2021, 19(11) Column
Atomic and Molecular Optics Diffraction, Gratings, and Holography Fiber Optics and Optical Communications Imaging Systems and Image Processing Lasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser Optics Optical Materials Biophotonics Nonlinear Optics Optical Design and Fabrication Physical Optics Quantum Optics and Quantum Information Microwave Photonics Solar Energy and Photovoltaics
Chinese Optics Letters 第19卷 第11期
We take
ion collision orientation combined fields In amplitude-modulation-type electroholography, the binary-weighted computer-generated hologram (BW-CGH) facilitates the gradation-expressible reconstruction of three-dimensional (3D) objects. To realize real-time gradation-expressible electroholography, we propose an efficient and high-speed method for calculating bit planes consisting of BW-CGHs. The proposed method is implemented on a multiple graphics processing unit (GPU) cluster system comprising 13 GPUs. The proposed BW-CGH method realizes eight-gradation-expressible electroholography at approximately the same calculation speed as that of conventional electroholography based on binary computer-generated holograms. Consequently, we were able to successfully reconstruct a real-time electroholographic 3D video comprising approximately 180,000 points expressed in eight gradations at 30 frames per second.
gradation-expressible electroholography binary-weighted computer-generated hologram digital micromirror device computer-generated hologram Compensation of turbulence-induced wavefront aberration with convolutional neural networks for FSO systems Download:611次
Download:611次
 Download:611次
Download:611次To reduce the atmospheric turbulence-induced power loss, an AlexNet-based convolutional neural network (CNN) for wavefront aberration compensation is experimentally investigated for free-space optical (FSO) communication systems with standard single mode fiber-pigtailed photodiodes. The wavefront aberration is statistically constructed to mimic the received light beams with the Zernike mode-based theory for the Kolmogorov turbulence. By analyzing impacts of CNN structures, quantization resolution/noise, and mode count on the power penalty, the AlexNet-based CNN with 8 bit resolution is identified for experimental study. Experimental results indicate that the average power penalty decreases to 1.8 dB from 12.4 dB in the strong turbulence.
free-space optical communication optical fiber wavefront aberration Due to the bandwidth limitation of the ultraviolet-C (UV-C) optical communication system and strong channel attenuation, it is difficult to transmit high-frequency signals. In this paper, the temporal ghost imaging (TGI) algorithm was first applied to the UV-C communication experimentally, and we realized the transmission of a 4 GHz signal through 95.34 MHz system bandwidth. The study indicates that the TGI algorithm can significantly improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) compared with the on–off keying method. Our research provides a new approach for alleviating transmission frequency limitation due to poor SNR and insufficient hardware bandwidth.
temporal ghost imaging UV-C communication ultra-high-frequency signal transmission Gain and laser performance of heavily Er-doped silica fiber fabricated by MCVD combined with the sol-gel method Download:531次
Download:531次
 Download:531次
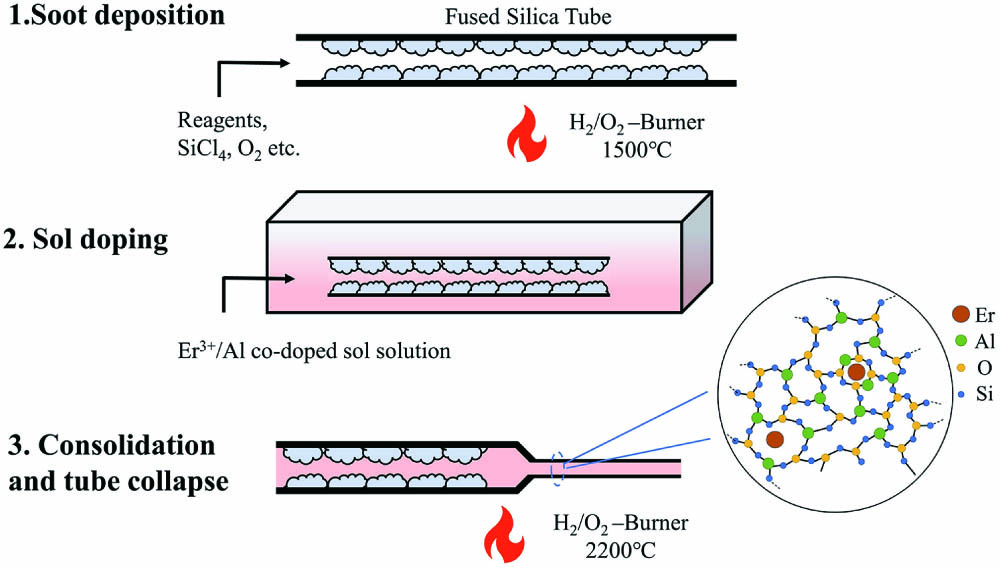
