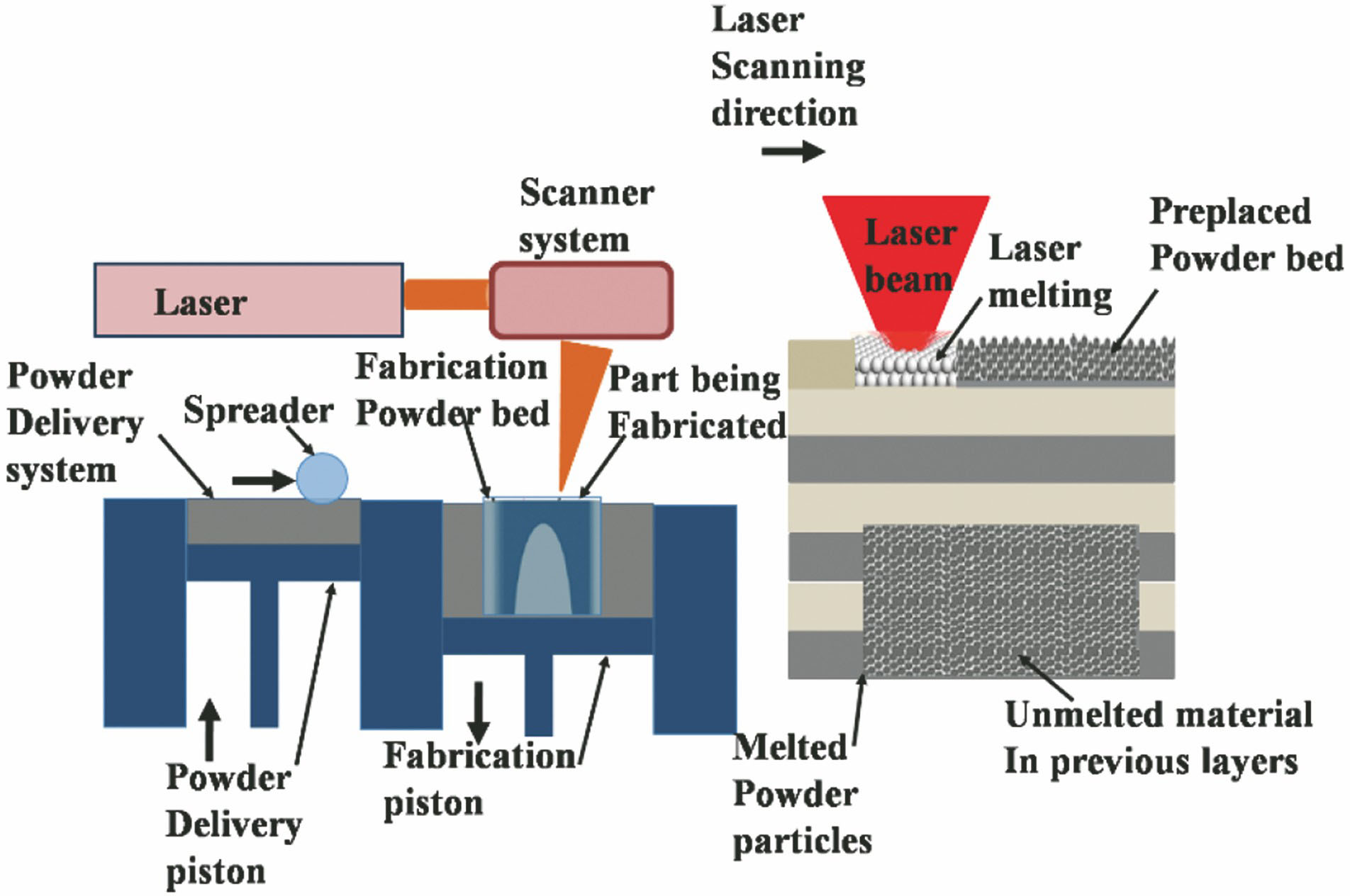
激光增材制造镁合金的研究现状及展望  下载: 2524次
下载: 2524次
朱兆雨, 陈长军, 张敏. 激光增材制造镁合金的研究现状及展望[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(19): 190006.
