Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Aerospace Laser Technology and Systems Department, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Shanghai Typhoon Institute, China Meteorological Administration, Shanghai 200030, China
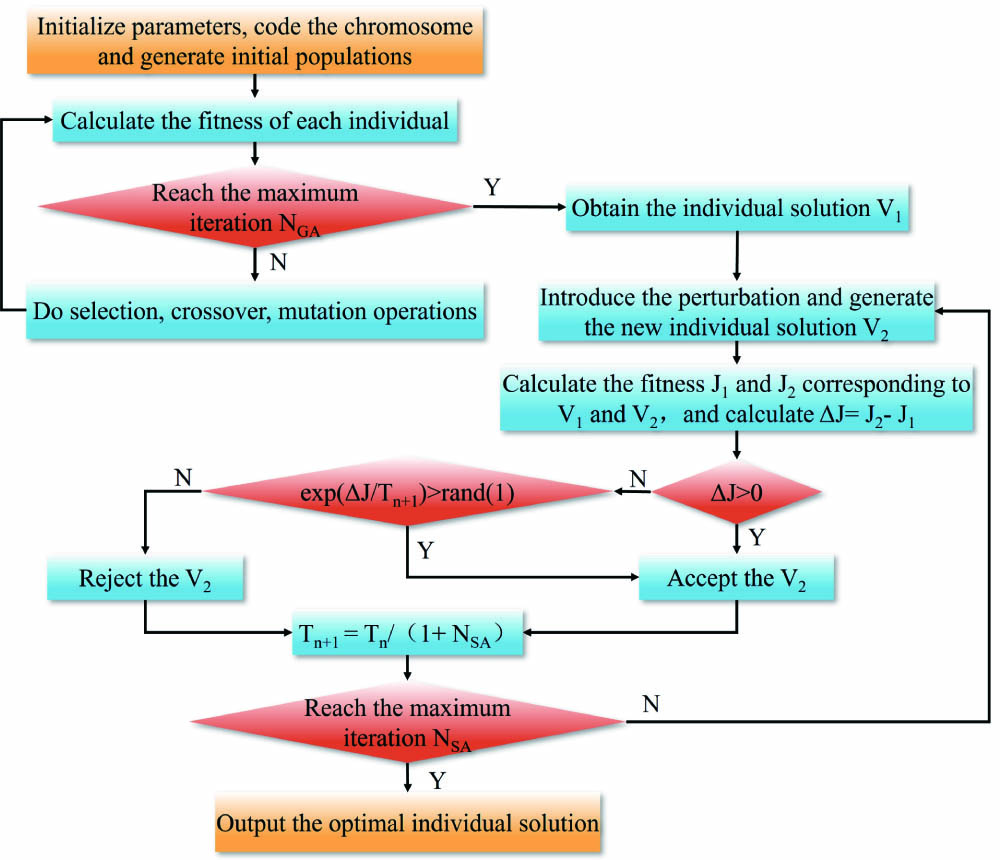
A method of spectrum estimation based on the genetic simulated annealing (GSA) algorithm is proposed, which is applied to retrieve the three-dimensional wind field of typhoon Nangka observed by our research group. Compared to the genetic algorithm (GA), the GSA algorithm not only extends the detection range and guarantees the accuracy of retrieval results but also demonstrates a faster retrieval speed. Experimental results indicate that both the GA and GSA algorithms can enhance the detection range by 35% more than the least squares method. However, the convergence speed of the GSA algorithm is 17 times faster than that of the GA, which is more beneficial for real-time data processing.
