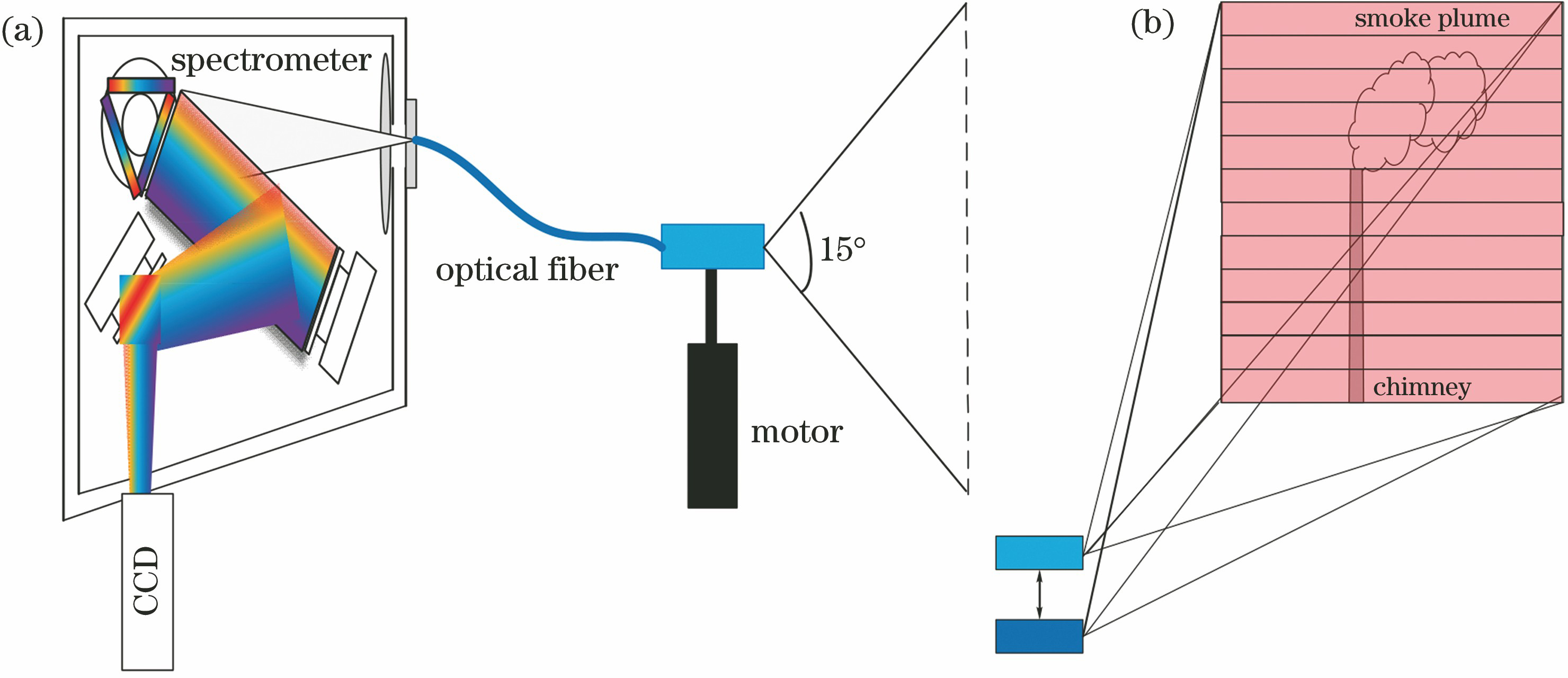
基于光谱遥测技术的烟羽二维分布快速成像  下载: 1458次封面文章
下载: 1458次封面文章
张强, 谢品华, 徐晋, 李昂, 胡肇琨, 田鑫, 黄业园, 刘文清. 基于光谱遥测技术的烟羽二维分布快速成像[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(9): 0930002.
Qiang Zhang, Pinhua Xie, Jin Xu, Ang Li, Zhaokun Hu, Xin Tian, Yeyuan Huang, Wenqing Liu. Two-Dimensional Fast Imaging of Smoke Plumes Based on Spectral Telemetry[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(9): 0930002.
[1] General S, Bobrowski N, Pöhler D, et al. Airborne I-DOAS measurements at Mt. etna: BrO and OClO evolution in the plume[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2015, 300: 175-186.
[2] Meier A C, Schönhardt A, Bösch T, et al. High-resolution airborne imaging DOAS measurements of NO2 above Bucharest during AROMAT[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2017, 10(5): 1831-1857.
[3] Lee H, Irie H, Ryu J, et al. Lower tropospheric aerosol measurements by MAX-DOAS during severe Asian dust period[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 2009, 43(12): 1208-1217.
[4] Pikelnaya O, Flynn J H, Tsai C, et al. Imaging DOAS detection of primary formaldehyde and sulfur dioxide emissions from petrochemical flares[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2013, 118(15): 8716-8728.
[5] 刘进, 司福祺, 周海金, 等. 机载成像差分吸收光谱技术测量区域NO2二维分布研究[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(3): 034217.
Liu J, Si F Q, Zhou H J, et al. Observation of two-dimensional distributions of NO2 with airborne imaging DOAS technology[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(3): 034217.
