基于耦合混沌半导体激光器之间双向信号传输的研究  下载: 807次
下载: 807次
1 引言
近年来,由于混沌在激光雷达、相干断层、神经网络、生物学、经济和安全通信等方面的诸多应用,吸引了众多研究者的关注。混沌是具有内在确定性的类噪声随机过程,其非周期、有界以及对初始条件的敏感性使其在通信传输方面具有极大的优点[1-2]。在一个利用混沌载波进行传输的安全通信系统中,常常使用半导体激光器(SL)相互耦合增加其自由度来产生混沌信号[3-4],其最大的特征是利用混沌信号作为信号的载波,由于混沌具有同步和稳健性的特征,故可以实现传输信息的解码。在传输信号时,发射机输出的混沌载波充当了传送信号的载体。由于信号的振幅远小于混沌载波的波动,因此很难将信号从混沌载波中分离出来。具体地说,为了实现信号解码,发射机需要与接收机高度相似,只有当接收机产生的混沌载波与发射机产生的混沌载波同步时才能通过监测接收机输出与输入的同步误差来恢复信号。因此,混沌同步是实现整个混沌传输系统的关键[5-6]。基于SLs的双向混沌保密通信已经成为了研究的热点[7]。
本文通过同时调制两完全相同的半导体激光器的相位实现了信号的双向传输,这两激光器中的阈值电流、光子/载流子衰减速率、线宽增强因子、微分增益因子以及饱和系数等均一致。参数相同是两束激光实现同步混沌载波的基础。在数值模拟中,两束激光先通过部分透光的平面镜相互耦合产生混沌动力,完全同步后,将需要传输的两个信号同步调制进入两个激光器的反馈相位中。最后,通过监测接收机输出与输入之间的同步误差,恢复传输信号。
2 理论模型
基于混沌的双向信息传输系统的体系结构如
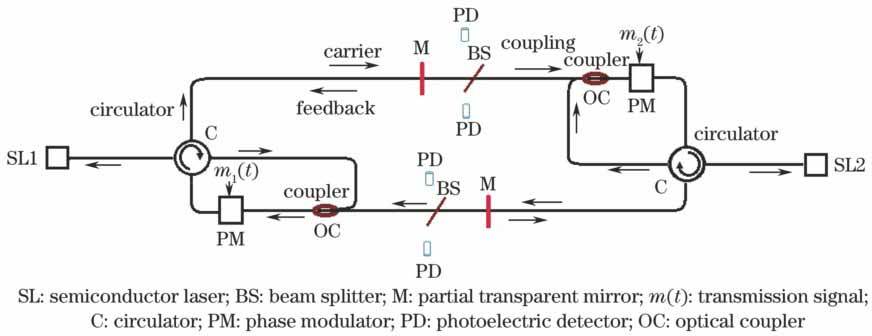
图 1. 基于混沌的双向信息传输系统的示意图
Fig. 1. Schematic of chaos-based bidirectional signal transmission system
基于Lang-Kobayashi速率方程和文献[ 8-9]可知,两个SLs的速率方程可以写成
式中:
因此,在激光器中注入的光是反馈和耦合的总和,为了保证同步性,需要各自激光器的反馈耦合总和相等,而且默认反馈的延迟时间和耦合时间远远大于激光的松弛振荡时间。定义相关系数来量化混沌同步的质量:

图 2. 耦合-反馈系数平面的互相关系数
Fig. 2. Cross-correlation coefficient in the oupling-feedback coefficients plane
式中:
3 同步性和稳健性分析
首先,通过奇异吸引子的相图来确定系统是否能产生混沌载波,然后利用同步图来说明两束激光之间的同步性是否存在,最后通过调制相位来研究同步的稳健性。在该系统中,若是耦合系数大,反馈系数太小,将会阻碍混沌载波的产生;相反,反馈系数大,耦合系数过小将会影响同步的性能。因此,有必要优化反馈以及耦合的参数。根据仿真,得到了关于在不同的耦合系数和反馈系数下两束混沌载波的互相关系数,如

