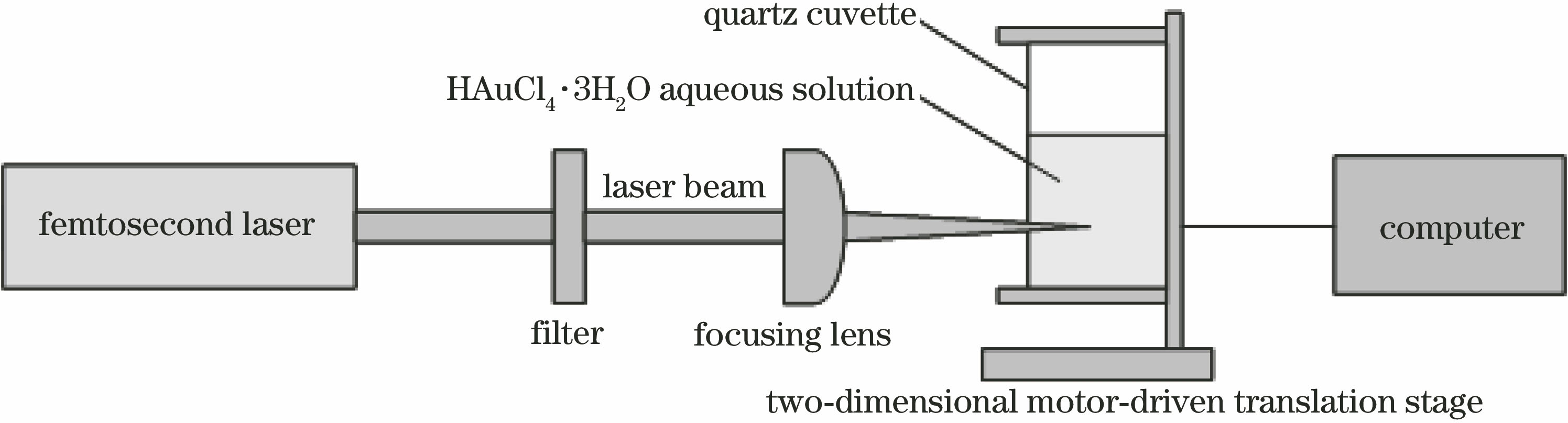
飞秒激光烧蚀氯金酸水溶液制备金纳米粒子  下载: 881次
下载: 881次
杜传梅, 吕良宏, 张明旭. 飞秒激光烧蚀氯金酸水溶液制备金纳米粒子[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(8): 0803003.
Du Chuanmei, Lü Lianghong, Zhang Mingxu. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles by Femtosecond Laser Ablation in Chloroauric Acid Trihydrate Aqueous Solution[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(8): 0803003.
[4] 金静, 朱守俊, 宋玉彬, 等. 银/碳点复合纳米粒子的构筑及其SERS研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(10): 291-292.
[5] Zoladek S, Rutkowska I A, Blicharska M. Evaluation of reduced-graphene-oxide-supported gold nanoparticles as catalytic system for electroreduction of oxygen in alkaline electrolyte[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 233: 113-122.
[9] 李明, 李凯伟, 代方, 等. 基于金纳米棒放大的高灵敏度纳米光纤生化传感器[J]. 光学学报, 2015, 35(12): 1206001.
[15] 张洁, 陈俞霖, 朱永. 碳纳米管和金属纳米粒子复合结构的拉曼光谱特性研究[J]. 中国激光, 2012, 39(11): 1115001.
[16] Hvolbæk B. Janssens T V W, Clausen B S, et al. Catalytic activity of Au nanoparticles[J]. Nanotoday, 2007, 2(4): 14-18.
[23] 周树清, 马国佳, 王春华, 等. 飞秒激光诱导钛合金表面形貌变化的规律[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(9): 0902003.
[24] 杜玲艳, 吴志明, 胡征, 等. 飞秒激光制备掺杂黑硅及其应用进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2015, 52(10): 100005.
杜传梅, 吕良宏, 张明旭. 飞秒激光烧蚀氯金酸水溶液制备金纳米粒子[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(8): 0803003. Du Chuanmei, Lü Lianghong, Zhang Mingxu. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles by Femtosecond Laser Ablation in Chloroauric Acid Trihydrate Aqueous Solution[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(8): 0803003.