1 滁州学院 机械与电气工程学院,滁州 239000
2 安庆师范大学 电子工程与智能制造学院,安庆 246133
光谱检测是鉴别物质类型、掌握物质含量的重要手段。凹面光栅作为光谱检测仪的核心器件,其成像质量直接影响检测质量,影响凹面光栅的成像质量归类为像差消除与分辨率提升两个方面。综述了光谱检测仪研制、像差消除与分辨率提升的研究进展; 总结了各方案消除像差、提高分辨率的技巧、特色以及需满足的条件; 最后展望了基于凹面光栅的光谱检测未来可能发展方向。
光谱学 衍射与光栅 成像 光谱 检测技术 像差 分辨率 spectroscopy diffraction and gratings imaging spectra detection technology aberration resolution

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics & School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
We propose a design of single-mode orbital angular momentum (OAM) beam laser with high direct-modulation bandwidth. It is a microcylinder/microring cavity interacted with two types of second-order gratings: the complex top grating containing the real part and the imaginary part modulations and the side grating. The side grating etched on the periphery of the microcylinder/microring cavity can select a whispering gallery mode with a specific azimuthal mode number, while the complex top grating can scatter the lasing mode with travelling-wave pattern vertically. With the cooperation of the gratings, the laser works with a single mode and emits radially polarized OAM beams. With an asymmetrical pad metal on the top of the cavity, the OAM on-chip laser can firstly be directly modulated with electrical pumping. Due to the small active volume, the laser with low threshold current is predicted to have a high direct modulation bandwidth about 29 GHz with the bias current of ten times the threshold from the simulation. The semiconductor OAM laser can be rather easily realized at different wavelengths such as the O band, C band, and L band.
orbital angular momentum diffraction and gratings vertical emitting lasers microcavity devices semiconductor lasers single mode directly modulated laser Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(8): 081401
1 衢州职业技术学院 信息工程学院, 衢州 324000
2 北京工业大学 电子信息与控制工程学院 光电子技术实验室, 北京 100124
为了提高倒装发光二极管(LED)光提取效率的同时实现单偏振光输出, 建立了正装、倒装和集成金属亚波长光栅倒装LED 3种模型, 采用RSOFT软件进行仿真对比及器件优化,并进行了理论分析和模拟验证。结果表明, 倒装LED虽然可以提高光提取效率但对P-GaN层厚非常敏感, 无法单偏振光输出; 集成了金属亚波长光栅的倒装LED可以不受P-GaN层厚影响, 实现单偏振光输出, 但要输出稳定偏振光, 受光栅参量和介质过渡层厚度影响非常显著;优化后的结构可以实现57.63%的光提取效率, 偏振消光比达到25.8dB。该研究对制造高性能蓝光LED具有一定的指导作用。
衍射与光栅 光提取效率 RSOFT软件 发光二极管 消光比 单偏振 diffraction and gratings light extraction efficiency RSOFT software light-emitting diode extinction ratio single polarization
1 山东师范大学物理与电子科学学院光场调控及应用中心,山东省光学与光子器件重点实验室, 山东 济南 250014
2 苏州大学物理科学与技术学院, 江苏 苏州 215006
涡旋光束具有螺旋波前、携带相位奇点和轨道角动量等物理特性,在粒子操控、量子信息、超分辨成像、光通信等领域具有重要的应用,并已成为学术界的研究热点。得益于相干光学理论的快速发展,将相干性作为新的自由度引入涡旋光束中,提出新型涡旋光束即部分相干涡旋光束。相较于完全相干涡旋光束,部分相干涡旋光束具有独特的物理内涵和光学特性,尤其是对其相干性和拓扑荷的联合调控会引发一系列奇特的新物理效应(如相干奇点、光束整形、偏振态转换、自修复等)。回顾了部分相干涡旋光束的基本理论及发展历程,着重对部分相干涡旋光束的理论模型、传输特性、实验产生、实验测量和应用基础研究进行了阐述。
物理光学 衍射与光栅 涡旋光束 相位奇点 相干性 相干奇点
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Modal analysis of the 1×3 highly efficient reflective triangular grating operating in the 800 nm wavelength under normal incidence for TE polarization is presented in this Letter. The rigorous coupled wave analysis and simulated annealing algorithm are used to design this beam splitter. The reflective grating consists of a highly reflective mirror and a transmission grating on the top. The mechanism of the reflective triangular grating is clarified by the simplified modal method. Then, gratings are fabricated by direct laser writing lithography.
050.0050 Diffraction and gratings 050.1950 Diffraction gratings Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(4): 040902

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
2 College of Information Science and Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
3 College of Physical Science and Technology, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
We present a technique for fabricating a fluorescence enhancement device composed of metal nanoparticles (NPs) and porous silicon (PSi) diffraction grating. The fluorescence emission enhancement properties of the PSi and the fluorescence enhancement of the probe molecules are studied on PSi gratings. The fluorescence enhancement of the probe molecules on a fluorescence enhancement device is further improved through the deposition of metal NPs onto the PSi grating. In comparison to metal NP/PSi devices, metal NP periodic distributions can produce a stronger fluorescence enhancement that couples with the PSi grating fluorescence enhancement to achieve an overall three-fold enhancement of the fluorescence intensity.
050.0050 Diffraction and gratings 230.0230 Optical devices Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(11): 110501

