
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
2 Centre for Advanced Laser Applications, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Garching, Germany
3 John Adams Institute for Accelerator Science, Oxford, UK
Presented is a novel way to combine snapshot compressive imaging and lateral shearing interferometry in order to capture the spatio-spectral phase of an ultrashort laser pulse in a single shot. A deep unrolling algorithm is utilized for snapshot compressive imaging reconstruction due to its parameter efficiency and superior speed relative to other methods, potentially allowing for online reconstruction. The algorithm’s regularization term is represented using a neural network with 3D convolutional layers to exploit the spatio-spectral correlations that exist in laser wavefronts. Compressed sensing is not typically applied to modulated signals, but we demonstrate its success here. Furthermore, we train a neural network to predict the wavefronts from a lateral shearing interferogram in terms of Zernike polynomials, which again increases the speed of our technique without sacrificing fidelity. This method is supported with simulation-based results. While applied to the example of lateral shearing interferometry, the methods presented here are generally applicable to a wide range of signals, including Shack–Hartmann-type sensors. The results may be of interest beyond the context of laser wavefront characterization, including within quantitative phase imaging.
artificial neural networks compressed sensing high-power laser characterization wavefront measurement High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2023, 11(3): 03000e32

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Institute of Photonic Chips, Shanghai, China
2 University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, Centre for Artificial-Intelligence Nanophotonics, Shanghai, China
The creation of biomimetic neuron interfaces (BNIs) has become imperative for different research fields from neural science to artificial intelligence. BNIs are two-dimensional or three-dimensional (3D) artificial interfaces mimicking the geometrical and functional characteristics of biological neural networks to rebuild, understand, and improve neuronal functions. The study of BNI holds the key for curing neuron disorder diseases and creating innovative artificial neural networks (ANNs). To achieve these goals, 3D direct laser writing (DLW) has proven to be a powerful method for BNI with complex geometries. However, the need for scaled-up, high speed fabrication of BNI demands the integration of DLW techniques with ANNs. ANNs, computing algorithms inspired by biological neurons, have shown their unprecedented ability to improve efficiency in data processing. The integration of ANNs and DLW techniques promises an innovative pathway for efficient fabrication of large-scale BNI and can also inspire the design and optimization of novel BNI for ANNs. This perspective reviews advances in DLW of BNI and discusses the role of ANNs in the design and fabrication of BNI.
direct laser writing neuron interface neural tissue engineering artificial neural networks Advanced Photonics
2022, 4(3): 034002
1 中国科学院 半导体研究所, 北京 100083
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100089
3 中国科学院 脑科学与智能技术卓越创新中心, 上海 200031
4 半导体神经网络智能感知与计算技术北京市重点实验室, 北京 100083)
为改善目前激活函数Tanh硬件化时资源消耗大, 精度低的问题, 提出了一种二阶近似和误差补偿相结合的Tanh函数近似算法。该方法首先对传统二阶近似函数的系数进行log2变换, 以便于硬件实现。然后根据近似函数的误差曲线, 划分补偿区间, 以提高函数精度。在此基础上设计了可硬件实现Tanh函数的电路结构, 在ModelSim平台下进行功能仿真, 并在SMIC 018 μm工艺下进行逻辑综合。实验结果表明, 所实现电路的最大绝对误差为0007 8, 是8 bit输出位宽所能表示的最高精度。
Tanh函数 二阶近似 硬件实现 人工神经网络 Tanh function second-order approximation hardware implementation artificial neural networks
江苏海洋大学 电子工程学院,江苏 连云港 222005
近年来自适应光学(AO)系统向着小型化和低成本化趋势发展,无波前探测自适应光学(WFSless AO)系统由于结构简单、应用范围广,成为目前相关领域的研究热点。硬件环境确定后,系统控制算法决定了WFSless AO系统的校正效果和系统收敛速度。新兴的深度学习及人工神经网络为WFSless AO系统控制算法注入了新的活力,进一步推动了WFSless AO系统的理论发展与应用发展。在回顾前期WFSless AO系统控制算法的基础上,全面介绍了近年来卷积神经网络(CNN)、长短期记忆神经网络(LSTM)、深度强化学习在WFSless AO系统控制中的应用,并对WFSless AO系统中各种深度学习模型的特点进行了总结。概述了WFSless AO技术在天文观测、显微成像、眼底成像、激光通信等领域的应用。
自适应光学 无波前探测 深度学习 人工神经网络 adaptive optics wavefront sensorless deep learning artificial neural networks 强激光与粒子束
2021, 33(8): 081004

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Institute of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
The analog photonics link (APL) is widely used in microwave photonics. However, in wideband and multi-carrier systems, the third inter-modulation distortion (IMD3) and cross-modulation distortion (XMD) will jointly limit the spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) of links. In this paper, we experimentally present a linearized wideband and multi-carrier APL, in which the IMD3 and XMD are mitigated simultaneously by using artificial neural networks with transfer learning (TL-ANN). In this experiment, with different artificial neural networks, which are trained with the knowledge obtained from the two- or three-sub-carrier system, the IMD3 and XMD are suppressed by 21.71 dB and 11.11 dB or 22.38 dB and 16.73 dB, and the SFDR is improved by 13.4 dB or 14.3 dB, respectively. Meanwhile, compared with previous studies, this method could reduce the training time and training epochs to 16% and 25%.
