induced superradiance of ionized nitrogen molecules[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2015, 115(13): 133203.
[48] Liu Y, Ding P J, Ibrakovic N, et al. Unexpected sensitivity of nitrogen ions superradiant emission on pump laser wavelength and duration[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2017, 119(20): 203205.
[49] Britton M, Laferrière P, Ko D H, et al. Testing the role of recollision in N2+ air lasing[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(13): 133208.
[50] Xu H L, Lötstedt E, Iwasaki A, et al. Sub-10-fs population inversion in N2+ in air lasing through multiple state coupling[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 8347.
[51] Yao J P, Jiang S C, Chu W, et al. Population redistribution among multiple electronic states of molecular nitrogen ions in strong laser fields[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2016, 116(14): 143007.
[52] Zhang Q, Xie H Q, Li G H, et al. Sub-cycle coherent control of ionic dynamics via transient ionization injection[J]. Communications Physics, 2020, 3: 50.
[53] Chen J M, Yao J P, Zhang H S, et al. Electronic-coherence-mediated molecular nitrogen-ion lasing in a strong laser field[J]. Physical Review A, 2019, 100(3): 031402.
[54] Zhang A, Liang Q Q, Lei M W, et al. Coherent modulation of superradiance from nitrogen ions pumped with femtosecond pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(9): 12638-12646.
[55] Mysyrowicz A, Danylo R, Houard A, et al. Lasing without population inversion in N2+[J]. APL Photonics, 2019, 4(11): 110807.
[56] Yao J P, Chu W, Liu Z X, et al. Generation of Raman lasers from nitrogen molecular ions driven by ultraintense laser fields[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2018, 20(3): 033035.
[57] Liu Z X, Yao J P, Chen J M, et al. Near-resonant Raman amplification in the rotational quantum wave packets of nitrogen molecular ions generated by strong field ionization[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(8): 083205.
[58] Yuan L Q, Hokr B H, Traverso A J, et al. Theoretical analysis of the coherence-brightened laser in air[J]. Physical Review A, 2013, 87(2): 023826.
[59] Talebpour A, Abdel-Fattah M, Bandrauk A D, et al. Spectroscopy of the gases interacting with intense femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Laser Physics, 2001, 11(1): 68-76.
[60] Kartashov D, Ališauskas S, Pugžlys A, et al. Theory of a filament initiated nitrogen laser[J]. Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 2015, 48(9): 094016.
[61] Sprangle P, Peñano J, Hafizi B, et al. Remotely induced atmospheric lasing[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98(21): 211102.
[62] Shneider M N, Baltuška A, Zheltikov A M. Population inversion of molecular nitrogen in an Ar: N2 mixture by selective resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 110(8): 083112.
[63] Xie H Q, Li G H, Chu W, et al. Backward nitrogen lasing actions induced by femtosecond laser filamentation: influence of duration of gain[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2015, 17(7): 073009.
[64] Itikawa Y. Cross sections for electron collisions with nitrogen molecules[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 2006, 35(1): 31-53.
[65] Heard H G. Ultra-violet gas laser at room temperature[J]. Nature, 1963, 200(4907): 667.
[66] Yao J P, Xie H Q, Zeng B, et al. Gain dynamics of a free-space nitrogen laser pumped by circularly polarized femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(16): 19005-19013.
[68] Ding P J, Oliva E, Houard A, et al. Lasing dynamics of neutral nitrogen molecules in femtosecond filaments[J]. Physical Review A, 2016, 94(4): 043824.
[69] Ding P J, Escudero J C, Houard A, et al. Nonadiabaticity of cavity-free neutral nitrogen lasing[J]. Physical Review A, 2017, 96(3): 033810.
[71] Li G H, Jing C R, Zeng B, et al. Signature of superradiance from a nitrogen-gas plasma channel produced by strong-field ionization[J]. Physical Review A, 2014, 89(3): 033833.
