Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 School of Physics and Electronics, Central South University, Changsha 410012, China
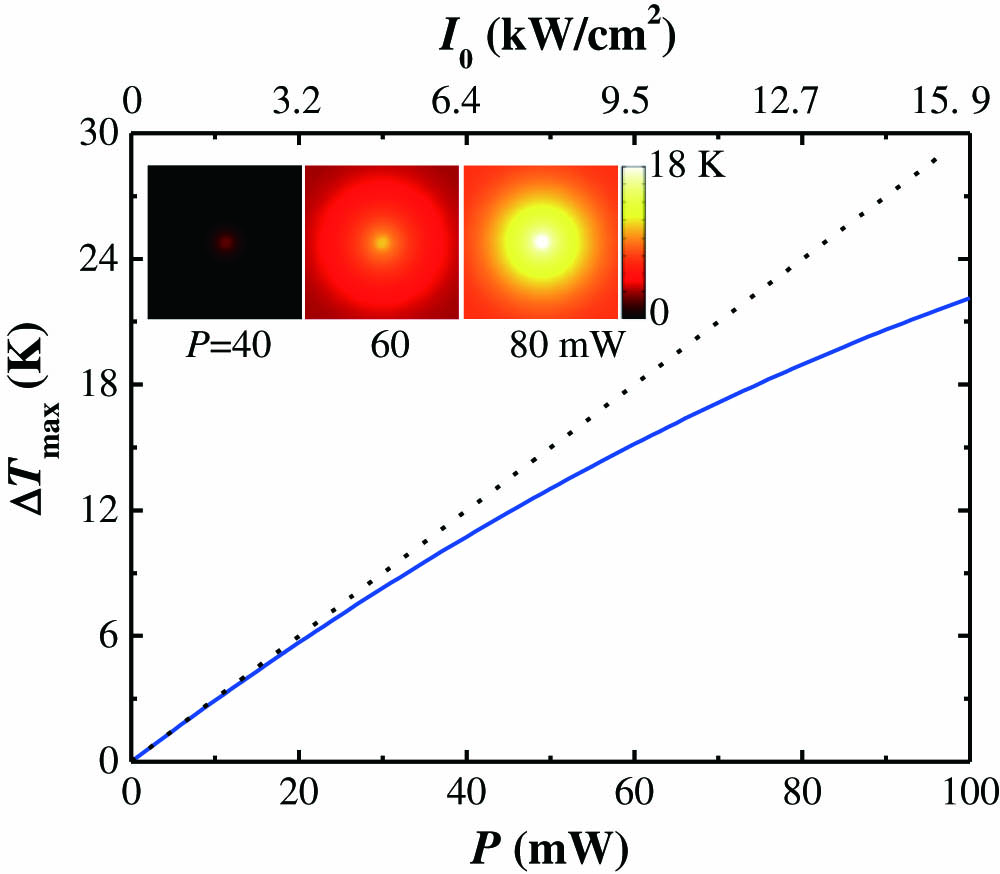
Understanding the nonlinear optical effect of novel materials plays a crucial role in the fields of photonics and optoelectronics. Herein, we theoretically and experimentally investigate the simultaneous presence of third-order locally refractive nonlinearity and thermally induced nonlocal nonlinearity saturation. We present analytical expressions for the closed-aperture Z-scan trace and the number of spatial self-phase modulation (SSPM) rings, which allows one to unambiguously and conveniently separate the contributions of local and nonlocal nonlinear refraction in the case that both effects occur simultaneously. As a test, we study both the local and thermally induced nonlocal nonlinear refraction in fullerene/toluene solution by performing continuous-wave Z-scan and SSPM measurements at two different wavelengths. This work enriches the understanding of the physical mechanism of the optical nonlinear refraction effect in solution dispersions of nanomaterials, which can be exploited for nonlinear photonic devices.
190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in 190.4870 Photothermal effects Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(6): 061901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Faculty of Science and Technology, Communication University of China, Beijing 100024, China
2 Department of Physics, Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio 43210, USA
Five conical harmonic beams are generated from the interaction of femtosecond mid-infrared (mid-IR) pulses at a nominal input wavelength of 1997 nm with a 2D LiNbO3 nonlinear photonic crystal with Sierpinski fractal superlattices. The main diffraction orders and the corresponding reciprocal vectors involved in the interaction are ascertained. Second and third harmonics emerging at external angles of 23.82° and 36.75° result from nonlinear erenkov and Bragg diffractions, respectively. Three pathways of fourth-harmonic generation are observed at external angles of 14.21°, 36.5°, and 53.48°, with the first one resulting from nonlinear erenkov diffraction, and the other two harmonics are generated via different cascaded processes.
