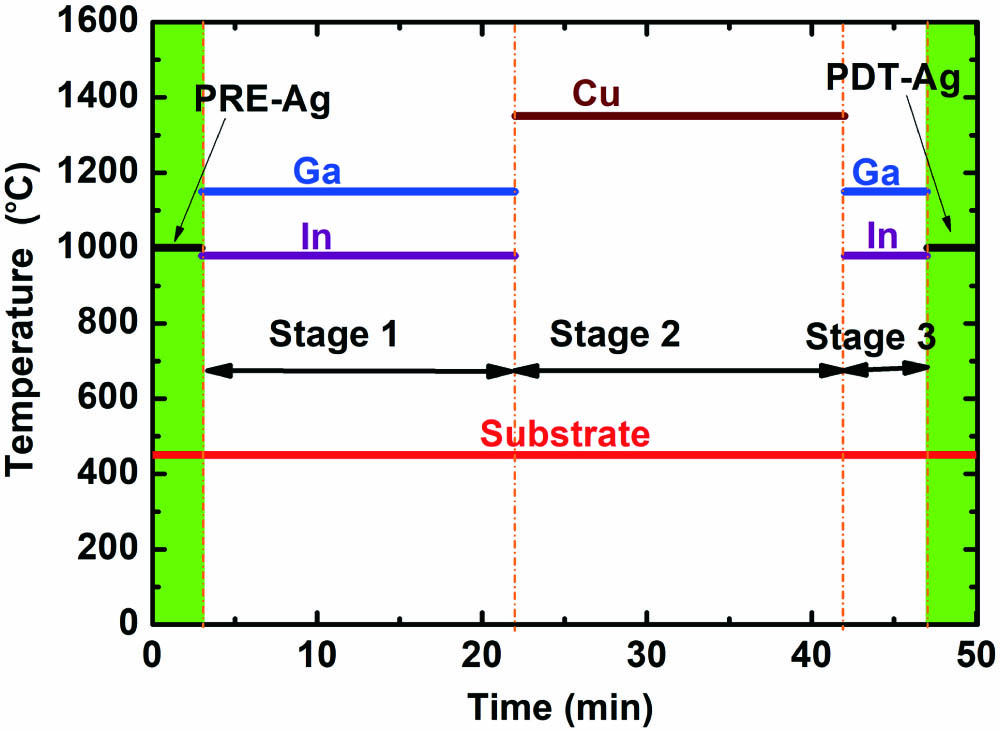
Incorporation of Ag into Cu(In,Ga)Se2 films in low-temperature process
Zhaojing Hu, Yunxiang Zhang, Shuping Lin, Shiqing Cheng, Zhichao He, Chaojie Wang, Zhiqiang Zhou, Fangfang Liu, Yun Sun, Wei Liu. Incorporation of Ag into Cu(In,Ga)Se2 films in low-temperature process[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2021, 19(11): 114001.
[1] M. Nakamura, K. Yamaguchi, Y. Kimoto, Y. Yasaki, T. Kato, H. Sugimoto. Cd-free Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2 thin-film solar cell with record efficiency of 23.35%. IEEE J. Photovoltaics, 2019, 9: 1863.
[2] Y. Wang, S. Lv, Z. Li. Review on incorporation of alkali elements and their effects in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2021, 96: 179.
[3] H. Fan, Y. Mu, C. Liu, Y. Zhu, G. Liu, S. Wang, Y. Li, P. Du. Random lasing of CsPbBr3 perovskite thin films pumped by modulated electron beam. Chin. Opt. Lett., 2020, 18: 011403.
[4] P. Liang, C. Chueh, T. S. Williams, K.-Y. Alex. Roles of fullerene-based interlayers in enhancing the performance of organometal perovskite thin-film solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater., 2015, 5: 1402321.
[5] Z. Zhang, Z. Lü, X. Yang, H. Chai, L. Meng, T. Yang. 25 Gb/s directly modulated ground-state operation of 1.3 µm InAs/GaAs quantum dot lasers up to 75°C. Chin. Opt. Lett., 2020, 18: 071401.
[6] B. S. Tosun, R. Feist, A. Gunawan, K. Mkhoyan, S. A. Campbell, E. Aydil. Improving the damp-heat stability of copper indium gallium diselenide solar cells with a semicrystalline tin dioxide overlayer. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2012, 101: 270.
