Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Optoelectronic Information, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
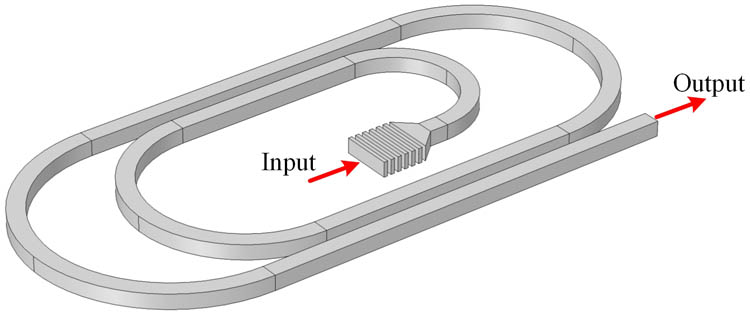
Optical biosensors with a high sensitivity and a low detection limit play a highly significant role in extensive scenarios related to our daily life. Combined with a specific numerical simulation based on the transfer matrix and resonance condition, the idea of novel single-waveguide-based microresonators with a double-spiral-racetrack (DSR) shape is proposed and their geometry optimizations and sensing characteristics are also investigated based on the Vernier effect. The devices show good sensing performances, such as a high quality factor of 1.23×105, a wide wavelength range of over 120 nm, a high extinction ratio (ER) over 62.1 dB, a high sensitivity of 698.5 nm/RIU, and a low detection limit of 1.8×10 5. Furthermore, single-waveguide-based resonators can also be built by cascading two DSR structures in series, called twin-DSRs, and the results show that the sensing properties are enhanced in terms of quasi free spectral range (FSR) and ER due to the double Vernier effect. Excellent features indicate that our novel single-waveguide-based resonators have the potential for future compact and highly integrated biosensors.
280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 230.5750 Resonators 230.3990 Micro-optical devices 230.3120 Integrated optics devices Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(1): 010006

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Photonics Research Center, Department of Electrical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, China
The uses of optical fibers are numerous, and over the past few decades, they have extended from optical fiber communications to a wide variety of sensing applications. In particular, fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensors inscribed in single-mode optical fibers offer significant advantages over more conventional electrical sensors and have been successfully deployed in many different industries. In this Review, we review the applications of intrinsic FBG pressure and flow sensors in oil and gas and the deployment of FBG sensing networks in railways. The promising prospect of using polymer FBGs in wearable medical devices is also described.
060.3735 Fiber Bragg gratings 280.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 280.4991 Passive remote sensing Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 120007

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 SZU-NUS Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Science & Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 College of Physics and Energy, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
An ultrasensitive biosensor based on hybrid structure and composed of long-range surface plasmon polariton (LRSPP) and dielectric planar waveguide (PWG) modes is proposed. Both PWG and LRSPP modes have strong resonances to form strong coupling between the two modes, and the two modes can couple to enhance sensitivityof sensors. In the hybrid structure, PWG is composed of cytop–Si–cytop multilayers and the LRSPP configuration is composed of cytop–metal–sensing medium multilayer slabs. The highest imaging sensitivities of 2264 and 3619 RIU?1 were realized in the proposed sensors based on Au and Al-monolayer graphene, respectively, which are nearly 1.2 and 1.9 times larger than the 1910 RIU?1 sensitivity of the conventional LRSPR sensor (LRSPP sensor). Moreover, it is demonstrated that the PWG-coupled LRSPP biosensor is applicable to the sensing medium, with refractive index in the vicinity of 1.34.of Guangdong Province (2016B050501005); Science and Technology Project of Shenzhen (JCYJ20140828163633996, JCYJ20150324141711667); Natural Science Foundation ofSZU (201452, 201517, 827-000051, 827-000052, 827-000059).
Remote sensing and sensors Remote sensing and sensors Sensors Sensors Remote sensing and sensors Remote sensing and sensors Biological sensing and sensors Biological sensing and sensors Optical sensing and sensors Optical sensing and sensors Surface plasmons Surface plasmons Photonics Research
2016, 4(6): 06000262
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems, Ministry of Education of China, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
2 College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
3 Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing 401122, China
4 Chongqing Engineering Research Center of Graphene Film Manufacturing, Chongqing 401329, China
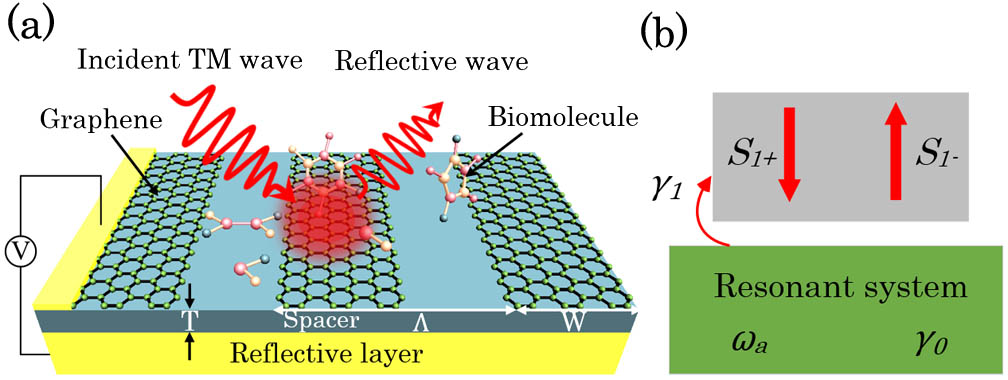
We propose a reflection-type infrared biosensor by exploiting localized surface plasmons in graphene ribbon arrays. By enhancing the coupling between the incident light and the resonant system, an asymmetric Fabry–Perot cavity formed by the ribbons and reflective layer is employed to reshape the reflection spectra. Simulation results demonstrate that the reflection spectra can be modified to improve the figure of merit (FOM) significantly by adjusting the electron relaxation time of graphene, the length of the Fabry–Perot cavity, and the Fermi energy level. The FOM of such a biosensor can achieve a high value of up to 36/refractive index unit (36/RIU), which is ~4 times larger than that of the traditional transmission-type one. Our study offers a feasible approach to develop biosensing devices based on graphene plasmonics with high precision.
280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 240.6680 Surface plasmons 160.4236 Nanomaterials 260.3060 Infrared Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(8): 082801

