
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices and Institute of Optical Communication Materials, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
2 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
3 Guangdong Engineering Technology Research and Development Center of Special Optical Fiber Materials and Devices, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
4 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fiber Laser Materials and Applied Techniques, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
Transverse mode instability (TMI) has become the major limitation for power scaling of fiber lasers with nearly diffraction-limited beam quality. Compared with a co-pumped fiber laser, a counter-pumped fiber laser reveals TMI threshold enhancement through a semi-analytical model calculation. We demonstrated a 2 kW high-power counter-pumped all-fiberized laser without observation of TMI. Compared with the co-pumped scheme, the TMI threshold is enhanced at least 50% in counter-pumped scheme, moreover, stimulated Raman scattering and four-wave mixing are suppressed simultaneously.
Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators Thermal effects Instabilities and chaos Photonics Research
2017, 5(2): 02000077

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physical Science and Technology, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
2 e-mail: zmwu@swu.edu.cn
The time-delay signature (TDS) of chaos output in a 1550 nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) subject to fiber Bragg grating (FBG) feedback is investigated experimentally. Autocorrelation function (ACF) and mutual information (MI) are used for quantitatively identifying the TDS of chaos. For various bias currents, the TDS evolution with the feedback strength is different, as the FBG provides wavelength-selective feedback. Furthermore, based on the TDS map of the FBG feedback VCSEL (FBGF-VCSEL) in the parameter space of feedback strength and bias current, the optimal TDS suppression regions, where the dominant polarization mode of FBGF-VCSEL locates at the edge of the main lobe of FBG reflection spectrum, have been determined. Finally, for comparative purpose, the TDS of chaos in mirror feedback VCSEL (MF-VCSEL) also has been presented, and the results show that an FBGF-VCSEL possesses better TDS suppression performance than an MF-VCSEL.(XDJK2016D060).
Semiconductor lasers Semiconductor lasers Fiber Bragg gratings Fiber Bragg gratings Instabilities and chaos Instabilities and chaos Photonics Research
2017, 5(1): 01000006
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physical Science and Technology, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
2 e-mail: gqxia@swu.edu.cn
Polarization switching (PS) characteristics in a 1550 nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) subject to circularly polarized optical injection (CPOI) are experimentally investigated. The results show that, under different biased current, a solitary 1550 nm VCSEL can oscillate at y polarization mode (y mode), two polarization components (PCs) coexistence or x polarization mode (x mode). The PS characteristics induced by CPOI for the VCSEL operating at y mode and x mode are analyzed and the evolutions of dynamical states with the injected power are discussed. Additionally, the mappings of nonlinear dynamical states are given in the parameters space of the injected power and frequency detuning.
140.7260 Vertical cavity surface emitting lasers 190.3100 Instabilities and chaos 190.4360 Nonlinear optics, devices Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(2): 021401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Ministry of Education, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 611731, China
An external-cavity semiconductor laser with nonlinear optical feedback to generate broadband chaos with time delay signature (TDS) suppression is investigated. The system is composed of three semiconductor lasers, one of which is regarded as the chaos generator, while the other two play a role of a built-in nonlinear modulator in the external cavity of the generator. The results show that by properly setting the feedback strength and time delay of the first semiconductor laser in the nonlinear modulator, the TDS embedded in the intensity and phase time-series of the chaos can be effectively concealed in a wide range of frequency detuning.
