Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Intelligent Optical Sensing and Manipulation, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
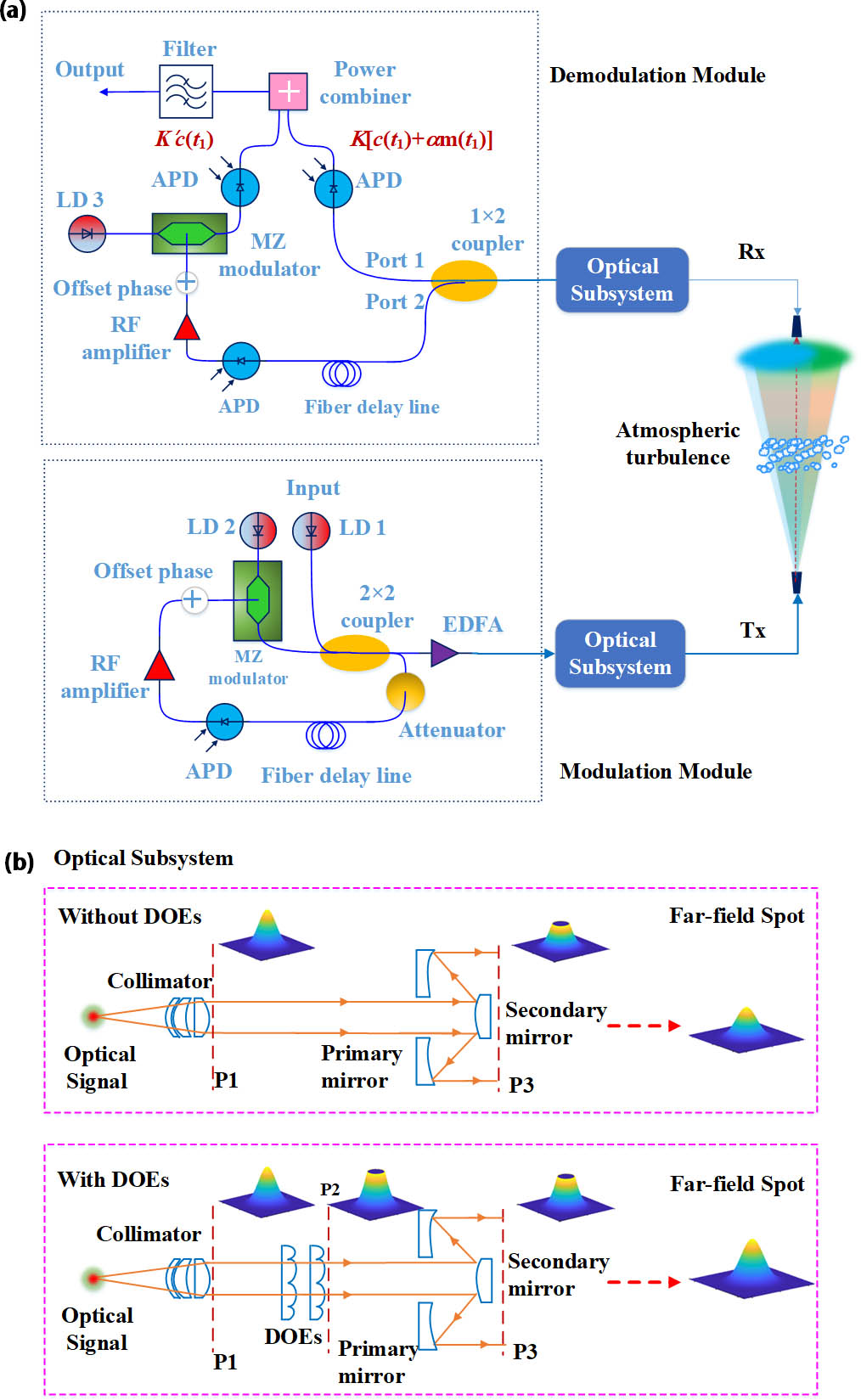
With the increasing demand for space optical communication security, space chaotic optical communication has attracted a great amount of attention. Compared with traditional space optical communication, a chaotic optical communication system has a higher bit error rate (BER) for its complex system design. In order to decrease the BER of space chaotic optical communication systems, we introduce two diffractive optical elements (DOEs) at a transmitting terminal (Tx). That is because the commonly used reflective optical antenna at Tx blocks the central part of the transmission beam, which leads to a great amount of power consumption. Introducing the DOEs into the optical subsystem at Tx can reshape the transmission beam from a Gaussian distribution to a hollow Gaussian distribution so that the block of the secondary mirror in the reflective optical antenna can be avoided. In terms of the DOE influence on communication quality, we give a BER model based on a minimum-shift-key (MSK) space uplink chaotic optical communication system to describe the DOE function. Based on the model, we further investigate the effect of the DOEs through analyzing the BER relationship versus basic system parameters based on the BER model. Both different mismatch conditions of chaotic systems and different atmospheric turbulence conditions are considered. These results will be helpful for the scheme design of space uplink chaotic optical communication systems.
chaotic-encrypted communication space uplink optical communication atmospheric turbulence effects diffractive optical element design minimum-shift-key bit error rate Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(7): 070601
1 中国科学院安徽光学精密机械研究所中国科学院大气光学重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230031
2 中国科学技术大学,安徽 合肥 230026
利用红光激光器、3M微晶棱镜阵列反光膜和长焦高速CCD相机构建的折返路径激光成像探测系统,进行了湍流大气中1 km传输路径上的 激光光斑回波成像探测实验,同时使用激光闪烁仪实时监测湍流强度变化。首先对获得的激光回波光斑图像的强度分布进行了 直观分析,比较了在不同湍流强度下折返路径激光光斑形态的差异,接着统计计算了不同湍流强度下,光斑光强概率密度分布与 光斑图像位置和区域面积大小的关系。结果表明: 折返路径下的激光传输光强起伏概率密度函数在光斑上的各处基本都 符合对数正态分布,但在质心附近的区域符合程度更高,且符合程度与接收面积大小呈负相关。同时湍流强度对回波 光斑平面上不同位置之间、不同接收区域大小之间符合正态分布程度的差异有一定影响。
大气光学 折返路径激光传输 大气湍流效应 微晶棱镜阵列 光强分布 概率密度分布 atmospheric optics retro-reflective laser transmission atmospheric turbulence effects microcrystalline prism array intensity distribution probability density distribution 大气与环境光学学报
2018, 13(4): 241





