Gamma-Gamma大气湍流下相干光通信分集接收技术研究  下载: 1171次
下载: 1171次
1 引言
自由空间相干光通信因具有接收灵敏度高、传输速率高、保密性好、终端质量低和功耗低等优势,在未来空间信息组网中的应用前景广阔[1]。星地激光通信作为空间信息组网的重要组成部分,其通信链路经过大气信道时,由于受到大气湍流的影响,接收平面会出现光强闪烁、光束漂移等现象,最终导致基于单天线接收的自由空间光通信(FSO)系统的通信性能无法得到保证。分集接收技术通过在接收端使用多个光学天线接收光信号,当接收天线间隔大于大气相干长度时,各支路接收信号是相互独立的,将其适当地合并,可有效改善大气湍流对空间通信系统性能的影响[2]。
目前,主要的大气湍流信道模型有:对数正态分布、
本文在现有研究的基础上,对不同强度大气湍流信道Gamma-Gamma分布模型下,分集接收技术对相干接收系统性能的影响进行了系统研究。对比MRC、SC合并算法,给出了基于EGC分集接收的系统误码率(BER)和通信中断概率(OP)表达式;在不同大气湍流强度及接收支路数下,通过数值仿真,分析了采用不同合并算法时分集接收系统的BER和OP,并与传统的单天线接收系统进行了比较。
2 系统与信道模型
2.1 接收系统模型
基于空间分集的FSO相干接收系统示意图如
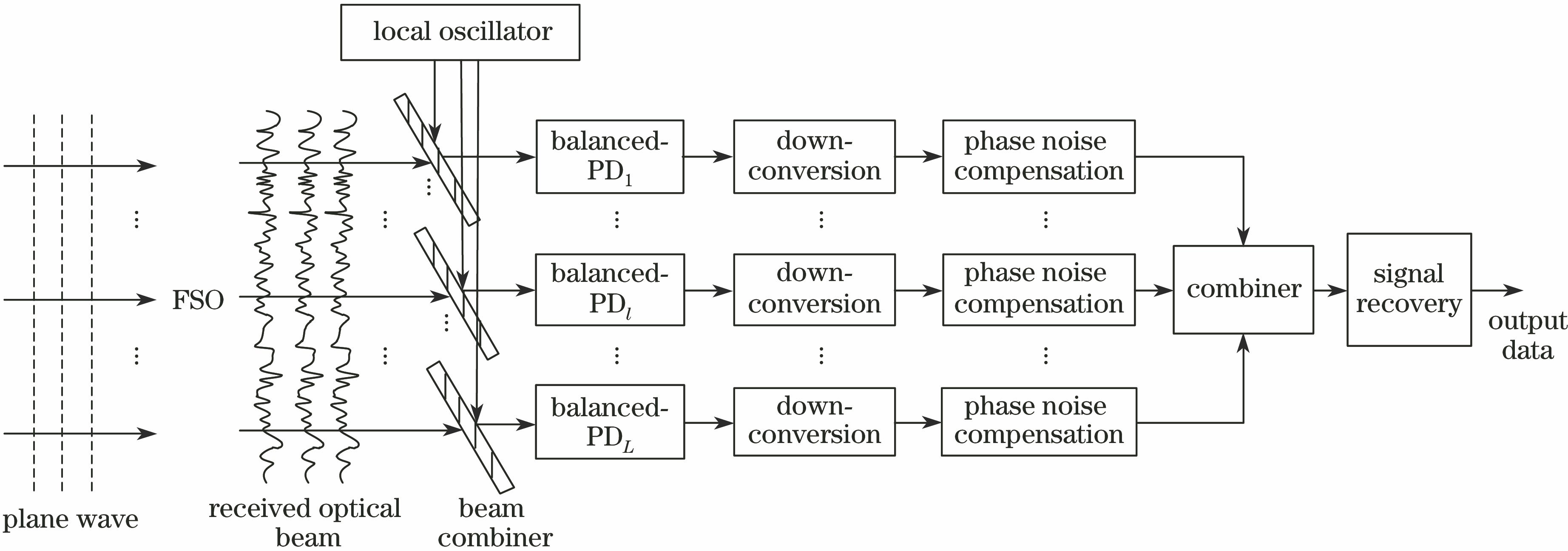
图 1. 基于空间分集的FSO相干接收系统示意图
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of coherent receiver system based on spatial diversity for FSO
当相干接收机工作在量子噪声极限下时,即接收系统仅受散粒噪声的影响,
式中:
2.2 信道模型
Gamma-Gamma模型假设在大气湍流信道下,小尺度涡流产生衍射效应,大尺度涡流产生折射效应,小尺度涡流被大尺度涡流调制[16],接收端光信号均值归一化光辐照度
式中:K
3 基于分集接收的FSO系统性能分析
基于二进制相移键控(BPSK)调制、差分接收的FSO分集接收系统的BER可表示为[10]
式中:
式中:erfc(·)为误差函数;
当SNR低于一定阈值
3.1 最大比合并
MRC算法,通过加权合并,使得合并输出SNR为各支路SNR之和[14],则采用MRC合并算法时,输出信噪比为
根据(2)式和(3)式,通过变量替换、化简可得到
将(9)式代入(5)式,可得到系统BER为
引入Meijer G函数,erfc(
将(9)式代入(6)式,可得到系统中断概率为
3.2 选择合并
选择合并算法,即选择
为进一步数值仿真,对积分区间进行了归一化处理。将(14)式代入(5)式和(7)式,分别可得到基于SC的系统BER与OP:
式中:
3.3 等增益合并
EGC算法,是将各支路信号等增益合并[7],设加权系数为1,则合并输出信噪比可表示为
推导出
由于各支路接收信号相互独立,根据特征函数计算性质,可得
由特征函数逆公式,可将(19)式化简为
文献[
18]给出
将(21)式代入(20)式,通过变量替换
式中:1F1(
依照上述推导思路,推导基于EGC的系统OP。由上文推导可知
由特征函数逆公式,系统OP可表示为
交换积分顺序,并进行变量替换
4 仿真结果与分析
根据第3节对不同合并算法的FSO系统误码率、通信中断概率的推导,本节对不同强度大气湍流、不同接收支路数量

图 2. 不同大气湍流强度下,FSO-SISO系统误码率和通信中断概率随平均信噪比的变化。(a)系统误码率;(b)通信中断概率