Download:531次In this work, a heavily Er-doped fiber with an 8 µm core diameter and a numerical aperture of 0.13 was prepared by the modified chemical vapor deposition (MCVD) technique combined with the sol-gel method. The background loss and absorption coefficient at 1530 nm were measured to be 20 dB/km and 128 dB/m, respectively. Thanks to the sol-gel method, the fiber showed a good doping homogeneity, which was confirmed through unsaturable absorption measurement. The net gains of three 25, 45, and 75-cm-long fibers were measured in the range of 1520 to 1600 nm, and the highest gain reached above 23 dB at both 1530 and 1560 nm in 25 and 75-cm-long fibers, respectively. The short-cavity laser performance was measured using centimeter-scale fibers. The maximum output power of 12 mW was demonstrated in a 6.5-cm-long active fiber with a slope efficiency of 20.4%. Overall, the prepared heavily Er-doped silica fiber is a promising item to be applied in a high-repetition-rate or single-frequency fiber laser.
erbium-doped fiber short-cavity fiber laser sol-gel method Probabilistically shaped (PS) pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) is a promising technique for intra-data-center networks due to its superior performance, for which a low-complexity and cost-effective distributed matching method is critical. In this work, we propose an energy-level-assigned method to yield PS-PAM-4 signals with various bit rates based on variable probabilistic distributions. We experimentally demonstrate the proposed method in a 25 Gbaud PS-PAM-4 transmission over a bandwidth of approximately 10 GHz. Compared to a uniform PAM-4 system, the proposed multi-distributed PS-PAM-4 system approaches the hard decision threshold at a wide range of received optical power for different applications.
probabilistic shaping pulse amplitude modulation feed-forward equalizer This paper presents a polarization descattering imaging method for underwater detection in which the targets have nonuniform polarization characteristics. The core of this method takes the nonuniform distribution of the polarization information of the target-reflected light into account and expands the application field of underwater polarization imaging. Independent component analysis was used to separate the target light and backscattered light. Theoretical analysis and proof-of-concept experiments were employed to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in estimating target information. The proposed method showed superiority in accurately estimating the target information compared with other polarization imaging methods.
polarization imaging clear vision scattering We propose and demonstrate the generation of wideband chaos based on a dual-mode microsquare semiconductor laser with optical feedback. By adjusting the dual-mode intensity ratio and the feedback strength, wideband chaos covering more than 50 GHz in the RF spectrum is achieved. The standard and effective bandwidths of the chaotic signal are 31.3 GHz and 30.7 GHz with the flatness of 8.3 dB and 6.1 dB, respectively.
dual-mode laser micro laser chaos optical feedback Frequency-modulated continuous-wave dual-frequency LIDAR based on a monolithic integrated two-section DFB laser Download:661次
Download:661次
 Download:661次
Download:661次We demonstrate a high-resolution frequency-modulated continuous-wave dual-frequency LIDAR system based on a monolithic integrated two-section (TS) distributed feedback (DFB) laser. In order to achieve phase locking of the two lasers in the TS-DFB laser, the sideband optical injection locking technique is employed. A high-quality linear frequency-modulated signal is achieved from the TS-DFB laser. Utilizing the proposed LIDAR system, the distance and velocity of a target can be measured accurately. The maximum relative errors of distance and velocity measurement are 1.6% and 3.18%, respectively.