coherent Doppler lidar three-dimensional wind field retrieval genetic simulated annealing algorithm spectrum estimation typhoon Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 040101
1 河南理工大学测绘与国土信息工程学院,焦作 454000
2 中国科学院空天信息创新研究院,北京 100094
3 江苏省环境监测中心,南京 210019
利用卫星遥感反演水体中的悬浮物浓度对水质监测和保护具有重要意义,在悬浮物浓度反演过程中,如何避免或最大程度降低水体中叶绿素a、有色可溶性有机物(Colored Dissolved Organic Matter,CDOM)的干扰是当前的技术难点。文章针对可持续发展科学卫星1号(SDGSAT-1)MII传感器,利用Hydrolight辐射传输模型,从理论上挖掘只与悬浮物强相关的反演因子,以此构建适用于MII影像的太湖悬浮物浓度反演模型,通过水体的实测数据和遥感数据对模型应用效果进行验证。结果表明:反演因子$ R'{\text{(}}{B_{\text{5}}}{\text{/}}{B_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}} $与悬浮物浓度为强相关,同时与叶绿素a、CDOM浓度弱相关;利用$ R'{\text{(}}{B_{\text{5}}}{\text{/}}{B_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}} $作为反演因子构建的幂函数模型为最优反演模型;将幂函数模型分别应用于实测数据和2022年5月4日的太湖SDGSAT-1 MII数据,两次验证试验显示反演结果和现场测量结果具有较强一致性,模型适用性较好。该研究可为SDGSAT-1卫星在湖泊水体悬浮物浓度监测、水资源评估与保护等提供一些技术参考。
悬浮物浓度反演 可持续发展科学卫星1号 相关性 水体辐射传输模拟 遥感应用 suspended matter concentration retrieval SDGSAT-1 correlation water body radiative transfer simulation remote sensing applications 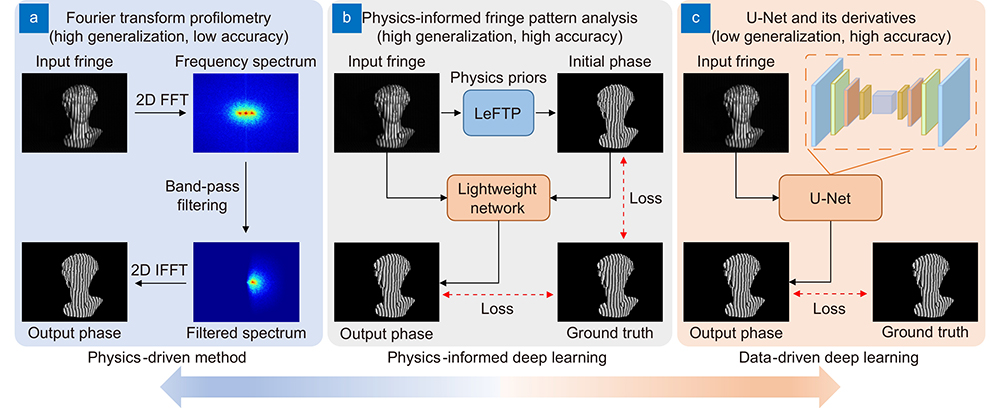
Wei Yin 1,2,3†Yuxuan Che 1,2,3†Xinsheng Li 1,2,3Mingyu Li 1,2,3[ ... ]Chao Zuo 1,2,3,****
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Smart Computational Imaging Laboratory (SCILab), School of Electronic and Optical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
2 Smart Computational Imaging Research Institute (SCIRI) of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210019, China
3 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Spectral Imaging & Intelligent Sense, Nanjing 210094, China
4 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam, Hong Kong SAR 999077, China
Recently, deep learning has yielded transformative success across optics and photonics, especially in optical metrology. Deep neural networks (DNNs) with a fully convolutional architecture (e.g., U-Net and its derivatives) have been widely implemented in an end-to-end manner to accomplish various optical metrology tasks, such as fringe denoising, phase unwrapping, and fringe analysis. However, the task of training a DNN to accurately identify an image-to-image transform from massive input and output data pairs seems at best na?ve, as the physical laws governing the image formation or other domain expertise pertaining to the measurement have not yet been fully exploited in current deep learning practice. To this end, we introduce a physics-informed deep learning method for fringe pattern analysis (PI-FPA) to overcome this limit by integrating a lightweight DNN with a learning-enhanced Fourier transform profilometry (LeFTP) module. By parameterizing conventional phase retrieval methods, the LeFTP module embeds the prior knowledge in the network structure and the loss function to directly provide reliable phase results for new types of samples, while circumventing the requirement of collecting a large amount of high-quality data in supervised learning methods. Guided by the initial phase from LeFTP, the phase recovery ability of the lightweight DNN is enhanced to further improve the phase accuracy at a low computational cost compared with existing end-to-end networks. Experimental results demonstrate that PI-FPA enables more accurate and computationally efficient single-shot phase retrieval, exhibiting its excellent generalization to various unseen objects during training. The proposed PI-FPA presents that challenging issues in optical metrology can be potentially overcome through the synergy of physics-priors-based traditional tools and data-driven learning approaches, opening new avenues to achieve fast and accurate single-shot 3D imaging.