Fig. 2. BER and OP change with average SNR of FSO-SISO system under different turbulence regions. (a) BER; (b) OP
仿真条件:假设接收各支路接收到的光信号相互独立,系统基于BPSK调制,接收机采用外差相干接收机制。单输入单输出(SISO)系统对应的BER、OP表达式参考文献[
13]。为了将
不同强度大气湍流信道Gamma-Gamma分布下,FSO-SISO系统BER、OP随平均SNR的变化如

图 3. 弱湍流下,基于不同接收天线数,不同合并算法的性能比较。(a)误码率;(b)通信中断概率
Fig. 3. Performance comparison with different numbers of receiving antennas under weak turbulence. (a) BER; (b) OP
弱大气湍流下,只有平均SNR低于某一临界值时,SC分集接收系统的BER才低于SISO系统的值,当平均SNR继续增加,SC分集接收系统的BER将明显高于SISO系统的值,如
中度大气湍流下,MRC、EGC分集接收对应的BER、OP均小于SISO系统,如

图 4. 中度湍流下,基于不同接收天线数,不同合并算法的性能比较。(a)误码率;(b)通信中断概率
Fig. 4. Performance comparison with different numbers of receiving antennas under moderate turbulence. (a) BER; (b) OP
分析接收天线数对分集接收系统性能的影响:强大气湍流下,基于SC的分集接收系统在低SNR时,接收天线数越多,SC接收对应的BER和OP越小,但随着平均SNR的增加,接收天线数越多,对应的BER和OP反而越大,如

图 5. 强湍流下,基于不同接收天线数,不同合并算法的性能比较。(a)误码率;(b)通信中断概率
Fig. 5. Performance comparison with different numbers of receiving antennas under strong turbulence. (a) BER; (b) OP
5 结论
研究了不同强度Gamma-Gamma大气湍流信道下FSO中的分集接收技术,基于BPSK调制和外差相干接收,推导了3种空间分集合接收技术对应的系统BER和OP,并对其进行了仿真分析。结果表明:总接收天线口径相同时,EGC、MRC分集接收可有效提高不同强度湍流下的相干通信系统性能,且接收天线数越大,其对系统性能的改善越明显,相同接收天线数下,MRC分集接收的性能优于EGC;SC分集接收仅在平均信噪比低于某一阈值时,相比于SISO系统性能有所改善,但性能仍次于MRC接收和EGC接收。从系统结构复杂度考虑,SC最简单,EGC次之,MRC最为复杂,且随着接收支路的增加,系统复杂度成倍增加。在实际工程应用中,可以根据需求,折中选择合适的合并方法及接收支路数。
[1] 幺周石. 相干激光空间数据传输系统及其多阶波前校正研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2010: 1- 12.
幺周石. 相干激光空间数据传输系统及其多阶波前校正研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2010: 1- 12.
Yao ZS. Space coherent laser data transmission system and multi-order correction[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2010: 1- 12.
