浙江大学极端光学技术与仪器全国重点实验室,光电科学与工程学院,先进光子学研究中心,嘉兴研究院智能光子研究中心,浙江大学杭州国际科创中心,浙江 杭州 310027
作为一种二维形式的超构材料,超构表面允许以前所未有的自由度对光的振幅、相位、偏振等维度进行灵活高效的调控,有望突破传统光学的限制,实现低成本、高性能、超轻超薄、功能新颖的新型光学元件,近年来引起了学术界和产业界越来越浓厚的研究兴趣。从物理机理、相位调控到正向设计方法,系统回顾了超构表面的设计原理。介绍了这些机理如何用于实现丰富的应用,包括功能复用、宽带宽、大视场、多层级联、非局域超构表面等,涵盖了最主要和最新的发展方向。最后,讨论了超构表面在走向实用化的道路上所面临的器件设计和加工制造上的挑战,并对领域未来的发展进行展望。
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electronic Information Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
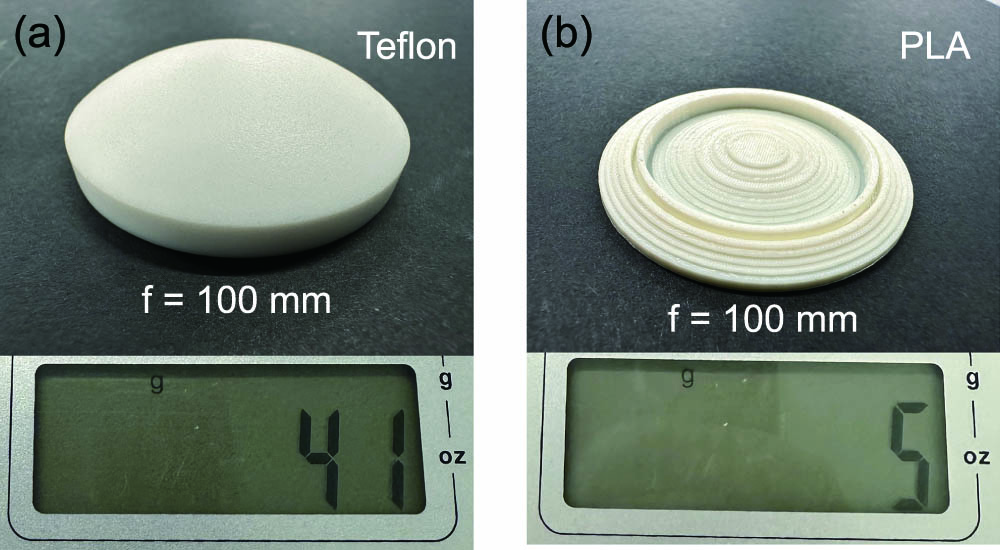
Terahertz (THz) lenses have numerous applications in imaging and communication systems. Currently, the common THz lenses are still based on the traditional design of a circular convex lens. In this work, we present a method for the design of a 3D-printed multilevel THz lens, taking advantage of the benefits offered by 3D printing technology, including compact size, lightweight construction, and cost-effectiveness. The approach utilizes an inverse design methodology, employing optimization methods to promise accurate performance. To reduce simulation time, we employ the finite-difference time-domain method in cylindrical coordinates for near-field computation and couple it with the Rayleigh–Sommerfeld diffraction theory to address far-field calculations. This technology holds great potential for various applications in the field of THz imaging, sensing, and communications, offering a novel approach to the design and development of functional devices operating in the THz frequency range.
THz lens 3D printing achromatic lens THz communication Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110006
1 中国科学院光电技术研究所薄膜光学相机总体室,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院大学光电学院,北京 100049
为实现大口径衍射光学系统宽波段成像,分析了传统衍射透镜基于Schupmann结构光路模型带宽增加带来的中继镜口径变大的问题,提出采用谐衍射透镜作为主镜构建大口径宽波段衍射光学系统,设计了口径为10 m谱段覆盖400~900 nm的大口径光学系统,中继镜的口径与传统设计相比减小了2.4 m。为验证该设计方法,设计一套口径为80 mm、光谱范围为400~900 nm的成像光学系统,并对该系统进行了成像实验,通过查看鉴别率靶图像无色差,验证了基于谐衍射透镜为主镜的宽波段成像设计方法,为大口径衍射光学系统设计提供了一种思路。
光学设计 宽波段 谐衍射 消色差 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(21): 2122003

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Sun Yat-sen University, School of Microelectronics Science and Technology, Zhuhai, China
2 Sun Yat-sen University, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Processing Chips and Systems, Zhuhai, China
On-chip focusing of plasmons in graded-index lenses is important for imaging, lithography, signal processing, and optical interconnects at the deep subwavelength nanoscale. However, owing to the inherent strong wavelength dispersion of plasmonic materials, the on-chip focusing of plasmons suffers from severe chromatic aberrations. With the well-established planar dielectric grating, a graded-index waveguide array lens (GIWAL) is proposed to support the excitation and propagation of acoustic graphene plasmon polaritons (AGPPs) and to achieve the achromatic on-chip focusing of the AGPPs with a focus as small as about 2% of the operating wavelength in the frequency band from 10 to 20 THz, benefiting from the wavelength-independent index profile of the GIWAL. An analytical theory is provided to understand the on-chip focusing of the AGPPs and other beam evolution behaviors, such as self-focusing, self-collimation, and pendulum effects of Gaussian beams as well as spatial inversions of digital optical signals. Furthermore, the possibility of the GIWAL to invert spatially broadband digital optical signals is demonstrated, indicating the potential value of the GIWAL in broadband digital communication and signal processing.