optical metrology deep learning physics-informed neural networks fringe analysis phase retrieval Opto-Electronic Advances
2024, 7(1): 230034
1 华中科技大学智能制造装备与技术全国重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430074
2 光谷实验室,湖北 武汉 430074
衍射场作为叠层衍射成像技术(ptychography)的重要约束,其信息的丰富度和准确性将直接影响重构质量。提出一种基于极大似然噪声估计的高动态范围(ML-HDR)叠层衍射成像方法,即在探测器线性响应假设下,构建复合高斯噪声模型,根据极大似然估计求解最优权重函数,由多张低动态范围衍射场合成高信噪比衍射场。对比了单次曝光、传统HDR和ML-HDR三种方法的重构质量。仿真和实验结果表明:相比单次曝光,ML-HDR能将动态范围拓宽8位,重构分辨率提升至2.83倍;相比传统HDR,ML-HDR能提高重构图像的均匀性和对比度,且无需额外标定硬件参数。
计算成像 叠层衍射成像术 高动态范围 相位恢复 极大似然估计 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(8): 0811011
1 国防科技大学理学院,湖南 长沙 410073
2 极端条件物理及应用湖南省重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410073
自本世纪初超快科学进入阿秒领域以来,阿秒脉冲以其超宽频谱和超短时间分辨,为研究阿秒时间尺度的瞬态过程提供了有力工具,推动了人们对光与物质相互作用以及微观超快动力学机制的理解。基于高次谐波的单个阿秒脉冲产生技术已日臻成熟,通过发展多种时空选通门技术,阿秒脉冲脉宽不断缩短,已达到的最短纪录为43 as。相较于阿秒脉冲的产生,对其精确测量与表征是深入研究和应用的基础,目前主流表征方法是通过阿秒条纹相机技术测量获得条纹能谱,进而从中提取阿秒脉冲的时域信息。首先简要回顾了高次谐波产生、单个阿秒脉冲选通及测量的发展,然后介绍了阿秒条纹相机技术的原理,并重点阐述了基于阿秒条纹能谱的表征算法,对其主要优缺点进行分析,最后对阿秒脉冲表征的发展进行了总结和展望。
非线性光学 单个阿秒脉冲 阿秒条纹相机 相位反演与表征
1 中国海洋大学信息科学与工程学部海洋技术学院,山东 青岛 266100
2 北京航空气象研究所,北京 100085
3 青岛镭测创芯科技有限公司,山东 青岛 266100
4 崂山实验室,山东 青岛 266237
5 中国海洋大学海洋高等研究院,山东 青岛 266100
为了提升大气物质边界层高度(AMBLH)的识别准确性,基于2020年11月至2021年11月在青岛开展的大气边界层(ABL)观测实验,提出了一种基于相干多普勒激光雷达(CDL)信噪比数据的AMBLH的综合反演方法,并应用此方法反演得到了青岛地区的AMBLH,其与探空仪反演结果的相关度为0.93。分析了青岛一年内的AMBLH发展情况,发现各月份AMBLH均有日变化特征,其中6、7月特征相对较弱,推测这与夏季来自海洋的东南风盛行有关。AMBLH月均值在全年呈起伏波动趋势,在冬末至春初、夏末至秋初的阶段逐步增大。AMBLH月均中位数4月最高、6月最低,AMBLH季度发展程度由高到低的顺序为春季、冬季、秋季、夏季,其中春季和冬季高度相近。AMBLH各季度日变化中抬升趋势出现的时间为夏季早于春季,秋季与春季相近并早于冬季。
大气光学 相干多普勒激光雷达 大气物质边界层高度 综合反演方法
1 兰州交通大学光电技术与智能控制教育部重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730070
2 轨道交通信息与控制国家级虚拟仿真实验教学中心,甘肃 兰州 730070
3 兰州交通大学电子与信息工程学院,甘肃 兰州 730070
针对增量运动恢复结构(SFM)算法在重建大规模无人机影像数据集时效率低、易产生场景漂移的问题,提出一种可并行化处理的增量SFM重建算法。首先,利用词汇树图像检索结果约束图像特征匹配的空间搜索范围,提高图像特征匹配的效率。其次,综合考虑特征匹配数量和无人机平台获取的全球定位系统(GPS)信息构建无向加权场景图,并选用归一化割算法将场景图划分为多个相互重叠的子集。然后,将每个子集分布在多核CPU上并行执行增量SFM重建算法。最后,基于子集间公共重建点和强相关子集优先被合并的策略实现子集合并。此外,结合GPS信息为光束法平差(BA)代价函数添加位置约束项,有效消除每次执行BA优化引入的误差。为了验证所提算法的有效性,在3个无人机数据集上进行实验,实验结果表明,所提算法相比原始增量SFM重建算法不仅显著提高了位姿估计和场景重建的效率,而且合理优化了重建结果的精度。
增量运动恢复结构 光束法平差 词汇树图像检索 归一化割 场景合并 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(8): 0811002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, United States
2 Friedrich-Alexander University, Erlangen, Germany
3 UC San Diego, La Jolla, California, United States
4 Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