[6] 王汝雯, 谢品华, 徐晋, 等. 基于近红外差分吸收光谱技术的大气中水汽柱浓度反演[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(2): 0201001.
[7] Cheng Y L, Wang S S, Zhu J, et al. Surveillance of SO2 and NO2 from ship emissions by MAX-DOAS measurements and the implications regarding fuel sulfur content compliance[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2019, 19(21): 13611-13626.
[8] Lohberger F, Hönninger G, Platt U. Ground-based imaging differential optical absorption spectroscopy of atmospheric gases[J]. Applied Optics, 2004, 43(24): 4711-4717.
[9] Lee H, Kim Y J, Lee C. Estimation of the rate of increase in nitrogen dioxide concentrations from power plant stacks using an imaging-DOAS[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2009, 152(1/2/3/4): 61-70.
[10] Platt U, Lübcke P, Kuhn J, et al. Quantitative imaging of volcanic plumes: results, needs, and future trends[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2015, 300: 7-21.
[11] Mons V, Wang Q, Zaki T A. Kriging-enhanced ensemble variational data assimilation for scalar-source identification in turbulent environments[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 398: 108856.
[12] van Zoest V, Osei F B, Hoek G, et al. Spatio-temporal regression kriging for modelling urban NO2 concentrations[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2019: 1-15.
[13] Sharan M, Gopalakrishnan S G. Mathematical modeling of diffusion and transport of pollutants in the atmospheric boundary layer[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2003, 160(1/2): 357-394.
[14] Sánchez-Sosa J E, Castillo-Mixcóatl J, Beltrán-Pérez G, et al. An application of the Gaussian plume model to localization of an indoor gas source with a mobile robot[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(12): 4375.
[15] Rakesh P T, Venkatesan R, Srinivas C V, et al. Performance evaluation of modified Gaussian and Lagrangian models under low wind speed: a case study[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2019, 133: 562-567.
[16] Wu Z Q, Liu C H. Parameterisation study of chemically reactive pollutant dispersion over idealised urban areas based on the Gaussian plume model[J]. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 2019, 65(1/2/3): 84-102.
[17] Jeong H, Kim E, Park M, et al. Numerical simulation of air pollutant dispersion using an in situ tracer experiment at a nuclear site[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2014, 73: 1-6.
[18] Shah A, Allen G, Pitt J R, et al. A near-field Gaussian plume inversion flux quantification method, applied to unmanned aerial vehicle sampling[J]. Atmosphere, 2019, 10(7): 396.
[19] Wang Y, Dörner S, Donner S, et al. Vertical profiles of NO2, SO2, HONO, HCHO, CHOCHO and aerosols derived from MAX-DOAS measurements at a rural site in the central western North China Plain and their relation to emission sources and effects of regional transport[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2019, 19(8): 5417-5449.
[20] Tan W, Liu C, Wang S S, et al. Tropospheric NO2, SO2, and HCHO over the East China Sea, using ship-based MAX-DOAS observations and comparison with OMI and OMPS satellite data[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 18(20): 15387-15402.
[21] Tian X, Xie P H, Xu J, et al. Long-term observations of tropospheric NO2, SO2 and HCHO by MAX-DOAS in Yangtze River Delta area, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 71: 207-221.
[22] Brinksma E J, Pinardi G, Volten H, et al. and 2006 Dandelions NO2 and aerosol intercomparison campaigns[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 2008, 113(D16): D16S46., 2005.
[23] 李昂, 谢品华, 刘文清, 等. 被动差分吸收光谱法测量区域内污染气体排放通量的方法研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2009, 29(1): 28-32.
[24] Balzani Lööv J M, Alfoldy B, Gast L F L, et al. Field test of available methods to measure remotely SOx and NOx emissions from ships[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2014, 7(8): 2597-2613.
[25] Berg N, Mellqvist J, Jalkanen J P, et al. Ship emissions of SO2 and NO2: DOAS measurements from airborne platforms[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2012, 5(5): 1085-1098.
[26] Hong Q Q, Liu C, Chan K L, et al. Ship-based MAX-DOAS measurements of tropospheric NO2, SO2, and HCHO distribution along the Yangtze River[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 18(8): 5931-5951.
[27] Wu F C, Xie P H, Li A, et al. Investigations of temporal and spatial distribution of precursors SO2 and NO2 vertical columns in the North China Plain using mobile DOAS[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 18(3): 1535-1554.
[29] Hendrick F, Müller J F, Clémer K, et al. Four years of ground-based MAX-DOAS observations of HONO and NO2 in the Beijing area[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2014, 14(2): 765-781.
张强, 谢品华, 徐晋, 李昂, 胡肇琨, 田鑫, 黄业园, 刘文清. 基于光谱遥测技术的烟羽二维分布快速成像[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(9): 0930002. Qiang Zhang, Pinhua Xie, Jin Xu, Ang Li, Zhaokun Hu, Xin Tian, Yeyuan Huang, Wenqing Liu. Two-Dimensional Fast Imaging of Smoke Plumes Based on Spectral Telemetry[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(9): 0930002.