
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Information Science and Engineering (ISE), Shandong University, Qingdao 266200, China
2 Neumem Co., Ltd, Hefei 230093, China
3 Key Laboratory of Microelectronic Devices and Integrated Technology, Institute of Microelectronics of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100084, China
4 Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
With the rapid development of machine learning, the demand for high-efficient computing becomes more and more urgent. To break the bottleneck of the traditional Von Neumann architecture, computing-in-memory (CIM) has attracted increasing attention in recent years. In this work, to provide a feasible CIM solution for the large-scale neural networks (NN) requiring continuous weight updating in online training, a flash-based computing-in-memory with high endurance (109 cycles) and ultra-fast programming speed is investigated. On the one hand, the proposed programming scheme of channel hot electron injection (CHEI) and hot hole injection (HHI) demonstrate high linearity, symmetric potentiation, and a depression process, which help to improve the training speed and accuracy. On the other hand, the low-damage programming scheme and memory window (MW) optimizations can suppress cell degradation effectively with improved computing accuracy. Even after 109 cycles, the leakage current (Ioff) of cells remains sub-10pA, ensuring the large-scale computing ability of memory. Further characterizations are done on read disturb to demonstrate its robust reliabilities. By processing CIFAR-10 tasks, it is evident that ~90% accuracy can be achieved after 109 cycles in both ResNet50 and VGG16 NN. Our results suggest that flash-based CIM has great potential to overcome the limitations of traditional Von Neumann architectures and enable high-performance NN online training, which pave the way for further development of artificial intelligence (AI) accelerators.
NOR flash memory computing-in-memory endurance neural network online training Journal of Semiconductors
2024, 45(1): 012301
江南大学 电子工程系 物联网技术应用教育部工程研究中心, 江苏 无锡 214122
Flash存算阵列在工作模式下需要用到不同内部驱动电压, 因此基于当前各类Dickson型电荷泵, 设计了一种针对Flash存算阵列的可调电荷泵。采用一种新型输出级的交叉耦合设计, 解决了传统电荷泵最后一级阈值电压导致的低泵送效率的问题, 并通过辅助MOS管增强了传统电荷泵中体源二极管对反向漏电流的抑制能力。55 nm CMOS工艺下的仿真结果表明, 与改进前的电荷泵相比, 在电源电压1.8 V和300 μA的工作电流下, 中间级反向漏电流减少了17.5%, 输出级反向漏电流减少了73.1%。无反馈调节时, 主电荷泵最高输出电压为9.56 V, 电压效率达88.51%。PFM可调制模式下, 可重构电荷泵能实现输出电压切换。
Flash存算器件 电荷泵 体源二极管 交叉耦合 flash memory device charge pump body-source diode cross-coupled
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Information Science and Engineering (ISE), Shandong University, Qingdao 266000, China
2 Shandong Sinochip Semiconductors Co. Ltd, Jinan 250101, China
3 Neumem Co., Ltd, Hefei 230088, China
4 Key Laboratory of Microelectronic Devices and Integrated Technology, Institute of Microelectronics of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029, China
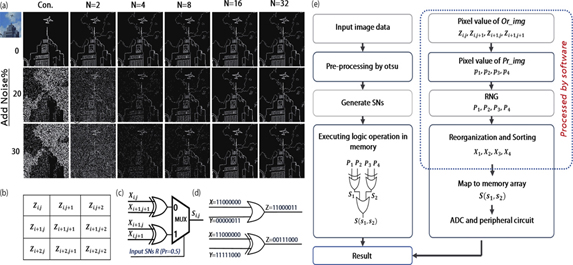
The “memory wall” of traditional von Neumann computing systems severely restricts the efficiency of data-intensive task execution, while in-memory computing (IMC) architecture is a promising approach to breaking the bottleneck. Although variations and instability in ultra-scaled memory cells seriously degrade the calculation accuracy in IMC architectures, stochastic computing (SC) can compensate for these shortcomings due to its low sensitivity to cell disturbances. Furthermore, massive parallel computing can be processed to improve the speed and efficiency of the system. In this paper, by designing logic functions in NOR flash arrays, SC in IMC for the image edge detection is realized, demonstrating ultra-low computational complexity and power consumption (25.5 fJ/pixel at 2-bit sequence length). More impressively, the noise immunity is 6 times higher than that of the traditional binary method, showing good tolerances to cell variation and reliability degradation when implementing massive parallel computation in the array.
in-memory computing stochastic computing NOR flash memory image edge detection Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(5): 054101

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Information Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 201210, China
2 Shanghai Huahong Grace Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation, Shanghai 200125, China
The temperature characteristics of the read current of the NOR embedded flash memory with a 1.5T-per-cell structure are theoretically analyzed and experimentally verified. We verify that for a cell programmed with a “10” state, the read current is either increasing, decreasing, or invariable with the temperature, essentially depending on the reading overdrive voltage of the selected bitcell, or its programming strength. By precisely controlling the programming strength and thus manipulating its temperature coefficient, we propose a new setting method for the reference cells that programs each of reference cells to a charge state with a temperature coefficient closely tracking tail data cells, thereby solving the current coefficient mismatch and improving the read window.The temperature characteristics of the read current of the NOR embedded flash memory with a 1.5T-per-cell structure are theoretically analyzed and experimentally verified. We verify that for a cell programmed with a “10” state, the read current is either increasing, decreasing, or invariable with the temperature, essentially depending on the reading overdrive voltage of the selected bitcell, or its programming strength. By precisely controlling the programming strength and thus manipulating its temperature coefficient, we propose a new setting method for the reference cells that programs each of reference cells to a charge state with a temperature coefficient closely tracking tail data cells, thereby solving the current coefficient mismatch and improving the read window.