[72] Zhong X Q, Miao Z M, Zhang L L, et al. Vibrational and electronic excitation of ionized nitrogen molecules in intense laser fields[J]. Physical Review A, 2017, 96(4): 043422.
[73] Lei M W, Wu C Y, Zhang A, et al. Population inversion in the rotational levels of the superradiant N2+ pumped by femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(4): 4535-4541.
[74] Miao Z M, Zhong X Q, Zhang L L, et al. Stimulated-Raman-scattering-assisted superfluorescence enhancement from ionized nitrogen molecules in 800-nm femtosecond laser fields[J]. Physical Review A, 2018, 98(3): 033402.
[75] Xu B, Jiang S C, Yao J P, et al. Free-space Ν2+ lasers generated in strong laser fields: the role of molecular vibration[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(10): 13331-13339.
[76] Arissian L, Kamer B, Rastegari A, et al. Transient gain from N2+ in light filaments[J]. Physical Review A, 2018, 98(5): 053438.
[77] Britton M, Lytova M, Laferrière P, et al. Short- and long-term gain dynamics in N2+ air lasing[J]. Physical Review A, 2019, 100: 013406.
[78] Zheng W, Miao Z M, Zhang L L, et al. Enhanced coherent emission from ionized nitrogen molecules by femtosecond laser pulses[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2019, 10(21): 6598-6603.
[79] Xie H Q, Zeng B, Li G H, et al. Coupling of N2+rotational states in an air laser from tunnel-ionized nitrogen molecules[J]. Physical Review A, 2014, 90(4): 042504.
[80] Zeng B, Chu W, Li G H, et al. Real-time observation of dynamics in rotational molecular wave packets by use of air-laser spectroscopy[J]. Physical Review A, 2014, 89(4): 042508.
[82] Wang T J, Ju J J, Daigle J F, et al. Self-seeded forward lasing action from a femtosecond Ti∶sapphire laser filament in air[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2013, 10(12): 125401.
[83] Chu W, Li G H, Xie H Q, et al. A self-induced white light seeding laser in a femtosecond laser filament[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2014, 11(1): 015301.
[84] Li H L, Hou M Y, Zang H W, et al. Significant enhancement of N2+ lasing by polarization-modulated ultrashort laser pulses[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 122: 013202.
[85] Xie H Q, Zhang Q, Li G H, et al. Vibrational population transfer between electronic states of N2+ in polarization-modulated intense laser fields[J]. Physical Review A, 2019, 100(5): 053419.
[86] Ando T, Lötstedt E, Iwasaki A, et al. Rotational, vibrational, and electronic modulations in N2+ lasing at 391 nm: evidence of coherent B2Σu+-X2Σg+-A2Πu coupling[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 123(20): 203201.
[87] Li H X, Song Q Y, Yao J P, et al. Air lasing from singly ionized N2 driven by bicircular two-color fields[J]. Physical Review A, 2019, 99(5): 053413.
[88] Clerici M, Bruhács A, Faccio D, et al. Terahertz control of air lasing[J]. Physical Review A, 2019, 99(5): 053802.
[89] KartashovD, MöhringJ, AndriukaitisG, et al. Stimulated amplification of UV emission in a femtosecond filament using adaptive control[C]//Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics 2012, San Jose, California. Washington, D.C.: OSA, 2012: QTh4E. 6.
[92] Jing C R, Yao J P, Li Z T, et al. Free-space air molecular lasing from highly excited vibrational states pumped by circularly-polarized femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 2015, 48(9): 094001.
[94] Andriukaitis G, Möhring J, Kartashov D, et al. Intense, directional UV emission from molecular nitrogen ions in an adaptively controlled femtosecond filament[J]. EPJ Web of Conferences, 2013, 41: 10004.
[95] KartashovD, HaesslerS, AlisauskasS, et al. Transient inversion in rotationally aligned nitrogen ions in a femtosecond filament[C]//Research in Optical Sciences, Messe Berlin, Berlin. Washington, D.C.: OSA, 2014: HTh4B. 5.