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Measuring Technology and Instruments, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 School of Electrical Engineering and Automation, Tianjin Polytechnic University, Tianjin 300387, China
3 Tianjin Nankai Hospital, Tianjin 300100, China
A CO2 sensor for capnography, based on a hollow waveguide (HWG) and tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS), is presented; the sensor uses direct absorption spectroscopy and requires neither frequent calibration nor optical filters, giving it a significant advantage over existing techniques. Because of the HWG, the CO2 measurement achieved a concentration resolution of 60 ppm at a measurement rate of 25 Hz, as characterized by Allan variance. The length of the HWG was selected to efficiently suppress the optical fringes. This setup is perfectly suited for the detection of CO2 by capnography, and shows promise for the potential detection of other breath gases.
120.3890 Medical optics instrumentation 300.6260 Spectroscopy, diode lasers 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(11): 111201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Specialty Fiber Optics and Optical Access Networks, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China
2 Laboratory for Microstructures, Shanghai University, Shanghai 00444, China
The optical fiber nanoprobe is prepared using spark fused taper and acid corrosion methods. With 3-ami-nopropyltrimethoxysilane coupling, gold nanoparticles are solidified onto the surface of fiber optic and then the optical fiber sensor is prepared using the surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) measurement of the cell solution. The SERS of the esophageal cancer cell solution is measured by direct detection and fiber detection methods. Similar results are obtained by both detection methods. SERS measurement of tissues and organs is done using the optical fiber sensor.
170.5660 Raman spectroscopy 170.1530 Cell analysis 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s2): S23002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
An optical fiber sensor for ultrathin layer sensing based on short-range surface plasmon polariton (SRSPP) is proposed, and the sensing characteristics are theoretically analyzed. Simulation results indicate that even for a detecting layer much thinner than the vacuum wavelength, a resolution as high as 3.7\times 10-6 RIU can be obtained. Moreover, an average thickness-detection sensitivity of 6.2 dB/nm is obtained, which enables the sensor to detect the thickness variation of the ultrathin layer up to tens of nanometers. The sensitive region of thickness could be adjusted by tuning the structure parameters.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 250.5403 Plasmonics 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(1): 010602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
An in-line Fabry-Perot (FP) refractive index (RI) sensor based on an intrinsic FP cavity and fabricated by the etching and fusion splicing method is proposed. The experimental results demonstrate that the sensor possesses a high resolution of 1508 nm/RIU for the measurement of acetylene gas RI. The temperatureresponse measurement shows that the sensor is insensitive to room temperature variations. The FP RI sensor is suitable for applications in biosensing and environmental monitoring because of its high sensitivity and structural simplicity, thereby making it suitable for low-cost mass production.
280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(8): 082802
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
2 School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710049, China
3 Key Laboratory of Xinjiang Biological Resources and Gene Engineering, College of Life Sciences and Technology, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
4 College of Information Science and Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
Porous silicon (PS) suitable for optical detection of immunoreaction is fabricated. The structure of immunosensor is prepared by the following steps: oxidization, silanization, glutaraldehyde cross-linker, and covalent binding of antibody. When antigen is added into the immunosensor, the Raman intensity is estimated to be linearly reduced according to the concentration of the surface protective antigen protein A (spaA) of below 4.0 μg·ml?1. The ultimate detection limit is 1.412×10^2 pg.ml^{?1}. Controlled experiments are also presented with non-immune antigen of the spaA, and results show that the immunosensor has high specificity. Compared with the conventional enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA), this method is quick, inexpensive, and label-free.
多孔硅 免疫传感器 猪丹毒丝菌表面保护性抗原A 拉曼光谱 光学检测 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 070.0070 Fourier optics and signal processing 070.4790 Spectrum analysis 280.0280 Remote sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(2): 022801
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Key Laboratory for Photoelectric Technology and Application, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025
2 College of Science, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025
3 No. 1 Middle School of Cheng Wu, Heze 274200
A novel structure of fiber optic biosensor and its principle are introduced. The sample is detected in microchannels of several microns diameter in fiber optic biosensors. The relation between the optic fiber tapered angle and the fluorescence incident angle is calculated in signal receiving part. As the sensor is a zero-order system, calculating formula of the static sensitivity is derived. When ZnSe nano-crystalline cluster is used for marking the molecules, the static sensitivity for fiber optic biosensors is calculated. At the same time, the relation between the static sensitivity and the ratio of exciting wavelength to fluorescence wavelength is presented.
光纤生物传感器 静态灵敏度 半导体纳米晶体团簇 微通道 锥度角 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 350.3950 Micro-optics Chinese Optics Letters
2008, 6(12): 922