5 UC Berkeley, Berkeley, California, United States
6 Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina, United States
We report tensorial tomographic Fourier ptychography (T2oFu), a nonscanning label-free tomographic microscopy method for simultaneous imaging of quantitative phase and anisotropic specimen information in 3D. Built upon Fourier ptychography, a quantitative phase imaging technique, T2oFu additionally highlights the vectorial nature of light. The imaging setup consists of a standard microscope equipped with an LED matrix, a polarization generator, and a polarization-sensitive camera. Permittivity tensors of anisotropic samples are computationally recovered from polarized intensity measurements across three dimensions. We demonstrate T2oFu’s efficiency through volumetric reconstructions of refractive index, birefringence, and orientation for various validation samples, as well as tissue samples from muscle fibers and diseased heart tissue. Our reconstructions of healthy muscle fibers reveal their 3D fine-filament structures with consistent orientations. Additionally, we demonstrate reconstructions of a heart tissue sample that carries important polarization information for detecting cardiac amyloidosis.
computational imaging three-dimensional imaging phase retrieval microscopy polarization-sensitive imaging label-free imaging Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(2): 026004
北京理工大学光电学院北京市混合现实与新型显示工程技术研究中心,北京 100081
融合几何光学的蒙日-安培方程方法和物理光学的迭代角谱算法,提出了一种复合型相位恢复方法。针对迭代角谱算法高度依赖初始值的问题,将蒙日-安培方程的解作为迭代初值,该初值通常比光强传输方程的解更准确。采用传统迭代角谱算法与混合输入输出算法的交替迭代策略,以避免算法过早陷入局部最优和迭代停滞。通过数值计算与仿真验证了所提复合型算法的优越性。
相位测量 相位恢复 蒙日-安培方程 迭代角谱算法 光强传输方程 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(5): 0512004
1 中国科学院空天信息创新研究院定量遥感信息技术重点实验室,北京 100094
2 中国科学院大学电子电气与通信工程学院,北京 100049
星载Mie散射激光雷达是当前应用最为广泛的获取全球尺度气溶胶剖面信息的探测设备。然而,大气气溶胶类型多样,通常假定气溶胶遵循特定模式并以此为先验,从而实现从激光雷达信号反演气溶胶消光系数廓线,但这一定程度上会影响反演精度的进一步提升。鉴于此,提出了一种基于星载激光雷达双通道信息的气溶胶消光系数廓线的迭代反演优化算法。该方法首先在给定的先验气溶胶模式下获得初始消光-后向散射比(即激光雷达比),并基于此分别反演两个通道的气溶胶消光系数和光学厚度。同时借助构建的气溶胶光学厚度与气溶胶质量柱总量之间的关系,得到两通道独立估计的大气气溶胶质量柱总量。最后以两通道大气气溶胶质量柱总量相同为约束,实现仅依赖激光雷达数据的激光雷达比及气溶胶相关光学参数的迭代优化。由于双通道激光雷达观测的限制,该方法适用于两种类型气溶胶混合下的反演,利用内蒙古包头地区的多年气溶胶背景场,对反演模型的精度和适用性进行了评估。与采用经验估算激光雷达比的Fernald方法反演结果相比,所提算法反演的气溶胶消光系数廓线在532 nm和1064 nm通道的平均精度分别提高了21.16%和3.00%。此外,还将该方法应用在CALIOP数据中,进一步验证了该反演模型的应用潜力。
Mie散射激光雷达 双通道信息 气溶胶消光系数 激光雷达比 迭代反演 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(5): 0501004