Yao ZS. Space coherent laser data transmission system and multi-order correction[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2010: 1- 12.
[6] Al-Habash A, Andrews L C, Phillips R L. Mathematical model for the irradiance probability density function of a laser beam propagating through turbulent media[J]. Optical Engineering, 2001, 40(8): 1554-1563.
Al-Habash A, Andrews L C, Phillips R L. Mathematical model for the irradiance probability density function of a laser beam propagating through turbulent media[J]. Optical Engineering, 2001, 40(8): 1554-1563.
[7] Andrews L C, Phillips R L, Hopen C Y, et al. Theory of optical scintillation[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1999, 16(6): 1417-1429.
Andrews L C, Phillips R L, Hopen C Y, et al. Theory of optical scintillation[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1999, 16(6): 1417-1429.
[8] 张慧颖, 李洪祚, 肖冬亚, 等. 大气湍流综合效应下空间分集接收性能研究[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(4): 0405002.
张慧颖, 李洪祚, 肖冬亚, 等. 大气湍流综合效应下空间分集接收性能研究[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(4): 0405002.
[9] 李晓燕, 张鹏, 佟首峰. Gamma-Gamma大气湍流下零判决门限差分探测自由空间光通信系统误码率性能[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(11): 1106001.
李晓燕, 张鹏, 佟首峰. Gamma-Gamma大气湍流下零判决门限差分探测自由空间光通信系统误码率性能[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(11): 1106001.
[11] Niu M, Cheng J, Holzman J F. Exact error rate analysis of equal gain and selection diversity for coherent free-space optical systems on strong turbulence channels[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(13): 13915-13926.
Niu M, Cheng J, Holzman J F. Exact error rate analysis of equal gain and selection diversity for coherent free-space optical systems on strong turbulence channels[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(13): 13915-13926.
[12] 柯熙政, 宋鹏, 裴国强. 无线激光通信中的多孔径接收技术研究[J]. 光学学报, 2011, 31(12): 1201003.
柯熙政, 宋鹏, 裴国强. 无线激光通信中的多孔径接收技术研究[J]. 光学学报, 2011, 31(12): 1201003.
[13] 赵嘉琦, 许银帆, 李洁慧, 等. 强背景光下可见光大气湍流信道建模及分集接收技术[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(3): 0301001.
赵嘉琦, 许银帆, 李洁慧, 等. 强背景光下可见光大气湍流信道建模及分集接收技术[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(3): 0301001.
[14] Ma J, Li K, Tan L, et al. Performance analysis of satellite-to-ground downlink coherent optical communications with spatial diversity over Gamma-Gamma atmospheric turbulence[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(25): 7575-7585.
Ma J, Li K, Tan L, et al. Performance analysis of satellite-to-ground downlink coherent optical communications with spatial diversity over Gamma-Gamma atmospheric turbulence[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(25): 7575-7585.
[15] 柯熙政, 刘妹. 湍流信道无线光通信中的分集接收技术[J]. 光学学报, 2015, 35(1): 0106005.
柯熙政, 刘妹. 湍流信道无线光通信中的分集接收技术[J]. 光学学报, 2015, 35(1): 0106005.
[16] NiuM, ChengJ, Holzman JF, et al. Coherent free-space optical transmission with diversity combining for gamma-gamma atmospheric turbulence[C]∥Communications (QBSC), 2010 25th Biennial Symposium on. IEEE, 2010: 217- 220.
NiuM, ChengJ, Holzman JF, et al. Coherent free-space optical transmission with diversity combining for gamma-gamma atmospheric turbulence[C]∥Communications (QBSC), 2010 25th Biennial Symposium on. IEEE, 2010: 217- 220.
[17] Gradshteyn IS, Ryzhik IM. Table of integrals, series, and products[M]. New York: Academic Press, 2014.
Gradshteyn IS, Ryzhik IM. Table of integrals, series, and products[M]. New York: Academic Press, 2014.
[19] Thomas FE. Thescintillation index in moderate to strong turbulence for the gaussian beam wave along a slant path[D]. Orlando: University of Central Florida, 2005.
Thomas FE. Thescintillation index in moderate to strong turbulence for the gaussian beam wave along a slant path[D]. Orlando: University of Central Florida, 2005.
Article Outline
孙晶, 黄普明, 幺周石. Gamma-Gamma大气湍流下相干光通信分集接收技术研究[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(7): 0706002. Jing Sun, Puming Huang, Zhoushi Yao. Diversity Reception Technology in Coherent Optical Communication over Gamma-Gamma Atmospheric Turbulence Channel[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(7): 0706002.