flash memory temperature coefficient reference cell flash array Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(4): 044102
1 湘潭大学材料科学与工程学院, 湖南湘潭 411105
2 上海精密计量测试研究所, 上海 201109
3 西北核技术研究院, 陕西西安 710024
4 中国原子能科学研究院, 北京 102488
基于中国原子能科学研究院的 HI-13加速器, 利用不同线性能量传输(LET)值的重离子束流对 4款来自不同厂家的 90 nm特征尺寸 NOR型 Flash存储器进行了重离子单粒子效应试验研究, 对这些器件的单粒子翻转(SEU)效应进行了评估。试验中分别对这些器件进行了静态和动态测试, 得到了它们在不同 LET值下的 SEU截面。结果表明高容量器件的 SEU截面略大于低容量的器件; 是否加偏置对器件的翻转截面几乎无影响; 两款国产替代器件的 SEU截面比国外商用器件高。国产替代器件 SEU效应的 LET阈值在 12.9 MeV·cm2/mg附近, 而国外商用器件 SEU效应的 LET阈值处于 12.9~32.5 MeV·cm2/mg之间。此外, 针对单粒子和总剂量效应对试验器件的协同作用也开展了试验研究, 试验结果表明总剂量累积会增加 Flash存储器的 SEU效应敏感性, 分析认为总剂量效应产生的电离作用导致了浮栅上结构中的电子丢失和晶体管阈值电压的漂移, 在总剂量效应作用的基础上 SEU更容易发生。
NOR型 Flash存储器 重离子 单粒子效应 总剂量效应 协同效应 NOR Flash memory heavy ions Single Event Effect(SEE) Total Ionizing Dose(TID) effect synergistic effects 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报
2022, 20(9): 877
针对核设施机电设备中控制系统存储单元耐辐射可靠性评价的需要, 以国产NOR型Flash存储器为研究对象, 对器件存储阵列浮栅单元的总剂量损伤阈值开展了实验研究。综合利用SMOTE算法和Bootstrap法建立了一种基于极小子样的器件耐辐照可靠性评价方法, 对被测样品校验失效剂量进行了统计分析。实验结果表明, 器件浮栅单元的主要失效模式为浮栅电荷损失造成的阈值电压降低, 平均校验错误剂量为(631.89±103.64)Gy(Si)。统计分析表明, 器件总剂量损伤阈值服从对数正态分布。基于SMOTE-Bootstrap的可靠性评价方法避免了传统Bootstrap再生样本过于集中的问题, 可应用于极小子样的可靠性评价。
总剂量效应 Flash存储器 可靠性分析 极小子样 total ionizing dose effect flash memory reliability analysis extremely small sample size
1 电子科技大学 中山学院,广东 中山528402
2 电子科技大学 自动化工程学院,四川 成都610054
3 电子科技大学 计算机科学与工程学院,四川 成都611731
Flash存储器常作为嵌入式大屏幕显示系统的显示信息存储设备,然而Flash存储器在使用时会存在诸如位反转等读写操作出错的问题,给系统的正常显示控制带来隐患。对Flash存储器存储误码率进行了分析,并结合显示数据存取的特点,设计了差错控制编码来实现Flash存储器下的显示数据差错控制。结合嵌入式控制系统的特点,设计了一种基于(31,26)循环汉明码编译码电路,在实际应用中可以将误码率降低至少1个数量级以上,提升了数据存储器抗突发干扰和随机干扰的能力,同时具有较低的设计复杂度。
嵌入式系统 误码率 Flash存储器 embedded system bit error rate flash memory
中国科学院空间应用工程与技术中心,北京 100094
分析了工业级Flash存储器件应用于空间电子产品时应考虑的温变规律和机理,并在-35~105 ℃的温度条件下对韩国三星公司生产的大容量Flash存储器件K9××G08U×D系列进行了温循试验和高温步进应力试验,以评估其空间应用的可行性。试验结果显示:这一系列存储器在温度变化的情况下,电性能参数会发生规律性变化,其中页编程时间随温度的升高线性增大,105 ℃比-35 ℃时页编程时间增加15%;块擦除时间在低温条件下明显增大。在-35 ℃低温条件下,块擦除时间比常温条件高出72%,在105 ℃高温条件下,块擦除时间比常温条件高出10%。试验表明Flash K9××G08U×D系列存储器能够在-35~105 ℃的环境下工作,器件可正常擦写读,坏块没有增加。页编程时间随着温度的增加而增加,但是,仍然在器件的最大页编程时间之内。但是,在低温环境下,擦除时间会明显增加,在空间应用时需为擦除操作预留足够的时间。
空间电子 Flash存储器 温变规律 实验Flash信号 space electronics Flash memory temperature variation law experimental Flash signal
1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院研究生院, 北京 100039
3 许昌许继昌南通信设备有限公司, 河南 许昌 461000
介绍了一种基于ARM9的彩色薄膜晶体管液晶显示模块(TFT-LCD)的设计和实现方法。为了解决图像及字符在液晶模块上的实时显示, 图像库及字符库存储在容量达64Mbyte的NAND Flash闪存中, 可以根据不同需求对图像库及字符库进行更新。模块支持24bit彩色RGB格式图像的显示, 还支持JPEG格式图像的显示, JPEG图像的解码功能在ARM9处理器上实现。模块采用串口方式与其他外接主控系统通信, 通过接收主控系统的不同指令, 可以实现对库中图像及字符显示的实时更改。在液晶屏LQ080V3DG01上已通过测试, 运行可靠。该模块已实际应用于图像显示设备中。
薄膜晶体管液晶显示器 闪存 JPEG解码 ARM ARM TFT-LCD flash memory JPEG decoder
School of Information and Communication Engineering, Tianjin Polytechnic University, Tianjin 300160, CHN





