1 燕山大学材料科学与工程学院亚稳材料制备技术与科学国家重点实验室, 秦皇岛 066004
2 唐山学院新材料与化学工程学院, 唐山 066000
本文采用湿法刻蚀法将单层石墨烯(G)与掺氟二氧化锡(FTO)薄膜复合在一起, 采用拉曼(Raman)光谱、聚焦离子束(FIB)和透射电子显微镜(TEM)研究了G/FTO双层薄膜的结构、表面和界面形貌、元素分布等信息; 采用基于原子力显微镜(AFM)的开尔文探针力显微镜(KPFM)和导电原子力显微镜(C-AFM)研究了FTO薄膜和G/FTO双层薄膜的形貌、接触电势差(CPD)、功函数、接触势垒。结果表明, FTO薄膜和G/FTO双层薄膜的接触电势差分别为-0.474、-0.441 V, 两者功函数分别为5.329、5.296 eV。与FTO薄膜相比, G/FTO双层薄膜的迁移率由21.26 cm2·V-1·s-1增加到23.82 cm2·V-1·s-1。FTO薄膜和G/FTO双层薄膜相应的势垒高度分别(0.39±0.06) V和(0.33±0.05) V, G/FTO双层薄膜的势垒高度更小。
石墨烯 掺氟二氧化锡 双层结构 接触特性 接触电势差 功函数 接触势垒 graphene fluorine doped tin dioxide bilayer structure contact characteristic contact potential difference work function contact barrier
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Radiology Technology, College of Health and Medical Technology, Middle Technical University (MTU), Baghdad, Iraq
2 Department of Physics, College of Education for Pure Science (Ibn-AL-Haitham), University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq
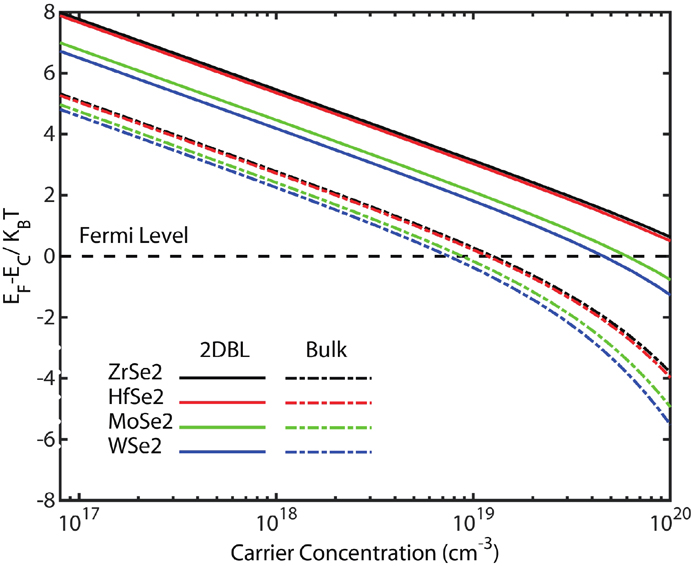
Significant advancements in nanoscale material efficiency optimization have made it feasible to substantially adjust the thermoelectric transport characteristics of materials. Motivated by the prediction and enhanced understanding of the behavior of two-dimensional (2D) bilayers (BL) of zirconium diselenide (ZrSe2), hafnium diselenide (HfSe2), molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2), and tungsten diselenide (WSe2), we investigated the thermoelectric transport properties using information generated from experimental measurements to provide inputs to work with the functions of these materials and to determine the critical factor in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials. Based on the Boltzmann transport equation (BTE) and Barden-Shockley deformation potential (DP) theory, we carried out a series of investigative calculations related to the thermoelectric properties and characterization of these materials. The calculated dimensionless figure of merit (ZT) values of 2DBL-MSe2 (M = Zr, Hf, Mo, W) at room temperature were 3.007, 3.611, 1.287, and 1.353, respectively, with convenient electronic densities. In addition, the power factor is not critical in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials but it can indicate a good thermoelectric performance. Thus, the overall thermal conductivity and power factor must be considered to determine the preference of thermoelectric materials.Significant advancements in nanoscale material efficiency optimization have made it feasible to substantially adjust the thermoelectric transport characteristics of materials. Motivated by the prediction and enhanced understanding of the behavior of two-dimensional (2D) bilayers (BL) of zirconium diselenide (ZrSe2), hafnium diselenide (HfSe2), molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2), and tungsten diselenide (WSe2), we investigated the thermoelectric transport properties using information generated from experimental measurements to provide inputs to work with the functions of these materials and to determine the critical factor in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials. Based on the Boltzmann transport equation (BTE) and Barden-Shockley deformation potential (DP) theory, we carried out a series of investigative calculations related to the thermoelectric properties and characterization of these materials. The calculated dimensionless figure of merit (ZT) values of 2DBL-MSe2 (M = Zr, Hf, Mo, W) at room temperature were 3.007, 3.611, 1.287, and 1.353, respectively, with convenient electronic densities. In addition, the power factor is not critical in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials but it can indicate a good thermoelectric performance. Thus, the overall thermal conductivity and power factor must be considered to determine the preference of thermoelectric materials.
