基于数字全息的云中冰晶微物理参数观测方法
As an important component of the cloud droplet spectrum, ice crystals exert important effects on global radiation budget balance, global climate change, hydrological cycle, and weather modification. Due to the limitation of observation means, the understanding about the microphysical characteristics of ice crystal particles is not perfect till now. At present, it is difficult to identify the mixed phase of 2-100 μm ice crystals from droplets, and there is a bottleneck to provide microphysical parameters of ice crystals. The lack of sufficient ice crystal detection data can cause large differences in the mean value of ice water paths in different models, especially in mixed-phase clouds. Therefore, we study the microphysical parameters of ice crystals.
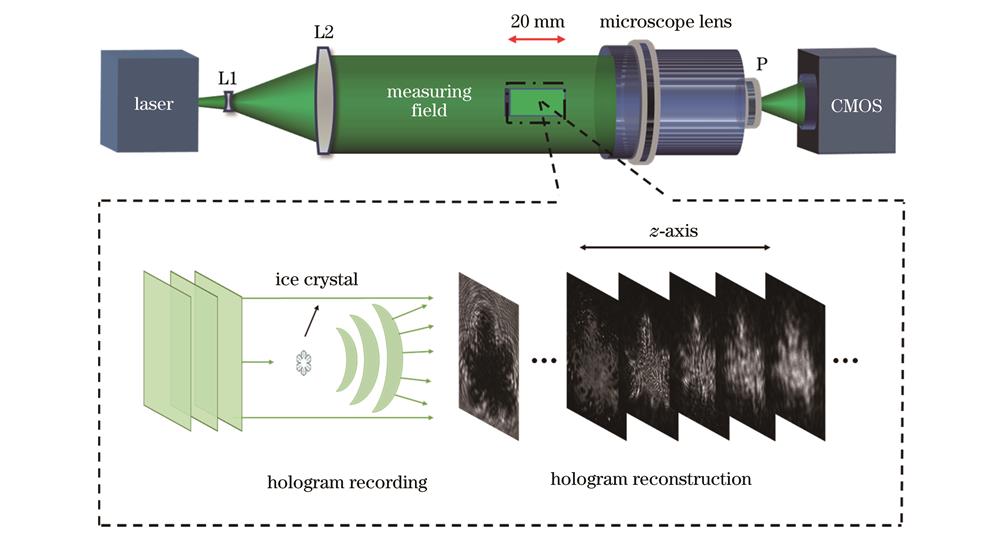
For these two problems, based on the digital holography theory, we propose to employ the global digital image fusion method, the local Tenengrad variance method, and the rotating caliper method for identifying mixed phase states of droplets and ice crystals in the cloud by combining the roundness concept of solid and liquid particles. Combined with optical image recognition technology, we obtain the area, perimeter, convex hull, and minimum enclosing rectangle data of ice crystals. Finally, the microphysical parameters of ice crystals are acquired by adopting the above data. The microphysical parameters of plate, dendritic and hexagonal ice crystals are obtained by observation experiments in low-temperature cloud chambers.
Some obvious conclusions can be obtained by adopting the proposed method. 1) By leveraging the rotating caliper method and the specific geometric parameter roundness F, the mixed phase identification of droplets and ice crystals in clouds is realized. Under the specific roundness threshold, the recognition rate of droplets and ice crystals is greater than 93% (Fig. 8). 2) Combined with optical image recognition technology, morphological data (the area, perimeter, convex hull, and minimum enclosing rectangle data) of ice crystal particles are obtained (Table 1). 3) The microphysical parameters of ice crystals are acquired by morphological data of ice crystals (Table 2). 4) When the digital hologram of ice crystal particles is obtained with the frequency of 30 frame/s, the three-dimensional kinetic velocity of ice crystal particles can also be acquired by this method (Fig. 11).
An ice crystal detection method based on a pulse-modulated laser, high-resolution optical system, and coaxial digital holography (DH) is presented. The local Tenengrad variance method, the rotating caliper method, and the specific geometric parameter roundness F are adopted for phase state identification of particles. To verify the validity of the detection method and identification algorithm, we observe the mixed particles of droplets and ice crystals in the cloud chamber. Additionally, the three-dimensional motion velocity and trajectory of ice crystals can be obtained from the sampling interval time and the three-dimensional coordinates and equivalent diameters of the center of mass at different time. This method solves the bottleneck problem that the existing observation technology cannot identify the phase states and obtain the microphysical parameters of ice crystals. Meanwhile, the method is of significance to improve the accuracy of numerical weather prediction and weather modification operation.
杨晨遇, 王骏, 张川, 周浩, 杨军胜, 岳治国, 梁谷, 刘晶晶, 华灯鑫. 基于数字全息的云中冰晶微物理参数观测方法[J]. 光学学报, 2024, 44(6): 0601017. Chenyu Yang, Jun Wang, Chuan Zhang, Hao Zhou, Junsheng Yang, Zhiguo Yue, Gu Liang, Jingjing Liu, Dengxin Hua. Observation Method of Microphysical Parameters of Ice Crystals in Cloud Based on Digital Holography[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2024, 44(6): 0601017.