[7] M. Schmidt, D. Braunger, R. Schäffler, H. W. Schock, U. Rau. Influence of damp heat on the electrical properties of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells. Thin Solid Films, 2000, 361–362: 283.
[8] H. Y. Sun, P. H. Li, Y. M. Xue, Z. X. Qiao, S. Liu. Effect of MoSe2 on the performance of CIGS solar cells. Optoelectron. Lett., 2019, 15: 428.
[9] Y. Zhang, S. Lin, Z. Hu, S. Cheng, Z. He, Z. Zhou, W. Liu, Y. Sun. Towards an optimized gallium gradient for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film via an improved constant low-temperature deposition process. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2020, 209: 110425.
[10] P. Jackson, D. Hariskos, R. Wuerz, O. Kiowski, A. Bauer, T. M. Friedlmeier, M. Powalla. Properties of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells with new record efficiencies up to 21.7%. Rapid Res. Lett., 2015, 9: 28.
[11] L. Zhang, Q. He, W. L. Jiang, F. F. Liu, C. J. Li, Y. Sun. Effects of substrate temperature on the structural and electrical properties of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2009, 93: 114.
[12] W. Li, L. Yao, K. Li, X. Li, B. Yang, S. Xu, S. Shi, C. Yi, M. Chen, Y. Feng, W. Li, Z. Lu, C. Yang. Enabling low-temperature deposition of high-efficiency CIGS solar cells with a modified three-stage co-evaporation process. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3: 4201.
[14] V. Achard, M. Balestrieri, S. Béchu, M. Jubault, M. Bouttemy, L. Lombez, T. Hildebrandt, N. Naghavi, A. Etcheberry, D. Lincot, F. Donsanti. Effect of Ga introduction during the second stage of a coevaporation process of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 layers at low temperature on polyimide substrates. Thin Solid Films, 2019, 669: 494.
[15] X. Liang, H. Zhu, J. Chen, D. Zhou, C. Zhang, Y. Guo, X. Niu, Z. Li, Y. Mai. Substrate temperature optimization for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells on flexible stainless steels. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 368: 464.
[16] V. Glazov, A. Pashinkin, V. Fedorov. Phase equilibria in the Cu-Se system, inorganic materials. Inorg. Mater., 2000, 36: 641.
[17] W. N. Shafarman, J. Zhu. Effect of substrate temperature and deposition profile on evaporated Cu(InGa)Se2 films and devices. Thin Solid Films, 2000, 361–362: 473.
[18] K. Kim, J. W. Park, J. S. Yoo, J.-S. Cho, H.-D. Lee, J. H. Yun. Ag incorporation in low-temperature grown Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells using Ag precursor layers. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2016, 146: 114.
[19] N. Valdes, J. Lee, W. Shafarman. Comparison of Ag and Ga alloying in low bandgap CuInSe2-based solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2019, 195: 155.
[20] J. Zhai, H. Cao, M. Zhao, C. Wang, Y. Li, H. Tong, Z. Li, S. Yin, D. Zhuang. Smooth and highly-crystalline Ag-doped CIGS films sputtered from quaternary ceramic targets. Ceram. Int., 2021, 47: 2288.
[21] Y. Zhao, S. Yuan, D. Kou, Z. Zhou, X. Wang, H. Xiao, Y. Deng, C. Cui, Q. Chang, S. Wu. High efficiency CIGS solar cells by bulk defect passivation through Ag substituting strategy. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 12: 12717.
[22] T. Adhikari, D. Pathak, T. Wagner, R. Jambor, U. Jabeen, M. Aamir, J. M. Nunzi. Structural, optical, electrochemical and photovoltaic studies of spider web like silver indium diselenide quantum dots synthesized by ligand mediated colloidal sol-gel approach. Opt. Mater., 2017, 73: 70.
[23] D. Pathak, R. K. Bedi, D. Kaur. Growth of AgInSe2 on Si(100) substrate by pulse laser ablation. Surf. Rev. Lett., 2010, 16: 917.
[24] X. Xu, J. Li, X. Yang, S. Pan, Y. Bi. Introduction of Ag nanoparticles by picosecond LIFT to improve the photoelectric property of AZO films. Chin. Opt. Lett., 2020, 18: 043101.