190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in 190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing 050.1940 Diffraction Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(5): 051901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Mathematics and Physics, Suzhou University of Science and Technology, Suzhou 215009, China
2 Department of Physics, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
Elliptic vortex solitons are investigated in anisotropic nonlocal media with more general formulations. We address the existence and dynamics of such solitons analytically and numerically. The solution of elliptic vortex solitons depends on the eccentricity of both the input beam and nonlocal response function. With different degrees of nonlocality, we numerically investigate the evolution of the elliptic vortex solitons, and find that, typically, the elliptic vortex solitons with single and double charges collapse into spiraling dipole- and tripole-like soliton clusters, respectively.
190.6135 Spatial solitons 190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(12): 121901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Higher-band self-trapping and oscillation (rotation) of nonlinear quadruple beams in two-dimensional (2D) square photonic lattices are numerically demonstrated. Under appropriate conditions of nonlinearity, a quadruple-like beam can self-trap into localized modes that reside in the second Bragg reflection gap through single-site excitation. By changing the initial orientation of the incident quadruple beam related to the lattices, periodic oscillations of the localized quadruple mode may be obtained. The localized quadruple state becomes a rotating doubly charged optical vortex (DCV) during rotation and should undergo charge-flipping when the rotating direction is reversed.
080.1238 Array waveguide devices 190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in 050.4865 Optical vortices Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(9): 090801
Author Affiliations
Abstract
A unified theory to construct exact optical rogue wave solutions of (1+1)-dimensional nonlinear Schrodinger equation with varying coefficients is proposed. The dynamics of the first-order optical rogue waves in nonlinear graded-index waveguide amplifiers exhibiting self-focusing or self-defocusing Kerr nonlinearity are also investigated. Moreover, under the suitable parameter condition, the propagation characteristics of the rogue waves in the nonlinear optical media are discussed. The properties of the optical rogue waves, such as width, amplitude, and position, can be controlled in the nonlinear optical media.
190.6135 Spatial solitons 190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(3): 031901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, The Key Laboratory of Space Applied Physics and Chemistry, Ministry of Education, School of Science, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an 710072, China
We demonstrate the rotating properties of Bragg reflections and spatial lattice solitons in rotating photonic lattices by analyzing the linear and nonlinear propagations of light. It reveals that the Bragg reflection of the light waves rotates synchronously with the lattices, leading to the rotation of the Bloch waves during propagations. In the presence of nonlinearity, rotating lattice solitons from different transmission bands can propagate in a relatively stable manner. However, reduced-symmetry solitons at point X2 cannot easily rotate synchronously with the lattice, owing to Coriolis forces. Moreover, additional angular momenta are added to the off-axis propagating solitons.
旋转光子晶格 布拉格反射 布洛赫波 空间孤子 080.1238 Array waveguide devices 190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(7): 070801
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Physics, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
We investigate the dynamics of strongly localized solitons trapped in remote troughs of radially periodic lattices with Kerr-type self-focusing nonlinearity. The rotary motion of solitons is found to be more stable for larger nonlinear wavenumbers, lower rotating velocity, and shorter radius of the trapping troughs. When the lattice is shrunk or expanded upon propagation, the solitons can be trapped in the original trough and move outward or inward, with their rotating linear velocity inversely proportional to the radius of the trapping troughs.
孤子 光学格子 190.0190 Nonlinear optics 190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in 190.6135 Spatial solitons Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(8): 791
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Tunable Laser Technology, Institute of Opto-Electronics, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001
We have observed a hole in the absorption profile of the homogeneously broadened absorption band of an Alexandrite crystal. With the spectral hole-burning technique that resulting from the periodic modulation of the ground state population at the beat frequency between the pump and the probe fields, we observed the slowdown the light propagation with the group velocity as slow as 12.5 m/s at room temperature. And the group velocity in the Alexandrite crystal depends on the amplitude modulation frequency, the power of laser beam and the orientation of the crystal lattice. The lower frequency or higher power leads to slower group velocity of light.
190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in 190.5530 Pulse propagation and solitons 190.5940 Self-action effects 270.1670 Coherent optical effects 270.5530 Pulse propagation and solitons Chinese Optics Letters
2005, 3(0s): 354