ZT thermoelectric property 2D-bilayer Boltzmann-transport equation TE power factor Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(3): 032001

Tingyuan Jia 1,2,3Shaoming Xie 1,2Zeyu Zhang 1,2,3,4,*Qinxue Yin 1,3[ ... ]Yuxin Leng 1,2,3,5,***
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics and CAS Center for Excellence in Ultra-intense Laser Science, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China
4 School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
5 School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 201210, China
Bilayer graphene, which is highly promising for electronic and optoelectronic applications because of its strong coupling of the Dirac–Fermions, has been studied extensively for the emergent correlated phenomena with magic-angle manipulation. Due to the low energy linear type band gap dispersion relationship, graphene has drawn an amount of optoelectronic devices applications in the terahertz region. However, the strong interlayer interactions modulated electron-electron and electron-phonon coupling, and their dynamics in bilayer graphene have been rarely studied by terahertz spectroscopy. In this study, the interlayer interaction influence on the electron-electron and the electron-phonon coupling has been assigned with the interaction between the two graphene layers. In the ultrafast cooling process in bilayer graphene, the interlayer interaction could boost the electron-phonon coupling process and oppositely reduce the electron-electron coupling process, which led to the less efficient thermalization process. Furthermore, the electron-electron coupling process is shown to be related with the electron momentum scattering time, which increased vividly in bilayer graphene. Our work could provide new insights into the ultrafast dynamics in bilayer graphene, which is of crucial importance for designing multi-layer graphene-based optoelectronic devices.
terahertz ultrafast spectroscopy bilayer graphene Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(9): 093701
1 中国科学院上海技术物理研究所 红外物理国家重点实验室, 上海 200083
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 上海师范大学 数理学院 物理系,上海 200234
4 国科大杭州高等研究院 物理与光电工程学院,浙江 杭州 310024
5 江苏省光伏科学与工程协同创新中心,江苏 常州 213164
传统外延阻挡杂质带探测器由于其材料物性和特殊的结构设计存在很强的反射,这些能量损失非常不利于器件的探测性能。报道了一种类光栅双层超构表面微结构阵列,并将此人工微结构引入到外延阻挡杂质带红外探测器以抑制对入射光的反射。实验结果显示,具有超构表面微结构阵列的器件在波长30 μm处反射率低于3%,在25.3~32.2 μm波段范围内反射率低于20%。同时,该超表面减反微结构对入射光的偏振还具有很强的选择性,符合第四代焦平面发展需求。
阻挡杂质带 红外探测器 减反 双层超表面 blocked impurity band infrared detector antireflection bilayer metasurfaces 
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics, Key Laboratory of Micro- and Nano-Photonic Structures (Ministry of Education) and Department of Physics, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Infrared Physics, Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200083, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
In this Letter, Ti–Si bilayer was deposited on white silk to achieve coloration of the silk. By controlling the thickness of the Ti layer and Si layer, the saturation and the hue of the color on the silk could be preciously modulated, respectively. The structural colors on the silk could cover the major colors in the International Commission on Illumination 1931 chromaticity diagram, and it exhibits good durability, which is demonstrated by rubbing and stretching treatments. The developed textile coloration method may provide an eco-friendly technology in the silk dyeing industry.