Zhaoyu Zhu, Changjun Chen, Min Zhang. Research Progress and Prospect of Laser Additive Manufacturing Technique for Magnesium Alloy[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(19): 190006.
[1] GuptaM,[\s]{1}Sharon[\s]{1}N[\s]{1}M[\s]{1}L.[\s]{1}Magnesium,[\s]{1}magnesium[\s]{1}alloys,[\s]{1}and[\s]{1}magnesium[\s]{1}composites[M].[\s]{1}Hoboken:[\s]{1}John[\s]{1}Wiley[\s]{1}&[\s]{1}Sons,[\s]{1}Inc.,[\s]{1}2010:[\s]{1}4-[\s]{1}21.[\s]{1}
[2] Mordike B L, Ebert T. Magnesium: properties-applications-potential[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2001, 302(1): 37-45.
[3] Froes F H, Eliezer D, Aghion E. The science, technology, and applications of magnesium[J]. JOM, 1998, 50(9): 30-34.
[4] Song G L, Atrens A. Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 1999, 1(1): 11-33.
[5] 史文方,[\s]{1}周昆.[\s]{1}我国镁合金的开发应用现状及展望[J].[\s]{1}汽车工艺与材料,[\s]{1}2004([\s]{1}6):[\s]{1}32-[\s]{1}37.[\s]{1}
Shi[\s]{1}WF,[\s]{1}ZhouK.[\s]{1}The[\s]{1}application[\s]{1}and[\s]{1}outlook[\s]{1}of[\s]{1}magnesium[\s]{1}alloy[\s]{1}development[\s]{1}in[\s]{1}China[J].[\s]{1}Automobile[\s]{1}Technology[\s]{1}&[\s]{1}Material,[\s]{1}2004([\s]{1}6):[\s]{1}32-[\s]{1}37.[\s]{1}
[6] 郑玉峰, 吴远浩. 处在变革中的医用金属材料[J]. 金属学报, 2017, 53(3): 257-297.
Zheng Y F, Wu Y H. Revolutionizing metallic biomaterials[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2017, 53(3): 257-297.
[7] Taltavull C, Shi Z, Torres B, et al. Influence of the chloride ion concentration on the corrosion of high-purity Mg, ZE41 and AZ91 in buffered Hank's solution[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2014, 25(2): 329-345.
[8] Gehrmann R, Frommert M M, Gottstein G. Texture effects on plastic deformation of magnesium[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2005, 395(1/2): 338-349.
[9] Singh S, Ramakrishna S, Singh R. Material issues in additive manufacturing:a review[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2017, 25: 185-200.
[10] Lee H. Lim C H J, Low M J, et al. Lasers in additive manufacturing: a review[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 2017, 4(3): 307-322.
[11] Zhang L C, Attar H. Selective laser melting of titanium alloys and titanium matrix composites for biomedical applications: a review[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2016, 18(4): 463-475.
[12] Lu Z L, Cao J W, Jing H, et al. Review of main manufacturing processes of complex hollow turbine blades[J]. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 2013, 8(2): 87-95.
[14] 文世峰, 季宪泰, 周燕, 等. 激光选区熔化成形模具钢的发展现状及前景[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(1): 011404.
[15] 刘金, 王薇茜, 程序, 等. 激光增材制造Ti60A钛合金的氧化行为[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(7): 0702007.
[16] 王宏芳, 田象军, 程序, 等. 热变形条件对激光增材制造TC18钛合金组织及变形行为的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(3): 0302008.
[17] Zhang M, Chen C J, Huang Y. Laser additive manufacturing foam aluminium-12 wt-% silicon with different addition TiH2 foaming agent[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2018, 34(8): 968-981.
[18] Li Y L, Gu D D. Parametric analysis of thermal behavior during selective laser melting additive manufacturing of aluminum alloy powder[J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 63: 856-867.
[19] 谢琰军, 杨怀超, 王学兵, 等. 激光参数和扫描策略对选择性激光熔化TC11合金成形性能的影响[J]. 粉末冶金工业, 2018, 28(2): 18-24.