140.1540 Chaos 140.5960 Semiconductor lasers 190.3100 Instabilities and chaos Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(9): 091404
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 MOE Key Laboratory of Weak Light Nonlinear Photonics and School of Physics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China
2 e-mail: tuchenghou@nankai.edu.cn
3 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures and School of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
5 e-mail: htwang@nju.edu.cn
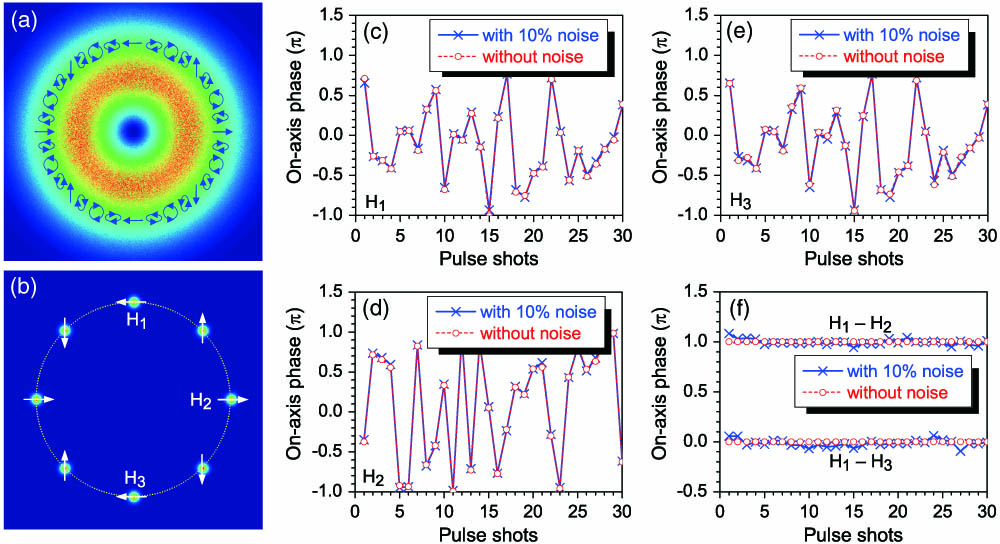
Femtosecond laser filamentation is generally initialized from unpredictable symmetry breaking caused by random noise, causing it to be barely controlled. However, it is always anticipated for stable and controllable filamentation. We present and demonstrate the idea that hybridly polarized vector fields with axial symmetry broken polarization, associated with a pair of orthogonally linearly polarized vortices carrying the opposite-handed orbital angular momenta, could achieve controllable and robust multiple filamentation. Here, our motivation is to unveil the underlying physics behind such controllable and robust multiple filamentation. The symmetry breaking should first be actively controllable and then be able to effectively inhibit random noise. Robust multiple filamentation is inseparable from the fact that the phases between the multiple filaments are always locked. In contrast, uncontrollable multiple filamentation is always accompanied with loss of phase, i.e., the multiple filaments become incoherent to each other. Our results may offer a suggestion for achieving controllable and robust multiple filamentation in other systems.and Equipment Development Project (2012YQ17004); Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics.
Polarization Polarization Self-focusing Self-focusing Kerr effect Kerr effect Ultrafast nonlinear optics Ultrafast nonlinear optics Instabilities and chaos Instabilities and chaos Femtosecond phenomena Femtosecond phenomena Photonics Research
2016, 4(5): 05000B29
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Center for Information Photonics & Communications, School of Information Science and Technology, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, China
A ring of three unidirectionally coupled semiconductor lasers (RTUC-SLs) is used to generate broadband chaos with no pronounced time-delay (TD) signature. Using the autocorrelation function and permutation entropy as the TD measures, we demonstrate that under suitable coupling strength, the loss of the TD signature of the lasers in the RTUC-SL configuration is achieved both for the intensity and the phase. These findings should prove valuable for developing high-quality optical chaos for potential applications, such as chaos-based communications and random number generation.
140.5960 Semiconductor lasers 190.3100 Instabilities and chaos Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(4): 041403
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Nanjing Xiaozhuang University, Nanjing 211171, China
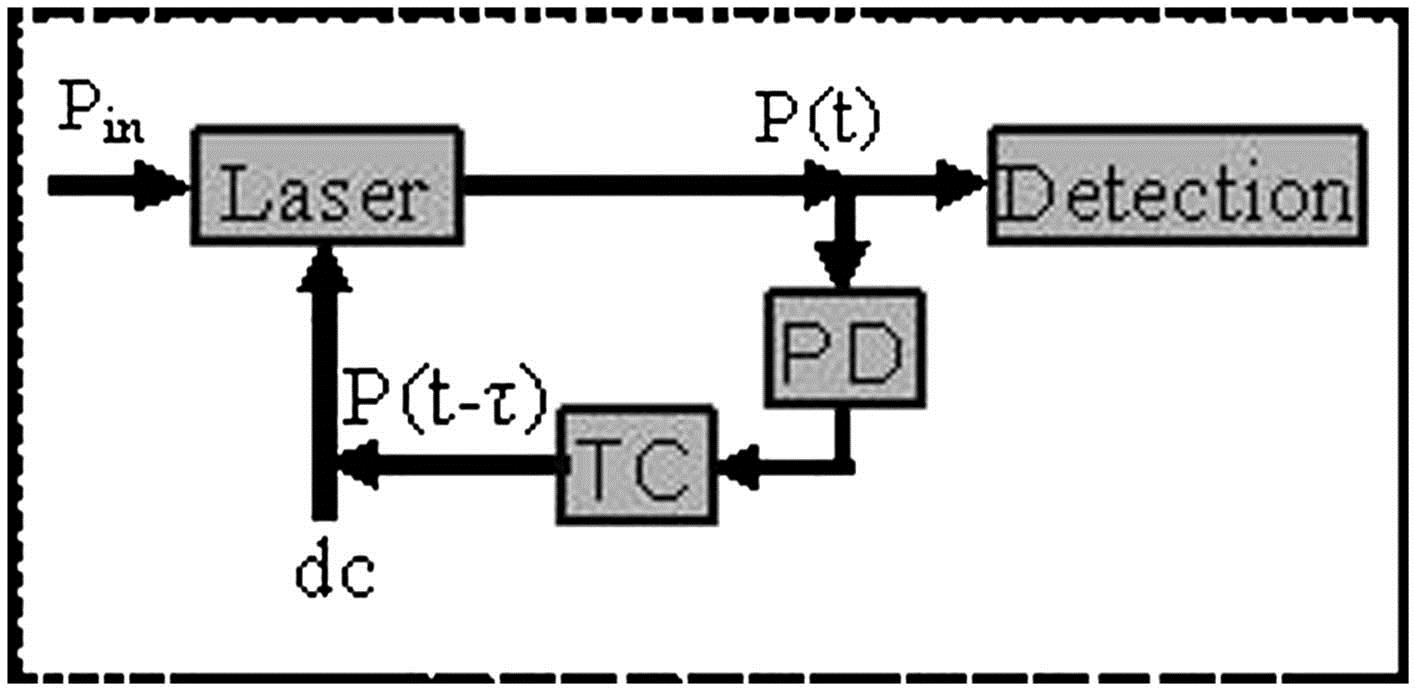
