Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Institute for Solid State Physics, The University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8581, Japan
2 Current affiliation: School of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong University, Qingdao 266237, China
A monolithic lens-window-prism (LWP) device, made of lithium fluoride (LiF) or magnesium fluoride (MgF2), was proposed. When either of the devices was fixed onto one end of a gas cell filled with Xe, it becomes a “wedge-crystal”-like device and was used to convert a 1 MHz femtosecond 347 nm laser to its third harmonic radiation at 10.7 eV. This led to an improved beam profile and a more compact and less lossy configuration. A stable output power of ~11 μW was demonstrated for 2 h using LiF-LWP. In addition, MgF2-LWP was also verified for its practicability at 10.7 eV.
140.7240 UV, EUV, and X-ray lasers 190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing 320.7090 Ultrafast lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(5): 051406
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Quantum Beam Science Directorate, Kansai Photon Science Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Kizugawa, Kyoto 619-0215, Japan
2 Graduate School for the Creation of New Photonics Industries, Hamamatsu 431-1202, Japan
Ablation dynamics of tungsten irradiated with a 70 fs laser pulse is investigated with X-ray interferometry and X-ray imaging using a 13.9 nm soft X-ray laser of 7 ps pulse duration. The evolution of high-density ablation front of tungsten (i.e., W) is presented. The ablation front expands to ~120 nm above the original target surface at 160 ps after femtosecond-laser irradiation with an expansion speed of approximately 750 m/s. These results will provide important data for understanding ablation properties of W, which is a candidate material of the first wall of magnetic confinement fusion reactors.
140.7240 UV, EUV, and X-ray lasers 350.3390 Laser materials processing 340.7440 X-ray imaging 340.7450 X-ray interferometry Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(7): 070002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Quantum Beam Science Directorate, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Kizugawa, Kyoto 619-0215, Japan
2 Joint Institute for High Temperatures, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow 125412, Russia
