1 中北大学仪器与电子学院,山西 太原 030051
2 中北大学山西省光电信息与仪器工程技术研究中心,山西 太原 030051
3 中北大学前沿交叉科学研究院,山西 太原 030051
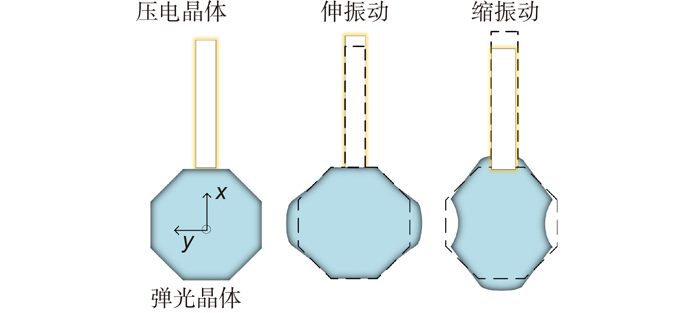
Overview: Overview: Photoelastic modulator, a high-quality thermo-mechanical coupling device composed of isotropic elastic optical crystal and piezoelectric crystal, is widely used in polarization measurement, spectral measurement, and many other fields. A high-voltage resonant circuit is adopted to generate the periodically changing high voltage amplitude, which is applied to both ends of the piezoelectric crystal to drive the photoelastic modulator to perform forced telescopic vibration, thus generating periodic birefringence. Although the quality factor of the photoelastic modulator is as high as 103, the photoelastic crystal in the photoelastic modulator will vibrate in length under the action of the piezoelectric crystal when driven by the high voltage. In addition, there will be thermal dissipation caused by dielectric loss and mechanical loss, some of which exchange heat with the environment, and the rest will raise the temperature of the photoelastic modulator itself. When the heat exchange between the photoelastic modulator and the external environment is happened before the heat balance, the resonant frequency will be changed, which will lead to the reduction of the modulator driving efficiency and the instability of the modulation amplitude. Standing from the perspective of mechanical point, the system can be equivalent to the vibration model of a damped spring-mass system. The system is an underdamped second-order system, and the modulator can also be equivalent to a RLC series resonant circuit from the electrical perspective. Therefore, when the temperature of the modulator changes, its electrical parameters and resonat will also vary. Therefore, this paper first analyzes the resonant frequency characteristics of the photoelastic modulator from the perspective of electricity, and establishes the equivalent circuit model of the photoelastic modulator and the composite resonant network model with the high-voltage resonant drive circuit. Meanwhile, the resonant network is analyzed, and the results show that when the phoyoelastic is in the resonant state, the modulator impedance and the inductance voltage amplitude of the high-voltage resonant circuit are both the smallest. Therefore, this paper designs a control and test system based on field programmable gate array (FPGA) by combining the above mentioned characteristic and applying the amplitude and frequency characteristics of the resonant network. FPGA completes the measurement of the inductance voltage amplitude and the demodulation of the photoelastic modulation signal through the digital phase-locked amplifier. After obtaining the inductance voltage amplitude, the real-time tracking of the minimum value of the inductance voltage amplitude can be obtained by FPGA, so that the tracking of the resonant frequency of the photoelastic modulator can be realized. By demodulating the modulated signal, the calibration optical path system of the photoelastic modulator is also capable of measuring the modulation amplitude of the modulator. Finally, this paper successfully builds the test system, and conducts the frequency sweep test to verify the feasibility of the resonance tracking system. The resonance tracking tests on the modulator are implemented at room temperature - 20℃ & 80℃ respectively. The results show that the test meets the requirements, and the maximum standard deviation of modulation amplitude is lower than 0.83% rad.