[96] Azarm A, Corkum P, Polynkin P. Optical gain in rotationally excited nitrogen molecular ions[J]. Physical Review A, 2017, 96(5): 051401.
[97] Xu H L, Lötstedt E, Ando T, et al. Alignment-dependent population inversion in N2+ in intense few-cycle laser fields[J]. Physical Review A, 2017, 96(4): 041401.
[98] Wan Y X, Xu B, Yao J P, et al. Polarization ellipticity dependence of N2+ air lasing: the role of coupling between the ground state and a photo-excited intermediate state[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2019, 36(10): G57-G61.
[99] Fu Y, Lötstedt E, Li H L, et al. Optimization of N2+ lasing through population depletion in the X2Σg+ state using elliptically modulated ultrashort intense laser fields[J]. Physical Review Research, 2020, 2: 012007.
[100] Zhang A, Lei M W, Gao J S, et al. Subfemtosecond-resolved modulation of superfluorescence from ionized nitrogen molecules by 800-nm femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(10): 14922-14930.
[101] Xu B, Yao J P, Wan Y X, et al. Vibrational Raman scattering from coherently excited molecular ions in a strong laser field[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(13): 18262-18272.
[102] Arissian L, Kamer B, Rasoulof A. Effect of rotational wave packets on the stimulated emission of nitrogen with light filament[J]. Optics Communications, 2016, 369: 215-219.
[104] Zhang H S, Jing C R, Li G H, et al. Abnormal dependence of strong-field-ionization-induced nitrogen lasing on polarization ellipticity of the driving field[J]. Physical Review A, 2013, 88(6): 063417.
[105] Zhong X Q, Miao Z M, Zhang L L, et al. Optimizing the 391-nm lasing intensity from ionized nitrogen molecules in 800-nm femtosecond laser fields[J]. Physical Review A, 2018, 97(3): 033409.
[106] Wang T J, Daigle J F, Ju J J, et al. Forward lasing action at multiple wavelengths seeded by white light from a femtosecond laser filament in air[J]. Physical Review A, 2013, 88(5): 053429.
[107] Wang P, Wu C Y, Lei M W, et al. Population dynamics of molecular nitrogen initiated by intense femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Physical Review A, 2015, 92(6): 063412.
[109] Li Z T, Zeng B, Chu W, et al. Generation of elliptically polarized nitrogen ion laser fields using two-color femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 21504.
[110] Li H L, Zang H W, Su Y, et al. Generation of air lasing at extended distances by coaxial dual-color femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Journal of Optics, 2017, 19(12): 124006.
[111] Jing C R, Xie H Q, Li G H, et al. Dynamic wavelength switching of a remote nitrogen or air laser with chirped femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2015, 12(1): 015301.
[112] Tong X M, Zhao Z X, Lin C D. Theory of molecular tunneling ionization[J]. Physical Review A, 2002, 66(3): 033402.
[113] Campbell JB, Wynne RH. Introduction to remote sensing[M]. New York: The Guilford Press, 2011.
[114] Chu W, Li H L, Ni J L, et al. Lasing action induced by femtosecond laser filamentation in ethanol flame for combustion diagnosis[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(9): 091106.
[115] Ding P J, Ruchkina M, Liu Y, et al. Femtosecond two-photon-excited backward lasing of atomic hydrogen in a flame[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(5): 1183-1186.