3 Institute for Academic Initiatives, Osaka University, Suita, Osaka, 565-0871, Japan
4 International Laser Center of M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia
5 The Graduate School for the Creation of New Photonics Industries, Hamamatsu, Shizuoka 431-1202, Japan
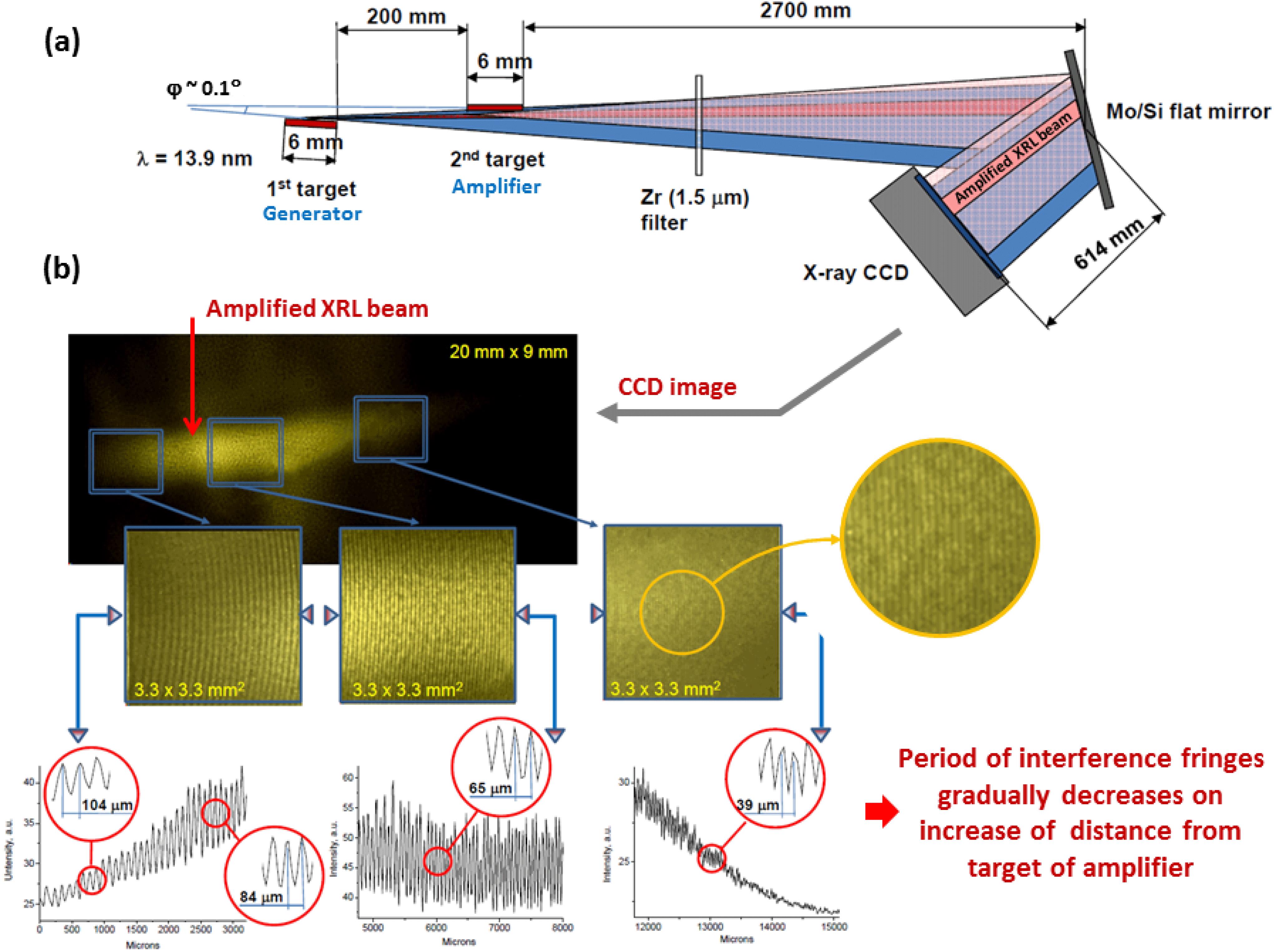
In the far field of the intensity distribution of the beam delivered by a two-stage transient–collisional excitation X-ray laser (XRL), a non-expected interference pattern that is stable from shot to shot has been discovered. It is demonstrated that the interference is caused by the emergence of an imaginary source in the amplifying plasma, which is phase matched to the radiation of the generator. The observed phenomenon is called an X-ray coherent mirage. To explain the obtained results, a new theoretical approach is developed. The basic essential conditions for formation of the X-ray mirage are formulated, and possible applications are discussed. This paper details the experiments, including the formulation of the necessary and sufficient conditions for formation of the X-ray mirage, and possible applications are discussed.
coherent seeded beams mirage phase-matching X-ray lasers X-ray plasma optics High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2014, 2(2): 02000e12
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) simulations and theoretical analyses on super-short pulse generated using freeelectron lasers (FELs) at perfect synchronism are carried out with the help of our 3D OSIFEL code. The evolution of longitudinal pulse width in the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) experiment is simulated. The results show that the optical pulse is compressed on successive passes due to the slippage between the optical and electron beams, and an ultra-short 221-fs optical pulse is finally obtained, which agrees with the experiment. Furthermore, to shorten wavelength such as soft ultraviolet (SUV) spectrum range, an ultra-short pulse generated at perfect synchronism is analyzed and studied. Finally, the relationship between the optical pulse length compressed and the peak electron beam current is calculated. It shows that the higher the electron beam current, the shorter the output FEL width length, due to the higher gain.