Nonlinear dynamics in an optoelectronic delayed feedback semiconductor laser and its application in sensing are studied. We analyze the theories of stability and period of the laser. A route to quasi-periodic bifurcation or a stochastic state from stability is numerically analyzed by shifting the feedback level. The induced dynamics are found to be in one of four distributions (stable, periodic pulsed, period-three pulsed, and undamping oscillating). An external injection into the laser results in the process being more or less the opposite with the conventional optical injection cases. Based on this process or the dynamic regimes, we present a modeling of the incoherent detection sensor using the nonlinear period-one characteristic of the laser. The sensor discriminates the injection light variation as a sensing signal via detecting the behaviors from the period-one laser.
040.5160 Photodetectors 140.5960 Semiconductor lasers 190.3100 Instabilities and chaos Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(4): 040401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
We report the experimental study on mode instabilities (MI) in large mode area step-index fibers by testing a 30/400 mm step-index fiber in a single-pass co-pumped all-fiberized amplifier, delivering up to ~550 W of extracted output power without MI. The pump power is increased well above the MI threshold to study the temporal dynamics of MI in detail, which are characterized by using both high-speed camera measurement with ~2200 frames per second and photodiode traces. The experimental results are compared with the theoretical results. The MI frequency component is seen to appear on top of system noise, such as electric noise, which shows that system noise may influence the onset of MI. The beam quality of the fiber amplifier is measured, which is ~1.4 before the onset of MI, and degrades gradually to ~2.1 after the onset of MI.
190.3100 Instabilities and chaos 060.2320 Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators 140.6810 Thermal effects Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s2): S20603
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The impulsive synchronization problem for semiconductor laser (SL) chaotic systems is studied. SL systems can be described by the rate equations governing photon density and carrier density. Because the carrier density is not easy to observe or measure, only photon density is used to design the impulsive controller. Several sufficient conditions for the synchronization of SL chaotic systems via impulsive control are derived. Numerical simulations are presented to show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
190.3100 Instabilities and chaos 140.1540 Chaos 140.5960 Semiconductor lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(10): 101901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We propose a power spectrum analysis method to directly identify the time delay of a chaotic semiconductor laser with optical feedback. By measuring the radio frequency (RF) power spectrum of the chaotic laser and performing an inverse Fourier transform, we can easily unveil all the time delay signatures, regardless of whether the chaotic output is induced by single or multiple feedback. This method successfully retrieves the two time delay signatures from the power spectrum of a semiconductor laser with double-cavity feedback.
190.3100 Instabilities and chaos 140.5960 Semiconductor lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(6): 061901