图 3. 相空间中(a) SL1、(b) SL2的吸引子图
Fig. 3. Diagram of attractors of (a) SL1 and (b) SL2 in phase space
结合实际的激光器,再根据相关的文献[
10],选取其余参数,如
通过仿真得到各激光器相空间的吸引子图,如
表 1. 实验所需参数值
Table 1. Parameter values used in simulation
|
假设SL1和SL2的初始光子数不同,数值求解方程(1)~(4)式,绘制了
![光功率的瞬时时间轨迹[SL2(红色)的轨迹垂直下移,以区别于SL1(蓝色)],插入图为SL1和SL2两种激光输出之间的互相关函数](/richHtml/zgjg/2018/45/5/0506001/img_4.jpg)
图 4. 光功率的瞬时时间轨迹[SL2(红色)的轨迹垂直下移,以区别于SL1(蓝色)],插入图为SL1和SL2两种激光输出之间的互相关函数
Fig. 4. Temporal traces of optical power of SL1 (blue),SL2 (red). Traces of SL2 have been shifted vertically to istinguish it from SL1. Insert shows the cross-correlation function between the two laser outputs
4 相移键控的双向信息传输
开关相移键控(OOPSK)方案应用于双向传输时,需要对两束激光器输入端的反馈相位进行相应的调制[11-13],分别为
差异值。混沌载波完全同步后,两个传输信号以1 Gbit·s-1的速率同时调制两束激光的反馈相位,利用一个合适的滤波器,对同步误差进行整形,如

图 6. (a)两束激光的传输信号m1(t)和m2(t);(b)传输信号差异的绝对值Δm(t);(c)由巴特沃斯滤波器整形后的同步误差的绝对值P1(t)-P2t;(d)通过P1(t)-P2t(blue)和m1(t)(red)以及解码发送信号m2(t)
Fig. 6. (a) Transmission signal of two lasers; (b) absolute value of difference of two lasers Δm(t); (c) synchronization errors P1(t)-P2t shaped by Butterworth filter; (d) decoding by P1(t)-P2t (blue) and m1(t) (red) to send signal m2(t)
绘制了解码信息之后的眼图,如
5 结论
基于两束激光的延迟速率方程,研究了两束激光的同步和稳健性。在没有外部扰动的情况下,即使是激光的初始值不一样,经过一段时间,激光器之间的同步误差也会趋于零,这意味着动力学的同步性是成立的。在设计中,每一个激光器不仅是一个发射机,而且是一个接收机,两种不同的信号都是通过同时调制两束激光的反馈相位进行加密。混沌的同步和稳健性表明:对于两个激光器,发送比特同时是0或1,同步可以保持,相反,同步将会被打破。通过监测发射机与接收机之间的同步误差,并将误差与本地信号进行比较,解调出发送者的信号,信号的眼图说明系统可以实现高质量传输。在此方案中,窃听者可以监控同步误差,但无法获取本地发送的比特位,因此该系统可以保证双向通信的安全性。
[2] Heidari-BateniG, McGillem C D, Tenorio M F. A novel multiple-address digital communication system using chaotic signals[C]. IEEE International Conference on Communications, 1992, 3( 3): 1232- 1236.
Heidari-BateniG, McGillem C D, Tenorio M F. A novel multiple-address digital communication system using chaotic signals[C]. IEEE International Conference on Communications, 1992, 3( 3): 1232- 1236.
[3] 王永胜, 赵彤, 王安帮, 等. 一种可产生高带宽混沌
王永胜, 赵彤, 王安帮, 等. 一种可产生高带宽混沌
[4] 张晓旭, 吴天安, 常凯歌, 等. 单端反馈互耦合垂直腔面发射激光器混沌输出的时延特征和带宽分析[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(5): 0501010.
张晓旭, 吴天安, 常凯歌, 等. 单端反馈互耦合垂直腔面发射激光器混沌输出的时延特征和带宽分析[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(5): 0501010.
. 的外腔半导体激光器的设计及其动态特性, [J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2017, 54(11): 111401.
. 的外腔半导体激光器的设计及其动态特性, [J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2017, 54(11): 111401.
[5] 李琼, 邓涛, 吴正茂, 等. 安全性增强的双向长距离混沌保密通信[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(1): 0106001.
李琼, 邓涛, 吴正茂, 等. 安全性增强的双向长距离混沌保密通信[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(1): 0106001.
Article Outline
李齐良, 卢珊珊, 包琪, 陈德望, 唐向宏, 胡淼, 曾然, 杨国伟. 基于耦合混沌半导体激光器之间双向信号传输的研究[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(5): 0506001. Li Qiliang, Lu Shanshan, Bao Qi, Chen Dewang, Tang Xianghong, Hu Miao, Zeng Ran, Yang Guowei. Bidirectional Signal Transmission Based on Two Coupled Chaotic Semiconductor Lasers[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45(5): 0506001.