Xie Y J, Yang H C, Wang X B, et al. Effects of laser parameters and scanning strategy on the forming properties of selective laser melting TC11 alloy[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2018, 28(2): 18-24.
[20] Wei K W, Gao M, Wang Z M, et al. Effect of energy input on formability, microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted AZ91D magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 611: 212-222.
[22] Zhang B C, Liao H L, Coddet C. Effects of processing parameters on properties of selective laser melting Mg-9%Al powder mixture[J]. Materials & Design, 2012, 34: 753-758.
[23] Liu C, Zhang M, Chen C J. Effect of laser processing parameters on porosity, microstructure and mechanical properties of porous Mg-Ca alloys produced by laser additive manufacturing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2017, 703: 359-371.
[24] Shuai C J, Yang Y W, Wu P, et al. Laser rapid solidification improves corrosion behavior of Mg-Zn-Zr alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 691: 961-969.
[25] Savalani M M, Pizarro J M. Effect of preheat and layer thickness on selective laser melting (SLM) of magnesium[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2016, 22(1): 115-122.
[26] Gai G S, Yang Y F, Jin L, et al. Particle shape modification and related property improvements[J]. Powder Technology, 2008, 183(1): 115-121.
[27] Froes F H, Mashl S J, Hebeisen J C, et al. The technologies of titanium powder metallurgy[J]. JOM, 2004, 56(11): 46-48.
[28] Niu H J. Chang I T H. Selective laser sintering of gas and water atomized high speed steel powders[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1999, 41(1): 25-30.
[29] KumarS.[\s]{1}Selective[\s]{1}laser[\s]{1}sintering/melting[M][\s]{1}//Hashmi[\s]{1}S,[\s]{1}Batalha[\s]{1}G[\s]{1}F,[\s]{1}van[\s]{1}Tyne[\s]{1}C[\s]{1}J,[\s]{1}et[\s]{1}al.[\s]{1}Comprehensive[\s]{1}materials[\s]{1}processing:[\s]{1}advances[\s]{1}in[\s]{1}additive[\s]{1}manufacturing[\s]{1}and[\s]{1}tooling.[\s]{1}Amsterdam:[\s]{1}Elsevier,[\s]{1}2014:[\s]{1}93-[\s]{1}134.[\s]{1}
[30] Gu D D, Shen Y F. Balling phenomena during direct laser sintering of multi-component Cu-based metal powder[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 432(1/2): 163-166.
[31] 田杰, 黄正华, 戚文军, 等. 金属选区激光熔化的研究现状[J]. 材料导报, 2017, 31(S1): 90-94, 101.
Tian J, Huang Z H, Qi W J, et al. Research progress on selective laser melting of metal[J]. Materials Review, 2017, 31(S1): 90-94, 101.
[33] Attar H, Prashanth K G, Zhang L C, et al. Effect of powder particle shape on the properties of in situ Ti-TiB composite materials produced by selective laser melting[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2015, 31(10): 1001-1005.
[34] Hu D, Wang Y, Zhang D F, et al. Experimental investigation on selective laser melting of bulk net-shape pure magnesium[J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 2015, 30(11): 1298-1304.
[35] Thijs L, Verhaeghe F, Craeghs T, et al. A study of the microstructural evolution during selective laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(9): 3303-3312.
[36] Zhang M, Chen C J, Liu C, et al. Study on porous Mg-Zn-Zr ZK61 alloys produced by laser additive manufacturing[J]. Metals, 2018, 8(8): 635.
[37] 刘晓英.[\s]{1}AZ91镁合金强化技术的研究[D].[\s]{1}济南:[\s]{1}济南大学,[\s]{1}2015.[\s]{1}
Liu[\s]{1}XY.[\s]{1}Research[\s]{1}of[\s]{1}AZ91[\s]{1}magnesium[\s]{1}alloy[\s]{1}strengthening[\s]{1}technology[D].[\s]{1}Jinan:[\s]{1}University[\s]{1}of[\s]{1}Jinan,[\s]{1}2015.[\s]{1}
[38] Wei K W, Wang Z M, Zeng X Y. Influence of element vaporization on formability, composition, microstructure, and mechanical performance of the selective laser melted Mg-Zn-Zr components[J]. Materials Letters, 2015, 156: 187-190.
