Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Photonic Chips, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
2 Centre for Artificial-Intelligence Nanophotonics, School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
3 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, and College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
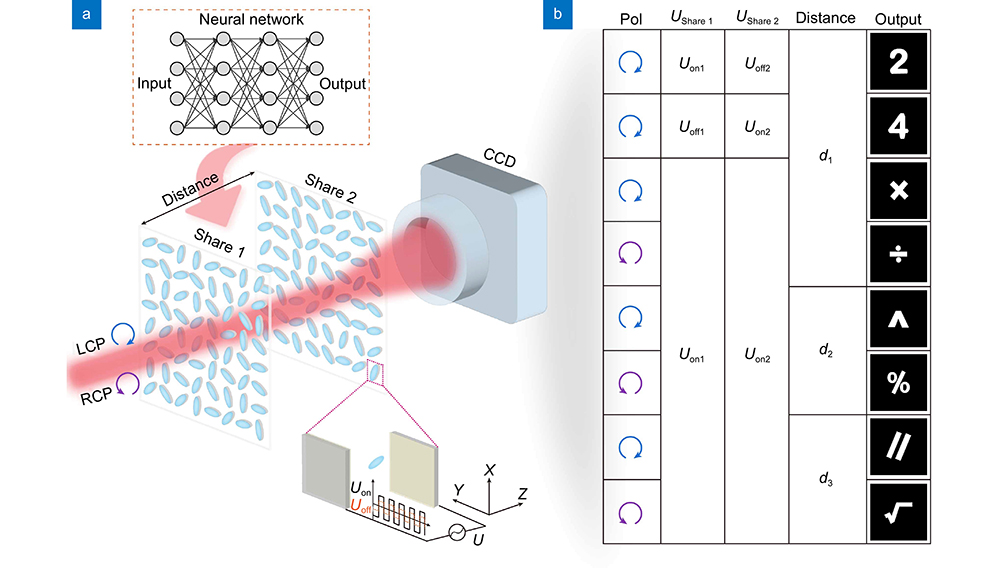
Secret sharing is a promising technology for information encryption by splitting the secret information into different shares. However, the traditional scheme suffers from information leakage in decryption process since the amount of available information channels is limited. Herein, we propose and demonstrate an optical secret sharing framework based on the multi-dimensional multiplexing liquid crystal (LC) holograms. The LC holograms are used as spatially separated shares to carry secret images. The polarization of the incident light and the distance between different shares are served as secret keys, which can significantly improve the information security and capacity. Besides, the decryption condition is also restricted by the applied external voltage due to the variant diffraction efficiency, which further increases the information security. In implementation, an artificial neural network (ANN) model is developed to carefully design the phase distribution of each LC hologram. With the advantage of high security, high capacity and simple configuration, our optical secret sharing framework has great potentials in optical encryption and dynamic holographic display.
holographic encryption optical secret sharing cascaded liquid crystal hologram multi-dimensional multiplexing Opto-Electronic Advances
2024, 7(1): 230121
1 北京电子科技学院网络空间安全系, 北京 100070
2 中国科学技术大学, 安徽 合肥 230026
针对现有量子密封拍卖协议中存在的报价隐私保护不够、恶意竞标者与第三方共谋等问题,提出了一种基于半量子安全直接通信的量子密封投标拍卖协议。该协议采用半量子安全直接通信,通信时拍卖方仅需拥有测量和反射粒子的能力;通过对投标方报价的保序加密,实现对报价的隐私保护;利用隐私比较,在无第三方参与的情况下,拍卖方也能比较保序加密后的报价信息。理论分析表明面对截获-重发、受控非门 (CNOT)、相位反转、共谋等攻击时,所提出协议仍具有较高的安全性,且与同类型量子拍卖协议相比,新协议通信效率不受投标人数的影响。
量子信息 量子拍卖 量子密封投标拍卖 半量子 保序加密 隐私比较 quantum information quantum auction quantum sealed-bid auction semi-quantum order preserving encryption private comparison
天津理工大学理学院天津市量子光学与智能光子学重点实验室,天津 300384
为了满足信息化时代对信息加密安全性的要求,提出一种基于激光诱导击穿光谱(LIBS)技术的信息安全加密方法。使用常用的葡萄糖酸锌片和去离子水配制的水溶液在白纸上书写需要加密的信息,通过分析白纸和涂抹葡萄糖酸锌水溶液的白纸的LIBS光谱,发现Zn I在328.23 nm、472.22 nm和481.05 nm处的光谱线可以解读加密信息。通过扫描获得载有加密信息的白纸上不同位置处的LIBS光谱,并进一步通过去除基线、归一化和光谱叠加提高光谱强度空间分布的对比度,使得加密信息较清晰完整地被解读出来。实验结果表明,该方法通过生活中常用的葡萄糖酸锌片,实现了高效隐藏信息提取,具有安全性高、成本低和制作便捷等优点,为LIBS在信息加密领域提供了新思路,具有一定的潜在应用价值。
光谱学 激光诱导击穿光谱 加密 葡萄糖酸锌 基线校正 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(5): 0530002

Xilin Yang 1,2,3†Md Sadman Sakib Rahman 1,2,3Bijie Bai 1,2,3Jingxi Li 1,2,3Aydogan Ozcan 1,2,3,*
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 University of California, Los Angeles, Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Los Angeles, California, United States
2 University of California, Los Angeles, Bioengineering Department, Los Angeles, California, United States
3 University of California, Los Angeles, California NanoSystems Institute (CNSI), Los Angeles, California, United States
