Chinese Optics Letters, 2020, 18 (12): 121402, Published Online: Oct. 23, 2020
Simultaneous generation of controllable double white light lasers by focusing an intense femtosecond laser pulse in air  Download: 771次
Download: 771次
Figures & Tables
Fig. 1. (a) Schematic of experimental setup. QWP is a zero-order quarter waveplate. ND filter is neutral density filter. (b) Input beam spatial profile and (c) typical forward beam pattern after filamentation (about 1.3 m away) on the screen taken by a digital camera (Nikon D7200). The laser pulse energy was 7.43 mJ.
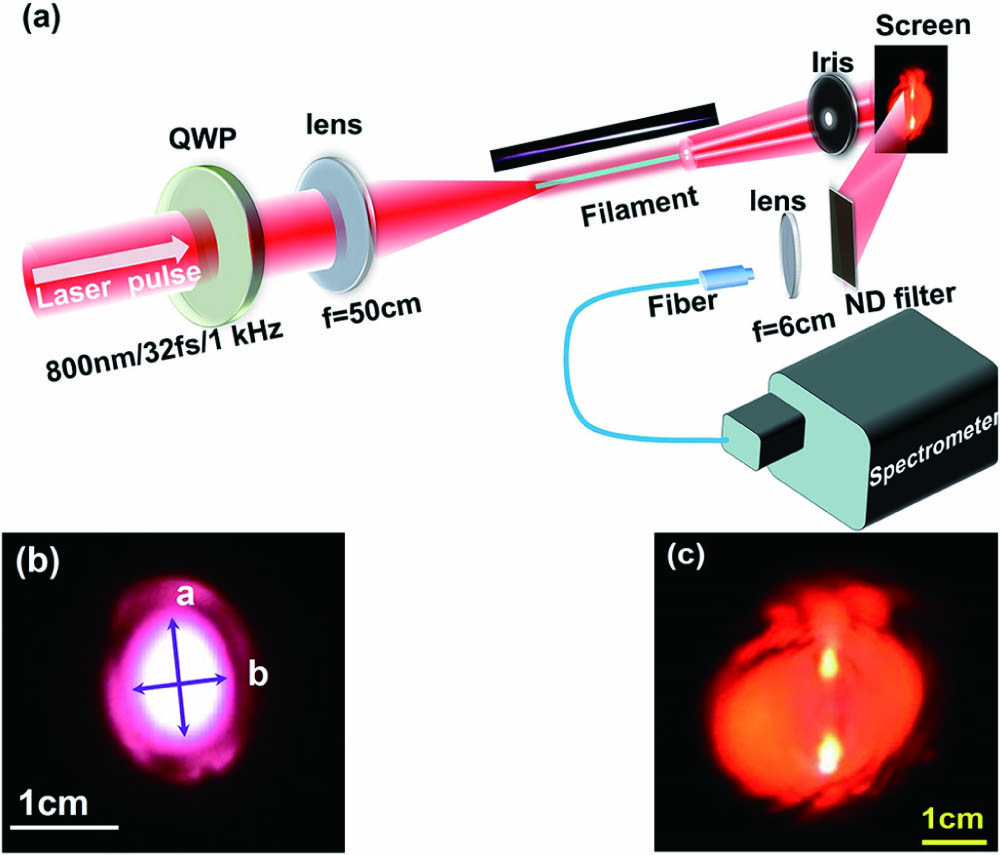
Fig. 2. (a) Real-color images of filaments in air with laser incident angle to the lens changing from 0 deg to 20 deg. Exposure time of the camera in (a) was 0.25 s. The energy of the linearly polarized laser pulse was 7.43 mJ. Corresponding forward white light beam patterns on the screen at different incident angles of (b) 0 deg, (c) 5 deg, (d) 10 deg, and (e) 20 deg. Exposure time of the camera in (b)–(e) was 0.02 s with an ND filter in front of the camera. There are 20 shots of white light beams accumulated in each image.

Fig. 3. (a) Filament fluorescence images under different polarization states taken by a camera with the exposure time of 0.25 s. The laser energy was 7.43 mJ. The laser polarization is LP (CP) when the QWP angle was 0 deg or 90 deg (45 deg). (b) The effective filament length as a function of the QWP angle (the laser polarization state) under different laser energies. (c) The corresponding forward white light spots in (a) as the polarization states of the laser changed from LP to CP. The exposure time of the camera in (c) was 0.02 s without the ND filter.

Fig. 4. (a) Normalized SC spectra of the upper and lower white light spots for LP filamenting pulses. The pulse energy was 7.43 mJ. (b) Spectra of white lights for LP, EP (the QWP angle was 30 deg), and CP. The spectral intensity is the integration of the spectral density of both the upper and lower white lights. (c) Spectral bandwidth of the SC versus different pump laser polarization states. The spectral bandwidth is defined by the full width of the spectral intensity curve at

Yaoxiang Liu, Tie-Jun Wang, Na Chen, Hao Guo, Haiyi Sun, Lu Zhang, Zheng Qi, Yuxin Leng, Zhanshan Wang, Ruxin Li. Simultaneous generation of controllable double white light lasers by focusing an intense femtosecond laser pulse in air[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2020, 18(12): 121402.