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Physical Electronics and Devices of the Ministry of Education & School of Science & Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Information Photonic Technique & Institute of Wide Bandgap Semiconductors, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
2 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 3, Singapore 117583, Singapore
Conventional periodic structures usually have nontunable refractive indices and thus lead to immutable photonic bandgaps. A periodic structure created in an ultracold atoms ensemble by externally controlled light can overcome this disadvantage and enable lots of promising applications. Here, two novel types of optically induced square lattices, i.e., the amplitude and phase lattices, are proposed in an ultracold atoms ensemble by interfering four ordinary plane waves under different parameter conditions. We demonstrate that in the far-field regime, the atomic amplitude lattice with high transmissivity behaves similarly to an ideal pure sinusoidal amplitude lattice, whereas the atomic phase lattices capable of producing phase excursion across a weak probe beam along with high transmissivity remains equally ideal. Moreover, we identify that the quality of Talbot imaging about a phase lattice is greatly improved when compared with an amplitude lattice. Such an atomic lattice could find applications in all-optical switching at the few photons level and paves the way for imaging ultracold atoms or molecules both in the near-field and in the far-field with a nondestructive and lensless approach.
(050.0050) Diffraction and gratings (270.1670) Coherent optical effects (050.5080) Phase shift (070.6760) Talbot and self-imaging effects. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 06000676

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Optics Department, University Complutense of Madrid, Faculty of Optics and Optometry, Av. Arcos de Jalon, 118, 28037 Madrid, Spain
2 Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Minia University, University Campus, 61519 El-Minya, Egypt
A metallic nanostructured array that scatters radiation toward a thin metallic layer generates surface plasmon resonances for normally incident light. The location of the minimum of the spectral reflectivity serves to detect changes in the index of refraction of the medium under analysis. The normal incidence operation eases its integration with optical fibers. The geometry of the arrangement and the material selection are changed to optimize some performance parameters as sensitivity, figure of merit, field enhancement, and spectral width. This optimization takes into account the feasibility of the fabrication. The evaluated results of sensitivity (1020 nm/RIU) and figure of merit (614 RIU?1) are competitive with those previously reported.
(130.6010) Sensors (240.6680) Surface plasmons (280.4788) Optical sensing and sensors (050.0050) Diffraction and gratings (290.0290) Scattering (230.0230) Optical devices. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 06000654
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Opto-Electronic Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 Laboratory of Optical Physics, Institute of Physics and Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
3 Quantum Engineering Research Center, Beijing Institute of Aerospace Control Devices, China Aerospace, Beijing 100094, China
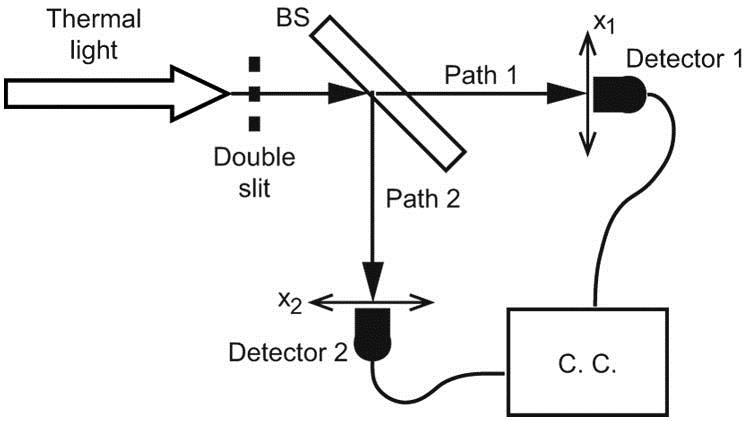
Ghost imaging and diffraction, inspired by the Hanbury Brown and Twiss effect, have potential in both classical and quantum optics regimes on account of their nonlocal characteristics and subwavelength resolution capability, and therefore have aroused particular interest. By extending the correspondence imaging scheme, we utilize the positive and negative intensity correlations in diffraction and perform subwavelength diffraction with pseudo-thermal light. In the experiment, a subwavelength (λ/2) resolution and a better signal-to-noise ratio (10.3% improvement) are simultaneously achieved. The scheme can be utilized as a complement to the existing ghost imaging scheme to improve image quality.
030.0030 Coherence and statistical optics 030.4280 Noise in imaging systems 050.0050 Diffraction and gratings 110.1650 Coherence imaging 110.6150 Speckle imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(4): 040301

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Physics, Optoelectronics and Energy, Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
2 Key Lab of Advanced Optical Manufacturing Technologies of Jiangsu Province and Key Lab of Modern Optical Technologies of Education Ministry of China, Suzhou 215006, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
A method for beam diffraction sidelobe suppression based on the combination of volume Bragg gratings (VBGs) with different thicknesses or periods for angular filtering is proposed and performed. Simulated and experimental results show that the beam diffraction sidelobe is reduced from 12% to less than 1% with the non-sidelobe angular filter. The non-sidelobe angular filtering based on VBGs with thicknesses of 2.5 and 2.9 mm is simulated and demonstrated. The near-field distribution of filtered beams through the non-sidelobe angular filter is obviously smoother than that of the single VBG. The near-field modulation and contrast ratio (C) of filtered beams are found to be improved 1.17 and 1.66 times that of the single VBG. The far-field C of the filtered beam is improved to about 100∶1 and the power spectral density analysis shows that the cutoff frequency of the angular filter is greatly optimized with the VBG combination.
050.0050 Diffraction and gratings 090.0090 Holography Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(6): 060502