analog photonics link modulation distortion artificial neural networks transfer learning Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(11): 113901
本文提出了一种多尺度补全卷积神经网络(MsiNet),用于光学相干层析(OCT)视网膜图像的分层。该网络充分利用了人眼视觉特性和视网膜层次特征。实验结果表明,与现有的视网膜分层网络相比,MsiNet能够实现更高的分层正确率,同时具有网络规模小和参数量少的特性。
图像处理 人工神经网络 断层成像 光学相干层析 中国激光
2021, 48(15): 1507004
华中科技大学光学与电子信息学院下一代互联网接入系统国家工程实验室&武汉光电国家研究中心, 湖北 武汉 430074
分布式光纤布里渊传感器可以测量上百公里光纤上每一点的温度和应变,被应用于桥梁、隧道、输电线路和油气管道等国家重大工程的状态监测。布里渊传感的核心是测量与光纤温度和应变相关的布里渊频移,一般通过测量光纤的布里渊信号谱来得到。布里渊谱的谱线理论上满足洛伦兹线型,其峰值所对应的频率即为布里渊频移。为了降低采样精度和噪声的影响,从布里渊谱中提取布里渊频移最常用的方法是洛伦兹曲线拟合法。然而曲线拟合对初始值敏感,当信噪比较低时,拟合误差显著增加,并且曲线拟合的运算时间较长,降低系统的响应速度。为了提高提取布里渊频移的精度和速度,研究人员采用机器学习算法处理布里渊谱以提取布里渊频移,从而取得比传统拟合算法更好的结果。本文主要介绍近几年机器学习算法在提取布里渊频移中取得的成果,包括奇异值分解、支持向量机和人工神经网络的应用原理和效果。
激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(13): 1306010
1 上海理工大学光子芯片研究院, 上海 200093
2 上海理工大学光电信息与计算机工程学院人工智能纳米光子学中心, 上海 200093
人工智能技术,特别是人工神经网络的创新引领了许多领域的应用革命,如网络搜索、计算机识别和语言、图像的识别技术。近年来纳米光子学的发展为传统的人工神经网络技术,特别是光学神经网络的发展带来了全新的物理视角以及截然不同的实现方法。一方面,纳米光子学是一门研究光与材料在纳米尺度相互作用的科学,可以带来全新的技术,如超分辨光学加工技术和超分辨光学成像技术,进而推动微纳尺度上多种功能的光学神经网络的实现。另一方面,纳米光子学中光子传播的多频段、高速度、低功耗的特点,促使了光学神经网络向着小体积、高密度、低功耗的方向发展。人工神经网络自身的发展也促使神经网络算法(如逆向设计、深度学习)在纳米光子学器件的设计中发挥前所未有的作用,以满足纳米光子学器件对自身功能、体积、集成度、计算功能的日益增长的要求。以神经网络的发展为起点,阐述人工神经网络特别是光学神经网络的发展趋势,以及人工神经网络与纳米光子学相互促进的发展历程。
光学器件 人工智能 人工神经网络 光学神经网络 纳米光子学 光学人工智能
东莞职业技术学院 电子与电气工程学院, 广东 东莞 523808
当前室内可见光通信系统大多考虑接收机静止的情况, 无法适用于日益增多的移动设备。为了解决可见光通信系统中移动接收机的解调问题, 提出了基于人工神经网络的可见光通信移动接收机方案。以广泛应用的二进制振幅键控调制技术为基础, 推导出可见光通信移动场景的检测方法和解调阈值; 通过动态时间规整技术提取光强度序列的距离特征, 利用遗传算法对特征集进行优化, 选择高显著性的少量特征子集; 将特征子集送入人工神经网络进行训练, 对二进制振幅键控解调阈值进行预测。实验结果显示, 方案有效降低了移动场景下可见光通信系统的误码率。
可见光通信 人工神经网络 调制解调器 遗传算法 特征选择 visible light communication artificial neural networks modulator and demodulator genetic algorithm feature selection
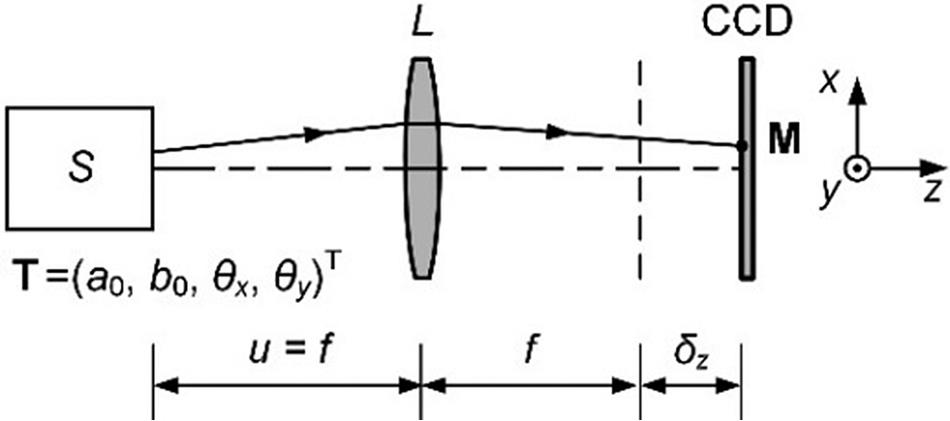
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute for Advanced Study, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
In laser-pointing-related applications, when only the centroid of a laser spot is considered, then the position and angular errors of the laser beam are often coupled together. In this study, the decoupling of the position and angular errors is achieved from one single spot image by utilizing a neural network technique. In particular, the successful application of the neural network technique relies on novel experimental procedures, including using an appropriate small-focal-length lens and tilting the detector, to physically enlarge the contrast of different spots. This technique, with the corresponding new system design, may prove to be instructive in the future design of laser-pointing-related systems.
artificial neural networks laser pointing pointing errors High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2020, 8(3): 03000e28