140.2600 Free-electron lasers (FELs) 140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 140.7240 UV, EUV, and X-ray lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(s2): S21401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
An improved method for stabilizing a frequency-quadrupled 214.5-nm tunable diode laser system is reported. Improvements to the method include a homemade logic circuit and the use of a Fabry-Perot optical spectrum analyzer as a transfer cavity. Lasers locked with this method exhibit megahertz-level frequency stability measured with an optical frequency comb referenced to a cesium atomic standard. The laser can be locked for hours to days, depending on experiment requirements. Being relatively inexpensive, stable, and robust, the control method can be applied to stabilizing essentially all lasers of deep ultraviolet wavelengths.
140.7240 UV, EUV, and X-ray lasers 140.2020 Diode lasers 120.2230 Fabry-Perot Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(3): 031401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Carrier-envelope phase effect of the monochromatic high frequency pulse generation from Thomson backscattering is investigated with an analytical model and verified by one dimensional particle in cell simulations. We show that the central frequency of the monochromatic light generated from Thomson backscattering is extremely sensitive to the carrier-envelope phase of the field driving the relativistic electron layers.
140.7240 UV, EUV, and X-ray lasers 290.5850 Scattering, particles 350.4990 Particles Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(s2): S21402
哈尔滨工业大学 可调谐(气体)激光技术国家级重点实验室,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
利用等离子体波导实现光场感应电离(OFI)X射线激光放大,一方面可以降低产生X射线激光的抽运激光阈值,从而提高由于自散焦而降低的有效激光功率密度;另一方面,由于等离子体中产生的大量电子被束缚在等离子体波导内,降低X光信号色散影响,可以大大提高激光增益长度,这是一种实现台上X射线激光新的抽运机制。详细介绍了光场感应电离X射线激光、强激光等离子体波导以及等离子体波导中光场感应电离X射线激光的研究进展。
光场感应电离 毛细管放电 等离子体波导 软X射线激光
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
Deep ultraviolet lasers have various applications in industries and scientific researches. For 266-nm ultraviolet (UV) laser generation, the good beam quality of 1064-nm laser and the elimination of gray-tracking effect of KTP crystal are two key factors. Using a dynamically stable resonator design, 1064-nm laser with an average power of 52 W is realized with repetition rate of 16 kHz. The measured M2 factor characterizing the beam quality is 1.5. By the elimination of gray-tracking effect of KTP crystal, an 18-W green laser is realized with the M2 factor of 1.6. Using a BBO crystal for the fourth harmonic generation, a 1.9-W 266-nm UV laser is achieved.
紫外激光 灰迹效应 谐振腔设计 140.7240 UV, EUV, and X-ray lasers 140.3515 Lasers, frequency doubled Chinese Optics Letters
2009, 7(6): 06502
Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Key Laboratory of Tunable Laser Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 1500802 School of Energy Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080
In a capillary discharge experiment for the neon-like argon lasing, we have proposed an experimental scheme to verify that the multi-spike of X-ray diode (XRD) signal is a multi-pulse laser or is a reflection of the laser pulse in the XRD. The ceramic capillary has an inner diameter of 3 mm and a length of 200 mm. At the gas pressure of 28 Pa and discharge current of 27 kA, stable lasing has been realized. The experimental results prove that the multi-spike of XRD signal is a reflection of the electromagnetic signal produced by the laser pulse in the XRD. The improved electrocircuit scheme of the XRD to minimize the reflection phenomena is also found.
软X射线激光 毛细管放电 软X射线探测 多脉冲激光 电磁波反射信号 140.7240 UV, EUV, and X-ray lasers 350.5400 Plasmas 340.7480 X-rays, soft x-rays, extreme ultraviolet (EUV) Chinese Optics Letters
2008, 6(5): 353
四川大学原子与分子物理研究所, 成都 6100652
瞬态碰撞激发X射线激光由于其所需驱动能量低、效率高和容易台式化等优点,极大地推动了X射线激光的发展。比较详细地总结了这一研究领域取得的突破性进展,并讨论了开展瞬态碰撞激发X射线激光的关键问题。
激光光学 瞬态碰撞激发 X射线激光 研究进展





