1 重庆大学光电技术及系统教育部重点实验室, 重庆 400044
2 重庆大学光电工程学院, 重庆 400044
3 中国科学院重庆绿色智能技术研究院, 重庆 400714
4 重庆市石墨烯薄膜制备工程技术研究中心, 重庆 401329
表面等离激元共振技术具有无需标记、 灵敏度高、 实时检测等优点, 已广泛应用于生物医疗、 环境监测及食品安全等领域。 相对于传统贵金属材料表面等离激元共振传感器而言, 铝表面等离激元共振传感器具有价格低廉、 共振光谱带宽小等优点, 已逐渐成为了该领域的研究热点。 针对铝材料存在与生物分子兼容性差、 易氧化等缺点, 利用石墨烯化学稳定性好、 比表面积大、 抗氧化能力强、 生物兼容性好等独特优势, 将其作为与被测分子直接接触的传感层, 提出了一种石墨烯覆盖铝纳米光栅的表面等离激元共振传感器。 首先, 基于多物理场有限元仿真软件建立了该传感器的物理模型, 分别分析了石墨烯层数和铝光栅结构参数(占空比、 高度、 周期)对传感器共振光谱的影响。 结果表明, 石墨烯与铝光栅的复合有效增强了入射光波与传感器的相互作用, 采用单层石墨烯与铝光栅复合时, 共振峰具有最窄的光谱带宽。 当铝纳米光栅结构Λ=600 nm, H=40 nm, η=70%时, 光谱反射率为零。 进一步分析了结构优化后的传感器的传感特性。 结果表明, 单层石墨烯覆盖铝纳米光栅传感器具有最高的品质因数24.5 RIU-1, 其灵敏度高达626 nm·RIU-1。 该传感器具有探测精度高、 分子兼容性好等优点, 能为生化分析、 环境监测和食品安全等领域提供一个新的绿色传感平台。
表面等离激元 共振光谱 石墨烯 铝纳米光栅 Surface plasmon Resonance spectra Graphene Aluminum nano-grating
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems, Ministry of Education of China, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
2 College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
3 Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing 401122, China
4 Chongqing Engineering Research Center of Graphene Film Manufacturing, Chongqing 401329, China
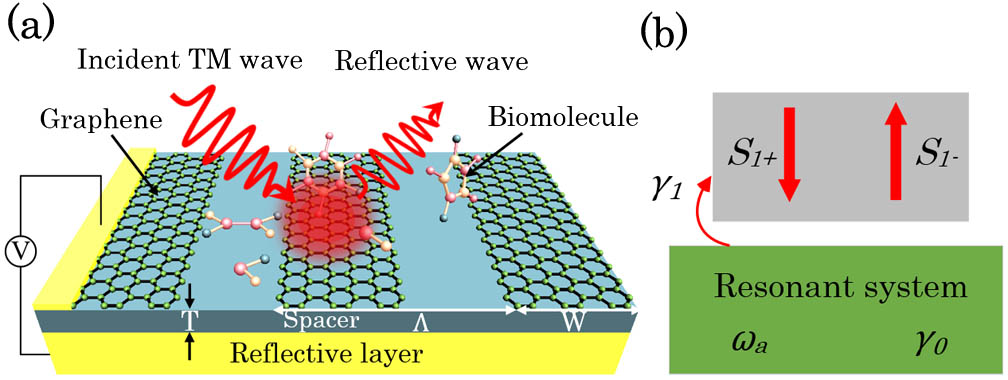
We propose a reflection-type infrared biosensor by exploiting localized surface plasmons in graphene ribbon arrays. By enhancing the coupling between the incident light and the resonant system, an asymmetric Fabry–Perot cavity formed by the ribbons and reflective layer is employed to reshape the reflection spectra. Simulation results demonstrate that the reflection spectra can be modified to improve the figure of merit (FOM) significantly by adjusting the electron relaxation time of graphene, the length of the Fabry–Perot cavity, and the Fermi energy level. The FOM of such a biosensor can achieve a high value of up to 36/refractive index unit (36/RIU), which is ~4 times larger than that of the traditional transmission-type one. Our study offers a feasible approach to develop biosensing devices based on graphene plasmonics with high precision.
280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 240.6680 Surface plasmons 160.4236 Nanomaterials 260.3060 Infrared Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(8): 082801