[25] G. Kim, W. M. Kim, J. K. Park, D. Kim, H. Yu, J. H. Jeong. Thin Ag precursor layer-assisted co-evaporation process for low-temperature growth of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11: 31923.
[26] Y. Zhang, Z. Hu, S. Lin, C. Wang, S. Cheng, Z. He, Z. Zhou, Y. Sun, W. Liu. Silver surface treatment of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 (CIGS) thin film: a new passivation process for the CdS/CIGS heterojunction. Solar RRL, 2020, 4: 2000290.
[27] B. Guo, Y. Wang, X. Zhu, M. Qin, D. Wan, A. F. Huang. Molybdenum thin films fabricated by RF and dc sputtering for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cell applications. Chin. Opt. Lett., 2016, 14: 043101.
[28] Z. Wang, D. Wan, F. Huang, F. Xu. Highly surface-textured and conducting ZnO:Al films fabricated from oxygen-deficient target for Cu(In, Ga)Se2 solar cell application. Chin. Opt. Lett., 2014, 12: 093101.
[29] S. Lin, W. Liu, Y. Zhang, S. Cheng, Y. Fan, Z. Zhou, Q. He, Y. Zhang, Y. Sun. Adjustment of alkali element incorporations in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films with wet chemistry Mo oxide as a hosting reservoir. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2018, 174: 16.
[30] J. H. Boyle, B. E. McCandless, W. N. Shafarman, R. W. Birkmire. Structural and optical properties of (Ag,Cu)(In,Ga)Se2 polycrystalline thin film alloys. J. Appl. Phys., 2014, 115: 223504.
[31] V. Achard, M. Balestrieri, M. Jubault, J. Posada, T. Hildebrandt, N. Naghavi, L. Lombez, D. Lincot, F. Donsanti. Study of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film growth at low temperature on polyimide substrate in a multi-stage coevaporation process for photovoltaic applications. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2018, 1: 5257.
[32] K. V. Sopiha, J. K. Larsen, O. Donzel-Gargand, F. Khavari, J. Keller, M. Edoff, C. Platzer-Björkman, C. Persson, J. S. Scragg. Phase separation and Ag grading in (Ag,Cu)(In,Ga)Se2 solar absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8: 8740.
[33] S. Essig, S. Paetel, T. M. Friedlmeier, M. Powalla. Challenges in the deposition of (Ag,Cu)(In,Ga)Se2 absorber layers for thin-film solar cells. J. Phys. Mater., 2021, 4: 024003.
[34] Y. Zhang, Z. Hu, S. Lin, S. Cheng, Z. He, C. Wang, Z. Zhou, Y. Sun, W. Liu. Facile silver-incorporated method of tuning the back gradient of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 films. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3: 9963.
[35] J. Chantana, T. Nishimura, Y. Kawano, S. Teraji, T. Watanabe, T. Minemoto. Examination of relationship between Urbach energy and open-circuit voltage deficit of flexible Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cell for its improved photovoltaic performance. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2019, 2: 7843.
[36] F. Pianezzi, P. Reinhard, A. Chirilă, S. Nishiwaki, B. Bissig, S. Buecheler, A. N. Tiwari. Defect formation in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films due to the presence of potassium during growth by low temperature co-evaporation process. J. Appl. Phys., 2013, 114: 194508.
[37] Y. Zhang, S. Lin, S. Cheng, Z. He, Z. Hu, Z. Zhou, W. Liu, Y. Sun. Boosting Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film growth in low-temperature rapid-deposition processes: an improved design for the single-heating knudsen cell. Engineering, 2020, 7: 534.
[38] X. Zhang, M. Kobayashi, A. Yamada. Comparison of Ag(In,Ga)Se2/Mo and Cu(In,Ga)Se2/Mo interfaces in solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9: 16215.
Zhaojing Hu, Yunxiang Zhang, Shuping Lin, Shiqing Cheng, Zhichao He, Chaojie Wang, Zhiqiang Zhou, Fangfang Liu, Yun Sun, Wei Liu. Incorporation of Ag into Cu(In,Ga)Se2 films in low-temperature process[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2021, 19(11): 114001.