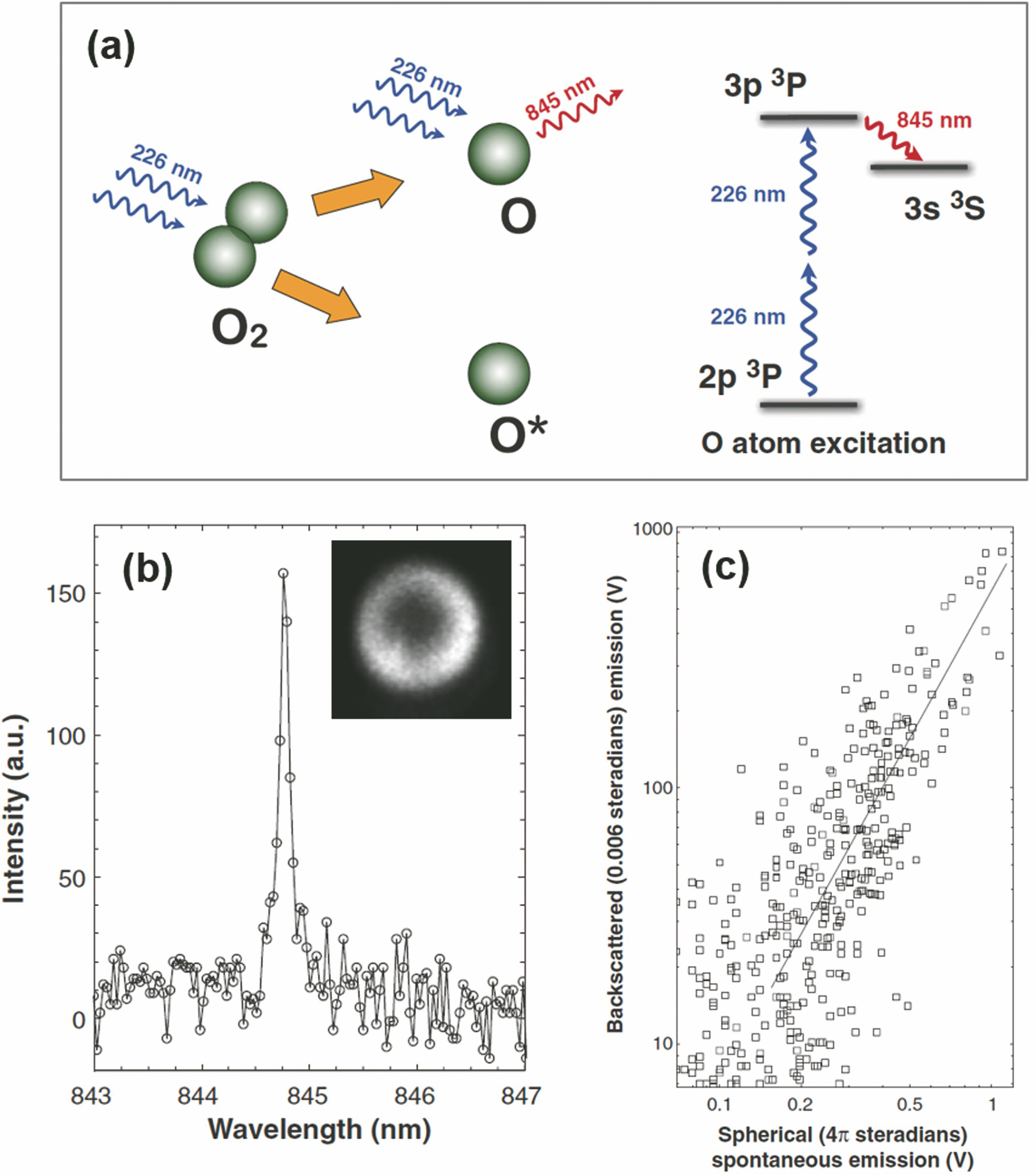
[116] Ding P J, Ruchkina M. Cont-Bernard D D, et al. Detection of atomic oxygen in a plasma-assisted flame via a backward lasing technique[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(22): 5477-5480.
[117] Ruchkina M, Ding P J, Ehn A, et al. Single-shot, spatially-resolved stand-off detection of atomic hydrogen via backward lasing in flames[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2019, 37(2): 1281-1288.
姚金平, 程亚. 空气激光:强场新效应和远程探测新技术[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47(5): 0500005. Jinping Yao, Ya Cheng. Air Lasing: Novel Effects in Strong Laser Fields and New Technology in Remote Sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(5): 0500005.