dual-frequency LIDAR integrated two-section DFB laser frequency-modulated continuous wave linear frequency modulation In this paper, we propose and demonstrate an adjustable-free and movable
thin disk laser telecentric cat’s eye adjustable-free laser In this paper, we demonstrate a scheme to tailor both longitudinal and transverse modes inside a laser cavity and constitute an eye-safe single longitudinal mode
Er:YAG single longitudinal mode cylindrical vector beam In this Letter, we demonstrated the switchable single- and dual-wavelength femtosecond soliton generation in single-mode Er-doped fiber lasers with the usage of carboxyl-functionalized graphene oxide (GO-COOH) saturable absorbers (SAs) for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. The fiber laser generated a stable single-wavelength conventional soliton at 1560.1 nm with a pulse duration of 548.1 fs. The dual-wavelength solitons centered at 1531.9 nm and 1555.2 nm with a spacing of approximately 23 nm can be obtained by adjusting the pump power of the cavity. Our experimental results indicated the GO-COOH has great potential to be used in ultrafast fiber lasers as broadband SAs.
fiber laser mode-locking dual-wavelength femtosecond soliton We proposed a periodic mid-infrared broadband chiral structure. Its unit cell consists of four indium tin oxide (ITO) helix subunits with different radii. The simulation results show that the flat-topped broadband circular dichroism (CD) can be achieved in the mid-infrared band by optimizing the parameters of helix structures. The simulation results also show that compared with the metallic (Ag and Au) helix structures, the ITO helix structure proposed exhibits evidently better broadband CD and optical activity, which provides a new idea for the design of broadband polarization state control devices in the mid-infrared band.
mid-infrared flat-topped broadband chiral helix metamaterial We report an interesting study of electric-field-induced transformation from a single domain ferroelectric state to the multiple domain ferroelectric state in a KTa1-xNbxO3 (KTN) crystal. Experimental results obtained using the confocal μ-Raman spectroscopy confirm the dynamic change of lattice structures induced by an external electric field. Furthermore, the dependence of relative permittivity on the applied voltage also indicates the transformation of ferroelectric states involving the processes of splintering, inversion, and re-formation of ferroelectric domains.
KTN ferroelectric state domain state transformation field-induced phenomenon Microrobots-assisted drug delivery and surgery have been always in the spotlight and are highly anticipated to solve the challenges of cancer in situ treatment. These versatile small biomedical robots are expected to realize direct access to the tumor or disease site for precise treatment, which requires real-time and high-resolution in vivo tracking as feedback for the microrobots’ actuation and control. Among current biomedical imaging methods, photoacoustic imaging (PAI) is presenting its outstanding performances in the tracking of microrobots in the human body derived from its great advantages of excellent imaging resolution and contrast in deep tissue. In this review, we summarize the PAI techniques, imaging systems, and their biomedical applications in microrobots tracking in vitro and in vivo. From a robotic tracking perspective, we also provide some insight into the future of PAI technology in clinical applications.
photoacoustic imaging PACT OR-PAM microrobots tracking clinical applications We demonstrate comprehensive investigation of the injection locking dynamics of a backscattered Brillouin laser in silica whispering-gallery-mode microcavity. Via injection locking, the Brillouin laser acquires highly correlated phase with the seed laser, enabling ultra-narrow bandwidth, high gain, and coherent optical amplification. Also, for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, the injection locked Brillouin laser is utilized to implement all-optical carrier recovery from coherent optical data signals. We show that by using the injection locked Brillouin laser as a local oscillator for self-homodyne detection, high-quality data receiving can be realized, even without traditional electrical compensations for carrier frequency and phase drifts.
optical microcavity stimulated Brillouin scattering laser injection locking self-homodyne detection Tilted-pulse-front-pumping (TPFP) lithium-niobate terahertz (THz) pulse sources are widely used in pump-probe and control experiments since they can generate broadband THz pulses with tens of microjoules of energy. However, the conventional TPFP setup suffers from limitations, hindering the generation of THz pulses with peak electric field strength over 1 MV/cm. Recently, a few setups were suggested to mitigate or even eliminate these limitations. In this paper, we shortly review the setups that are suitable for the generation of single-cycle THz pulses with up to a few tens of megavolts/centimeter focused electric field strength. The THz pulses available with the new layouts pave the way for previously unattainable applications that require extremely high electric field strength and pulse energy in the multi-millijoule range.