structural color silk coloration Ti-Si bilayer Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(5): 051601
大连理工大学机械工程学院, 辽宁 大连 116023
为改善光栅性能,基于遗传算法,并结合时域有限差分法,在可见光波段优化设计了一种双层亚波长金属光栅结构。经仿真分析,该结构能够实现蓝色波段的偏振滤波功能,透射率最大值能达到77%,消光比最大值达到20 dB,半峰全宽为35 nm。通过分析光栅参数对光栅性能的影响,证明该结构具有较大的工艺容差。相比以往的结构,优化后的光栅具有更好的透射性能和滤波性能,在偏振导航、偏振探测、显示器、成像传感器等领域具有良好的应用前景。
光栅 双层亚波长金属光栅 遗传算法 偏振滤波 时域有限差分方法 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(22): 220501
1 北京信息科技大学 仪器科学与光点工程学院, 北京 100192
2 北京航空航天大学 仪器科学与光点工程学院, 北京 100191
石墨烯对光的吸收率较低, 通过与光学谐振腔结合限制光场, 可有效提高石墨烯探测器件对入射光的吸收.以电磁场传输理论为基础, 推导了双层石墨烯光学谐振腔中的光场分布, 建立了谐振增强型光电探测器传输矩阵数理模型, 对Bernal-Stacked双层石墨烯的谐振增强型光电探测器结构参数进行数值计算, 并对探测器性能进行分析.结果表明, 设计的探测波长为1.06 μm谐振增强结构光电探测器, 双层石墨烯的光吸收率达到96.78%, 大幅提升了对微弱光信号的探测能力.
探测器 双层石墨烯 谐振增强 电磁场传输理论 photodetector bilayer graphene resonance enhancement electromagnetic field transmission theory
1 东华大学 应用物理系, 上海 201620
2 挪威能源技术研究所, Instituttveien 18, 2007 Kjeller
3 上海大学 分析测试中心, 上海 200444
4 广西大学 资源环境与材料学院, 广西 南宁 530004
采用磁控溅射制备Ga掺杂ZnO (GZO)/CdS双层膜在p型晶硅衬底上以形成GZO/CdS/p-Si异质结器件。纳米晶GZO/CdS双层膜的微结构、光学及电学特性, 通过XRD、SEM、XPS、紫外-可见光分光光度计和霍尔效应测试系统表征。GZO/CdS/p-Si异质结J-V曲线显示良好的整流特性。在±3 V时, 整流比IF/IR(IF和IR分别表示正向和反向电流)已达到21。结果表明纳米晶GZO/CdS/p-Si异质结具有好的二极管特性, 在反向偏压下获得高光电流密度。纳米晶GZO/CdS/p-Si异质结显示明显的光伏特性。由于CdS晶格常数在GZO和晶Si之间, 它能作为一个介于GZO和晶Si之间的缓冲层, 能有效地减少GZO和p-Si之间的界面态。因此, 我们获得了GZO/CdS/p-Si异质结明显光伏特性。
纳米晶GZO/CdS双层膜 磁控溅射 异质结 电流-电压(I-V)特性 nanocrystalline GZO/CdS bilayer films magnetron sputtering heterojunction current-voltage (I-V) characteristics
西安邮电大学 通信与信息工程学院, 西安 710121
为了展宽微带天线的3 dB轴比波束宽度(ARBW),提出采用双层介质基板结构与单点同轴线馈电、引入切角微扰和半圆槽的方式,设计出一款小型化宽ARBW的圆极化微带天线。该天线的尺寸可用中心波长(λ0)表示为0.408λ0×0.408λ0×0.036λ0,工作频率可覆盖IEEE 802.16e(3.5 GHz)频段。利用基于有限元法的仿真软件(Ansoft HFSS15.0)对天线进行优化设计,获得天线3 dB ARBW为230°~255°,电压驻波比(VSWR)小于2的带宽为290 MHz,峰值增益在3.5 GHz为4.11 dB。测试结果与仿真结果基本一致,表明采用该结构和设计方式可以展宽天线的ARBW。
双层介质 轴比波束宽度 圆极化 微带天线 bilayer dielectric substrates axial ratio beamwidth circular polarization microstrip antenna 强激光与粒子束
2017, 29(11): 113003





