Simultaneous dual-contrast three-dimensional imaging in live cells via optical diffraction tomography and fluorescence  Download: 645次
Download: 645次
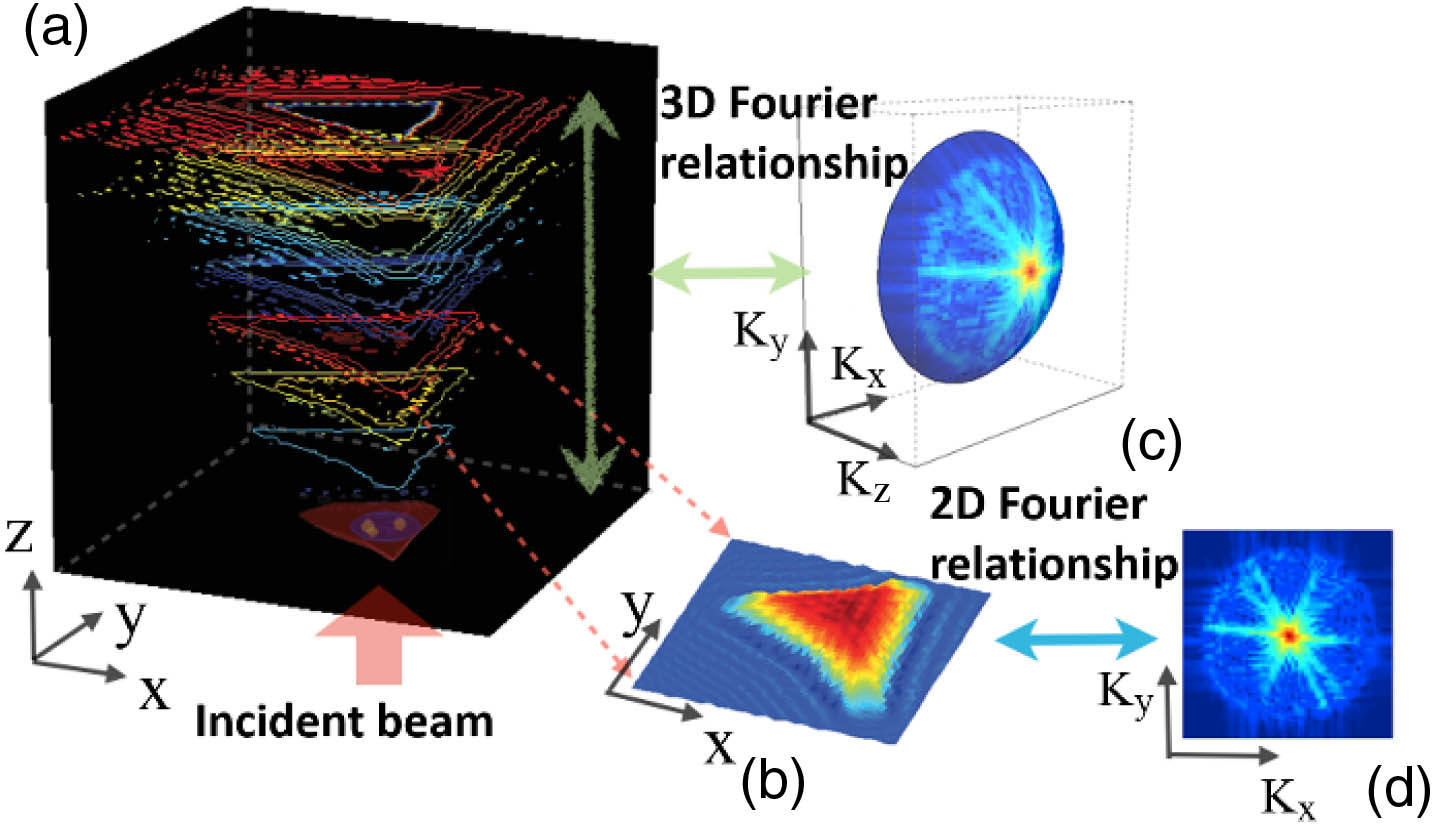
Chen Liu, Michael Malek, Ivan Poon, Lanzhou Jiang, Arif M. Siddiquee, Colin J. R. Sheppard, Ann Roberts, Harry Quiney, Douguo Zhang, Xiaocong Yuan, Jiao Lin, Christian Depeursinge, Pierre Marquet, Shan Shan Kou. Simultaneous dual-contrast three-dimensional imaging in live cells via optical diffraction tomography and fluorescence[J]. Photonics Research, 2019, 7(9): 09001042.
[17]
[27]
[39]
[41] D. Kumar, W. Cong, G. Wang. Monte Carlo method for bioluminescence tomography. Indian J. Exp. Biol., 2007, 45: 58-63.
Chen Liu, Michael Malek, Ivan Poon, Lanzhou Jiang, Arif M. Siddiquee, Colin J. R. Sheppard, Ann Roberts, Harry Quiney, Douguo Zhang, Xiaocong Yuan, Jiao Lin, Christian Depeursinge, Pierre Marquet, Shan Shan Kou. Simultaneous dual-contrast three-dimensional imaging in live cells via optical diffraction tomography and fluorescence[J]. Photonics Research, 2019, 7(9): 09001042.