terahertz pulse generation nonlinear optics ultrafast optics The vector dynamics of solitons are crucial but easily neglected for realizing vortex solitons. In this Letter, we investigate the effect of vector dynamics on cylindrical vector beams (CVBs) implementation and propose a novel technical method to realize femtosecond CVBs based on vector-locked solitons, which are presented as group-velocity-locked vector solitons (GVLVSs) in the experiment. The outstanding vector properties of GVLVSs not only greatly improve the efficiency of solitons converted into CVBs and output power of CVBs (2.4 times and 4.1 times that of scalar solitons and vector change periodical solitons, with the purity of 97.2%), but also relax the obstacle of ultrafast CVBs from the fundamental frequency to the harmonic regime (up to 198 MHz) for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. This is the highest repetition rate reported for ultrafast CVBs based on passive mode-locking. The investigation of the influence of solitons vector dynamics evolution on the realization of CVBs provides guidance for the excellent performance of ultrafast CVBs.
cylindrical vector beam ultrafast optical switch laser mode-locking To solve the issue of the contradiction between photovoltaic power generation and plant photosynthesis for sunlight demand, we propose a design method of multi-passband polymer multilayer optical structure. Using polycarbonate (PC) and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), two polymer materials with different refractive indices, the passband position and passband bandwidth are calculated and adjusted by the transmission matrix method and TFCalc software. A 450 nm, 660 nm, and 730 nm three-passband filter was realized by superimposing stacks of different band positions. The feasibility of the photovoltaic agriculture was confirmed by the power generation efficiency and the actual plant growth.
polymer multilayer film design multi-passband photovoltaic power generation photosynthesis photovoltaic agriculture Optical design of a compact and high-transmittance compressive sensing imaging system enabled by freeform optics Download:623次
Download:623次
 Download:623次
Download:623次Using compressive sensing for imaging has many applications, and it is an important branch of computational imaging. In this Letter, freeform surfaces are introduced in the hardware optical system design of a compressive sensing imager. The system works under the medium wave infrared band and realizes a
compressive sensing freeform optics compactness and high-transmittance joint optimization Liquid crystal devices for vector vortex beams manipulation and quantum information applications [Invited] Download:722次
Download:722次
 Download:722次
Download:722次Vector vortex beams (VVBs) have attracted significant attention in both classical and quantum optics. Liquid crystal (LC), beyond its applications in information display, has emerged as a versatile tool for manipulating VVBs. In this review, we focus on the functions and applications of typical LC devices in recent studies on controlling the space-variant polarized vortex light. Manipulation of VVBs through patterned nematic LC optical elements, patterned cholesteric LC optical elements, self-assembled defects, and LC spatial light modulators is discussed separately. Moreover, LC-based novel optical applications in the field of quantum information are reviewed.
liquid crystal vector beam q-plate orbital angular momentum entanglement two-photon interference Quantum random access codes (QRACs) are important communication tasks that are usually implemented in prepare-and-measure scenarios. The receiver tries to retrieve one arbitrarily chosen bit of the original bit-string from the code qubit sent by the sender. In this Letter, we analyze in detail the sequential version of the
quantum random access codes unsharp measurement prepare-and-measure scenario The analog photonics link (APL) is widely used in microwave photonics. However, in wideband and multi-carrier systems, the third inter-modulation distortion (IMD3) and cross-modulation distortion (XMD) will jointly limit the spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) of links. In this paper, we experimentally present a linearized wideband and multi-carrier APL, in which the IMD3 and XMD are mitigated simultaneously by using artificial neural networks with transfer learning (TL-ANN). In this experiment, with different artificial neural networks, which are trained with the knowledge obtained from the two- or three-sub-carrier system, the IMD3 and XMD are suppressed by 21.71 dB and 11.11 dB or 22.38 dB and 16.73 dB, and the SFDR is improved by 13.4 dB or 14.3 dB, respectively. Meanwhile, compared with previous studies, this method could reduce the training time and training epochs to 16% and 25%.
analog photonics link modulation distortion artificial neural networks transfer learning We demonstrate a chip-scale scheme of Brillouin instantaneous frequency measurement (IFM) in a CMOS-compatible doped silica waveguide chip. In the chip-scale Brillouin IFM scheme, the frequency-to-power mapping process is achieved by one-shot detection without additional time averaging and implemented by lock-in amplification, which successfully detects the Brillouin gain of the doped silica waveguide chip in the time domain. A Costas frequency modulated signal ranging from 8 GHz to 9 GHz is experimentally measured, and the frequency measurement errors are maintained within 58 MHz.
instantaneous frequency measurement stimulated Brillouin scattering lock-in amplification waveguide chip Chalcopyrite
CuSe2 thin film low-temperature deposition process Ag doping crystallinity Urbach energy 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