
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Academy for Engineering and Technology, Shanghai Institute for Advanced Communication and Data Science, Key Laboratory for Information Science of Electromagnetic Waves (MoE), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
Visible light communication (VLC) shows great potential in Internet of Vehicle applications. A single-input multi-output VLC system for Vehicle to Everything is proposed and demonstrated. A commercial car headlight is used as transmitter. With a self-designed 2 × 2 positive-intrinsic-negative (PIN) array, four independent signals are received and equalized by deep-neural-network post-equalizers, respectively. Maximum-ratio combining brings high signal-to-noise ratio and data rate gain. The transmission data rate reaches 1.25 Gb/s at 1 m and exceeds 1 Gb/s at 4 m. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first-time demonstration of beyond 1 Gb/s employing a commercial car headlight.
visible light communication Internet of Vehicle Vehicle to Everything single-input multi-output deep neural networks maximum-ratio combining Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(11): 110602
复旦大学通信科学与工程系电磁波信息科学教育部重点实验室, 上海 200433
随着无线通信领域的发展,具有诸多优点的可见光通信(VLC)已经发展成为了一种具有广阔前景的通信手段。然而,可见光通信中的各种非线性效应会给其信号处理带来诸多的困难,并恶化系统的性能。机器学习在解决非线性问题方面具有很大的优势和潜力,结合机器学习算法的可见光通信技术必然具有巨大的研究价值。已有研究表明,传统的机器学习算法如K-means、DBSCAN以及支持向量机(SVM)等在预均衡、后均衡、抗系统抖动,以及相位纠正等方面均有很好的表现。而深度神经网络(DNN)则因为其强大的非线性拟合能力能够更进一步提升VLC系统的性能。对以上几种方法进行了分析和介绍,并对其在可见光通信信号处理领域的应用进行了分析与总结,希望可以为机器学习解决可见光通信方面的各种非线性问题提供参考。
光通信 机器学习 非线性效应 信号处理 神经网络 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(1): 010001
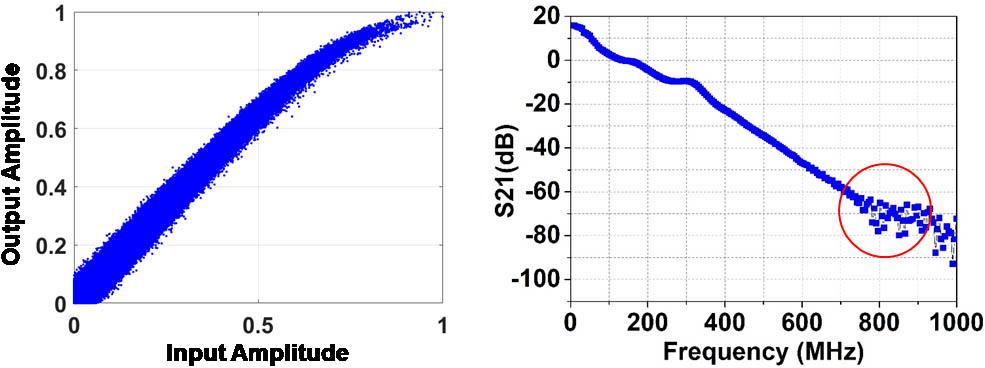
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Institute for Advanced Communication and Data Science, Key Laboratory for Information Science of Electromagnetic Waves (MoE), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
Underwater visible light communication (UVLC) is expected to act as an alternative candidate in next-generation underwater 5G wireless optical communications. To realize high-speed UVLC, the challenge is the absorption, scattering, and turbulence of a water medium and the nonlinear response from imperfect optoelectronic devices that can bring large attenuations and a nonlinearity penalty. Nonlinear adaptive filters are commonly used in optical communication to compensate for nonlinearity. In this paper, we compare a recursive least square (RLS)-based Volterra filter, a least mean square (LMS)-based digital polynomial filter, and an LMS-based Volterra filter in terms of performance and computational complexity in underwater visible light communication. We experimentally demonstrate 2.325 Gb/s transmission through 1.2 m of water with a commercial blue light-emitting diode. Our goal is to assist the readers in refining the motivation, structure, performance, and cost of powerful nonlinear adaptive filters in the context of future underwater visible light communication in order to tap into hitherto unexplored applications and services.
060.4510 Optical communications 070.4340 Nonlinear optical signal processing 120.2440 Filters Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 100011