弹光调制器 频率跟踪 相位调制幅度 幅频特性 photoelastic modulator frequency tracking phase modulation amplitude amplitude-frequency characteristics
哈尔滨理工大学 电气与电子工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
为解决非本征光纤法布里-珀罗(Extrinsic Fiber Fabry-Perot Interferometor, EFPI)在电力变压器内体绝缘安装困难且易损坏的问题, 设计了高灵敏度的EFPI传感器, 提出采用油腔结构的变压器油箱壁外置式安装方法。在阐述EFPI传感和液气介质下膜片振动原理的基础上, 分析了传感器检测灵敏度与其法-珀腔膜片尺寸的关系, 设计EFPI传感器法-珀腔膜片尺寸并制备传感器。然后, 设计外置油腔耦合结构, 采用压电陶瓷(Piezoelectric, PZT)声发射传感器构建EFPI传感器性能测试系统, 测得EFPI传感器的幅频特性和检测灵敏度。最后, 使用板-板电极和变压器实体模型搭建局放检测系统, 外置EFPI传感器与PZT传感器同时探测电极局放信号。实验结果表明: EFPI传感器的一阶固有谐振频率为113 kHz, 静压灵敏度为7.5 nm/kPa, 外置油腔耦合结构EFPI传感器局放超声信号的检测灵敏度高于传统的PZT传感器。外置结构可有效保护传感器膜片, 降低安装难度, 且避免了EFPI传感器置于变压器绝缘高场强度区域带来的安全隐患。
光纤传感器 法布里-珀罗传感器 局放超声检测 外置耦合 幅频特性 optical fiber sensor Fabry-Perot sensor partial discharge ultrasonic detection external coupling amplitude-frequency characteristics
1 兴义民族师范学院 物理系, 贵州 兴义 562400
2 河南师范大学 物理与信息工程学院, 河南 新乡 453007
在深入研究掺铒光纤和光纤光栅的基础上, 提出了一种基于掺铒光纤光栅环的微波光子滤波器结构模型。根据信号流程图得到了该微波光子滤波器的传输函数, 讨论了光纤耦合器的耦合系数、掺铒光纤增益、光纤光栅反射率和光纤环长对系统传输性能的影响。通过理论计算和仿真分析可知, 在光纤耦合器的耦合系数为0.5、掺铒光纤增益为2、光纤光栅反射率为1时, 得到的微波光子滤波器的滤波效果最好。
微波光子滤波器 掺铒光纤 光纤光栅 幅频特性 microwave optical filter erbium-doped fiber fiber Bragg grating amplitude-frequency characteristics
哈尔滨理工大学 电气与电子工程学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150040
根据多光束干涉原理制备了非本征光纤法珀(FP)型传感器,用于测量在液体中传播的超声波,分析了传感器灵敏度和幅频特性的影响因素,研究了其输出信号的特征。用镀膜的石英膜、尾纤端面和空气腔形成FP干涉腔。建立了传感器参数确定的方法,对石英膜的幅频特性进行了理论分析和实验验证。最后,建立了非本征光纤FP超声测量系统,讨论和验证了不同工作点状态对系统输出信号特征的影响。实验结果表明,本文制备的非本征法珀型超声传感器可以进行液体中超声的测量;传感器的一阶谐振频率为140 kHz,灵敏度为0.005 nm/Pa。该传感器的输出信号特征决定于工作点状态及输入信号的调制深度,当工作点位于工作曲线的线性区中点时,输出信号的灵敏度最高;当过调制时,输出信号出现倍频,可以扩大测量范围。
非本征法珀型超声传感器 工作点 输出信号 幅频特性 extrinsic fiber Fabry-Perot(FP) acoustic sensors operational point output signal amplitude-frequency characteristics
电子科技大学光电信息学院,四川,成都,610054
研究了无电感补偿和有电感补偿的一级和两级电阻分压器的幅频特性-3 dB频率与阶跃响应10%~90%上升时间的关系.无电感补偿一级分压器的-3 dB频率与阶跃响应上升时间之积为常数0.350;对无电感补偿两级分压器,该乘积在0.349附近很小范围内变动;对电感补偿一级分压器,该乘积由过冲决定,当过冲在0~10%范围内变化时,该乘积在0.35~0.29之间线性变化;对电感补偿两级分压器,该乘积随过冲和分压器参数变化,在不大于10%的确定过冲下,变化范围约为±10%;当两级分压器第一级的时间常数远大于第二级的时间常数时,可能难以在第二级进行有效的电感补偿.
电阻分压器 幅频特性 -3 dB频率 上升时间 Resistive voltage dividers Amplitude-frequency characteristics -3 dB frequency Risetime





