Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Instrument Science and Engineering, School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 Department of Electrical Engineering, School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 Southwest Institute of Technical Physics, Chengdu 610041, China
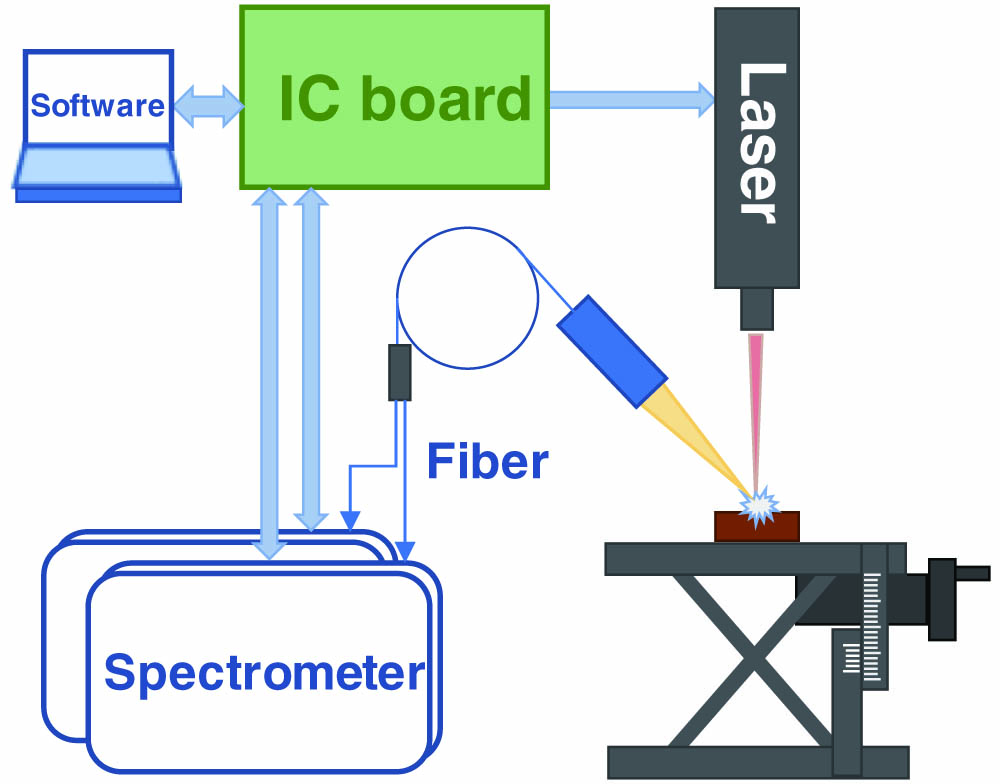
This paper investigates the combination of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to classify copper concentrate samples using pretrained CNN models through transfer learning. Four pretrained CNN models were compared. The LIBS profiles were augmented into 2D matrices. Three transfer learning methods were tried. All the models got a high classification accuracy of , with the highest at 96.2% for VGG16. These results suggested that the knowledge learned from machine vision by the CNN models can accelerate the training process and reduce the risk of overfitting. The results showed that deep CNN and transfer learning have great potential for the classification of copper concentrates by portable LIBS.
laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy convolutional neural networks classification flotation concentrate transfer learning Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(4): 043001
上海交通大学电子信息与电气工程学院仪器科学与工程系, 上海 200240
针对身份识别容易被仿冒和造假的问题,提出了一种利用近红外相机捕获手背静脉同时具有活体检测功能的身份识别方法,手背静脉图像提供静脉特征作为身份识别的依据,与此同时获取的脉搏波的周期性特征作为活体检测的标志。利用自行搭建的手背静脉和脉搏波捕获实验装置,研究了70个个体的手背静脉图像以及活体和假体的静脉图像特征,并提出了提高身份识别准确率的算法。采用主成分分析对活体静脉特征向量进行降维,降低分类算法的复杂度,结合马氏距离去除异常样本,以提高识别精度,再采用参数优化的随机森林算法和支持向量机算法实现了手背静脉的精准识别。结果表明:基于手背静脉特征结合随机森林算法和支持向量机算法可以对不同个体进行身份识别,识别准确率分别为99.28%和99.86%,识别时间分别为0.368 s和0.110 s。
图像处理 模式识别 近红外成像 手背静脉 活体检测 主成分分析 马氏距离