achromatic lens self-focusing lens graded-index lens waveguide array broadband focusing graphene plasmon Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(5): 056003
强激光与粒子束
2023, 35(7): 071008

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Zhengzhou University of Aeronautics, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhengzhou, China
2 Nanjing University, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing, China
3 South China University of Technology, College of Physics and Optoelectronics, Guangzhou, China
Metasurfaces have emerged as a flexible platform for shaping the electromagnetic field via the tailoring phase, amplitude, and polarization at will. However, the chromatic aberration inherited from building blocks’ diffractive nature plagues them when used in many practical applications. Current solutions for eliminating chromatic aberration usually rely on searching through many meta-atoms to seek designs that satisfy both phase and phase dispersion preconditions, inevitably leading to intensive design efforts. Moreover, most schemes are commonly valid for incidence with a specific spin state. Here, inspired by the Rayleigh criterion for spot resolution, we present a design principle for broadband achromatic and polarization-insensitive metalenses using two sets of anisotropic nanofins based on phase change material Ge2Sb2Se4Te1. By limiting the rotation angles of all nanofins to either 0 deg or 90 deg, the metalens with a suitable numerical aperture constructed by this fashion allows for achromatic and polarization-insensitive performance across the wavelength range of 4–5 μm, while maintaining high focusing efficiency and diffraction-limited performance. We also demonstrate the versatility of our approach by successfully implementing the generation of broadband achromatic and polarization-insensitive focusing optical vortex. This work represents a major advance in achromatic metalenses and may find more applications in compact and chip-scale devices.
metasurfaces broadband achromatic metalenses polarization insensitivity phase change materials of Ge2Sb2Se4Te1 Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(5): 056002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Resources and Environment, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
Metalens are planar lenses composed of the subwavelength arrays, which have unconventional and versatile functionalities to manipulate the light fields compared with the traditional lens. It is noted that the most metalens are designed in a monochromatic mode in the visible or mid-infrared range (mid-IR), however, the broadband range is needed in many practical applications, such as spectroscopy, sensing, and imaging. Here, we design and demonstrate a broadband achromatic dielectric metalens in the mid-IR range of 4 μm - 5 μm for near diffraction-limited (1.0λ) focusing. The broadband achromatic propagation and focusing of the metalens are designed and simulated by constructing and optimizing the phase profile. The Pancharatnam-Berry (P-B) phases of all the elements contribute to the main phase increment of the whole phase profile of the metalens. The additional phase is constructed and optimized by using the random search algorithm to obtain the optimized size of all the elements. The focusing efficiency of the achromatic metalens is also optimized and averaged as the result of phase optimization within a wide band for the building elements, while it is lowered comparing with the regular metalens without broadband achromatic designing. Using this combined designing approach, various flat achromatic devices with the broadband metalens can find a new way for full-color detection and imaging.
Broadbands achromatic metalens mid-IR Photonic Sensors
2023, 13(1): 230126
1 光电控制技术重点实验室,河南 洛阳 471000
2 中国航空工业集团有限公司洛阳电光设备研究所,河南 洛阳 471000
新一代红外对抗技术中,需要将红外高峰值功率激光耦合进红外传能光纤中进行传输。针对红外宽波段、高峰值功率激光进行光纤耦合时存在的问题,设计了一种光纤端帽参与聚焦的消色差耦合光学系统,能够对高峰值功率的2.1~4.6 μm红外激光进行光纤耦合,并且光纤端帽可以提高光纤端面的损伤阈值。然后,对消色差耦合光学系统进行了详细设计,并选择了最佳三片式消色差玻璃组合ZNS/MGF2/IRG206进行设计,最终在耦合系统焦距为35 mm时,该系统对2.1~4.6 μm波段的耦合效率达到92.74%。进一步分析可知,耦合光学系统最佳的焦距范围在35~47 mm,以及焦距在40 mm时,光纤对准最大容差为60 μm。
光学设计 耦合光学系统 光纤端帽 消色差 耦合效率 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(5): 0522007
1 浙江大学光电科学与工程学院,浙江 杭州 310027
2 福建福特科光电股份有限公司,福建 福州 350100
在纳米激光直写加工系统中,显微物镜是其中的关键部件,行业发展的趋势是在大数值孔径(NA)下具有更大的物方视场,并且能适应双光子聚合(Two-photon polymerization,TPP)胶折射率的变化。对比当前TPP效应研究所用显微物镜的指标,挖掘了物方视场、NA和镜片数的关系,并提出物镜的合成敏感度指标(Synthetic sensitivity index,Iss)。结合Iss设计了一款波段为500~800 nm、NA大于1.3、物方视场为1.0 mm的显微物镜。该物镜的设计结果为,调制传递函数曲线接近衍射极限,波像差均方根小于0.07λ,以内调焦方式来适应TPP胶折射率的变化。公差分析表明该设计结果具有可行性。
光学设计 大视场 大数值孔径 平场复消色差显微物镜 激光直写 微纳加工 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(5): 0518001