[39] 魏恺文, 王泽敏, 曾晓雁. AZ91D镁合金在激光选区熔化成形中的元素烧损[J]. 金属学报, 2016, 52(2): 184-190.
Wei K W, Wang Z M, Zeng X Y. Element loss of AZ91D magnesium alloy during selective laser melting process[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(2): 184-190.
[40] Block-Bolten A, Eagar T W. Metal vaporization from weld pools[J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1984, 15(3): 461-469.
[41] Parande G, Manakari V, Meenashisundaram G K, et al. Enhancing the hardness/compression/damping response of magnesium by reinforcing with biocompatible silica nanoparticulates[J]. International Journal of Materials Research, 2016, 107(12): 1091-1099.
[43] Steen W M. Laser material processing: an overview[J]. Journal of Optics A:Pure and Applied Optics, 2003, 5(4): S3-S7.
[44] Wang X Q, Gong X B, Chou K. Review on powder-bed laser additive manufacturing of Inconel 718 parts[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 2017, 231(11): 1890-1903.
[45] Hitzler L, Janousch C, Schanz J, et al. Direction and location dependency of selective laser melted AlSi10Mg specimens[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 243: 48-61.
[46] 陈德宁, 刘婷婷, 廖文和, 等. 扫描策略对金属粉末选区激光熔化温度场的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(4): 0403003.
[47] Hussein A, Hao L, Yan C Z, et al. Finite element simulation of the temperature and stress fields in single layers built without-support in selective laser melting[J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 52: 638-647.
[48] Parry L, Ashcroft I A, Wildman R D. Understanding the effect of laser scan strategy on residual stress in selective laser melting through thermo-mechanical simulation[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2016, 12(Part A): 1-15.
[50] Mercelis P, Kruth J P. Residual stresses in selective laser sintering and selective laser melting[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2006, 12(5): 254-265.
[51] 吴国华, 陈玉狮, 丁文江. 镁合金在航空航天领域研究应用现状与展望[J]. 载人航天, 2016, 22(3): 281-292.
Wu G H, Chen Y S, Ding W J. Current research, application and future prospect of magnesium alloys in aerospace industry[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2016, 22(3): 281-292.
[52] Kamrani S, Fleck C. Biodegradable magnesium alloys as temporary orthopaedic implants: a review[J]. BioMetals, 2019, 32(2): 185-193.
[53] 尹林, 黄华, 袁广银, 等. 可降解镁合金临床应用的最新研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2019, 38(2): 126-137.
Yin L, Huang H, Yuan G Y, et al. Latest research progress of biodegradable magnesium alloys in clinical applications[J]. Materials China, 2019, 38(2): 126-137.
[54] Windhagen H, Radtke K, Weizbauer A, et al. Biodegradable magnesium-based screw clinically equivalent to titanium screw in hallux valgus surgery: short term results of the first prospective, randomized, controlled clinical pilot study[J]. BioMedical Engineering OnLine, 2013, 12: 62.
[55] Zardiackas L D, Parsell D E, Dillon L D, et al. Structure, metallurgy, and mechanical properties of a porous tantalum foam[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2001, 58(2): 180-187.
[56] Yan C Z, Hao L, Hussein A, et al. Advanced lightweight 316L stainless steel cellular lattice structures fabricated via selective laser melting[J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 55: 533-541.
[57] Attar H, Löber L, Funk A, et al. Mechanical behavior of porous commercially pure Ti and Ti-TiB composite materials manufactured by selective laser melting[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2015, 625: 350-356.
朱兆雨, 陈长军, 张敏. 激光增材制造镁合金的研究现状及展望[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(19): 190006. Zhaoyu Zhu, Changjun Chen, Min Zhang. Research Progress and Prospect of Laser Additive Manufacturing Technique for Magnesium Alloy[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(19): 190006.