激光粉末床熔融制备金属骨植入物  下载: 1442次
下载: 1442次
Laser Powder Bed Fusion for Fabrication of Metal Orthopedic Implants
1 清华大学摩擦学国家重点实验室, 北京100084
2 清华大学机械工程系, 北京 100084
3 北京大学工学院材料科学与工程系, 北京 100871
4 北京大学第三医院骨科, 北京 100191
图 & 表
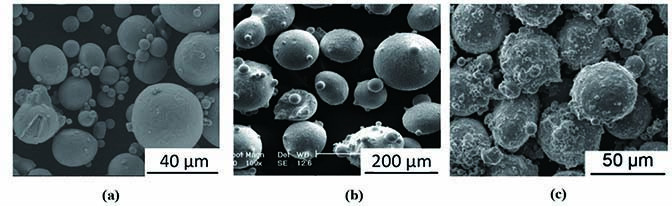
图 1. 采用GA法制备的金属粉末的SEM图像。(a) Ti6Al4V合金[22];(b) CoCrMo合金[23];(c) 316L不锈钢[24]
Fig. 1. SEM images showing metal powers prepared by gas atomization method. (a) Ti6Al4V alloy[22]; (b) CoCrMo alloy[23]; (c) 316L stainless steel[24]
下载图片 查看原文
图 2. L-PBF制造的骨科植入物。(a) Ti6Al4V髋臼杯[25];(b)钽膝关节植入物[26];(c) WE43颌骨植入物[27];(d)纯锌髋关节植入物[29]
Fig. 2. Orthopedics implants manufactured by L-PBF. (a) Ti6Al4V acetabular cup[25]; (b) tantalum knee joint implant[26]; (c) WE43 jaw implant[27]; (d) pure zinc hip joint implant[29]
下载图片 查看原文
图 3. 激光能量输入对致密度的影响[37-45]
Fig. 3. Influence of laser energy input on densification[37-45]
下载图片 查看原文
图 4. 医用金属激光增材制造成形件的拉伸性能[20-21,51-67]
Fig. 4. Tensile properties of medical metals manufactured by L-PBF[20-21,51-67]
下载图片 查看原文
图 5. L-PBF制备的金属骨科植入物[15]
Fig. 5. Metal orthopedic implants manufactured by L-PBF[15]
下载图片 查看原文
表 1常见医用金属的热物性参数[36]
Table1. Thermal physical parameters of common medical metals[36]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| Zn | Mg | Fe | Ti | Ta |
|---|
| Crystal structure | hcp | hcp | bcc/fcc | hcp/bcc | bcc | | Density (20 ℃) /(g·cm-3) | 7.14 | 1.74 | 7.874 | 4.5 | 16.65 | | Melt point (at 101325 Pa) /℃ | 419.5 | 650 | 1538 | 1660 | 2996 | | Boil point (at 101325 Pa) /℃ | 907 | 1091 | 2862 | 3287 | 5425 | | Heat conductivity (20 ℃) /(W·m-1·K-1) | 113 | 158 | 80 | | | | Heat capacity (20 ℃) /(J·kg-1·K-1) | 382 | 1360 | 444 | | | | Surface tension (melting) /(mN·m-1) | 782 | 559 | 1835 | 1588 | 2150 | | Viscosity (melting) /(mPa·s) | 3.85 | 1.25 | 6.93 | 4.54 | | | Oxidation | Low | High | Low | Mid | Mid |
|
查看原文
表 2L-PBF制造的不可降解金属力学性能
Table2. Mechanical properties of non-biodegradable metals built by L-PBF
| Material | Densification /% | Tensilestrength /MPa | Elongation /% | Hardness /HV | Elasticitymodulus /GPa | Reference |
|---|
| CP-Ti | 99.5 | 757 | 19.5 | 224 | 105 | [56] | | Ti6Al4V | 99.4 | 1170 | 11 | 364 | 120 | [54] | | Ti-25Nb | 99 | 748 | 19.9 | 264 | 83.5 | [57] | | Ti30Nb5Ta3Zr | 99.2 | 680 | 15.3 | 279 | 59.5 | [55] | | 316LSS | 99.5 | 584 | 41.9 | 225 | 167 | [58] | | Co28Cr6Mo | 99 | 1070 | 14.3 | 570 | - | [56] | | Co29Cr9W3Cu | 99 | 1038 | 12.5 | 571 | - | [57] | | Ta | 99.6 | 310 | 30 | 120 | 185 | [83] |
|
查看原文
表 3不同方法制造的可降解镁合金和锌合金的晶粒尺寸和力学性能
Table3. Grain size and mechanical properties of biodegradable Zn and Mg-based alloys manufactured by different methods
| Process | Material | Density /% | Grain size /μm | Tensile strength /MPa | Elongation /% |
|---|
| WE43[76] | 99.8 | 1.1 | 308 | 12.2 | | L-PBF | Pure Zn[74] | 99.9 | 5.6 | 134 | 10.4 | | Pure Zn[20] | 97.4 | - | 61.3 | 1.7 | | Zn-2WE43[21] | 99.9 | 2 | 299 | 1.8 | | WE43[76] | - | 1.3 | 307 | 22.4 | | Extrusion | Pure Zn[106] | - | 20 | 100 | 7.5 | | Pure Zn[69] | - | <10 | 167 | 39 | | Zn-0.8Mg[69] | - | <10 | 380 | 10 | | Casting | WE43[76] | - | 44.3 | 189 | 4.4 | | Pure Zn[107] | - | - | 18 | 0.32 |
|
查看原文
尹浜兆, 秦瑜, 温鹏, 郑玉峰, 田耘. 激光粉末床熔融制备金属骨植入物[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47(11): 1100001. Yin Bangzhao, Qin Yu, Wen Peng, Zheng Yufeng, Tian Yun. Laser Powder Bed Fusion for Fabrication of Metal Orthopedic Implants[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(11): 1100001.
 下载: 1442次
下载: 1442次