As an optical processor, a diffractive deep neural network (D2NN) utilizes engineered diffractive surfaces designed through machine learning to perform all-optical information processing, completing its tasks at the speed of light propagation through thin optical layers. With sufficient degrees of freedom, D2NNs can perform arbitrary complex-valued linear transformations using spatially coherent light. Similarly, D2NNs can also perform arbitrary linear intensity transformations with spatially incoherent illumination; however, under spatially incoherent light, these transformations are nonnegative, acting on diffraction-limited optical intensity patterns at the input field of view. Here, we expand the use of spatially incoherent D2NNs to complex-valued information processing for executing arbitrary complex-valued linear transformations using spatially incoherent light. Through simulations, we show that as the number of optimized diffractive features increases beyond a threshold dictated by the multiplication of the input and output space-bandwidth products, a spatially incoherent diffractive visual processor can approximate any complex-valued linear transformation and be used for all-optical image encryption using incoherent illumination. The findings are important for the all-optical processing of information under natural light using various forms of diffractive surface-based optical processors.
optical computing optical networks machine learning diffractive optical networks diffractive neural networks image encryption Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(1): 016010

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shenzhen University, Institute of Microscale Optoelectronics, Nanophotonics Research Centre, State Key Laboratory of Radio Frequency Heterogeneous Integration, Shenzhen, China
2 Research Institute of Intelligent Sensing, Research Center for Humanoid Sensing, Zhejiang Lab, Hangzhou, China
The use of orbital angular momentum (OAM) as an independent dimension for information encryption has garnered considerable attention. However, the multiplexing capacity of OAM is limited, and there is a need for additional dimensions to enhance storage capabilities. We propose and implement orbital angular momentum lattice (OAML) multiplexed holography. The vortex lattice (VL) beam comprises three adjustable parameters: the rotation angle of the VL, the angle between the wave normal and the z axis, which determines the VL’s dimensions, and the topological charge. Both the rotation angle and the VL’s dimensions serve as supplementary encrypted dimensions, contributing azimuthally and radially, respectively. We investigate the mode selectivity of OAML and focus on the aforementioned parameters. Through experimental validation, we demonstrate the practical feasibility of OAML multiplexed holography across multiple dimensions. This groundbreaking development reveals new possibilities for the advancement of practical information encryption systems.
orbital angular momentum lattice multiplexed holography vortex lattice beam information encryption Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(1): 016005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Key Laboratory of Intelligent Optical Sensing and Manipulation, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, and College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
2 School of Instrumentation and Optoelectronic Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
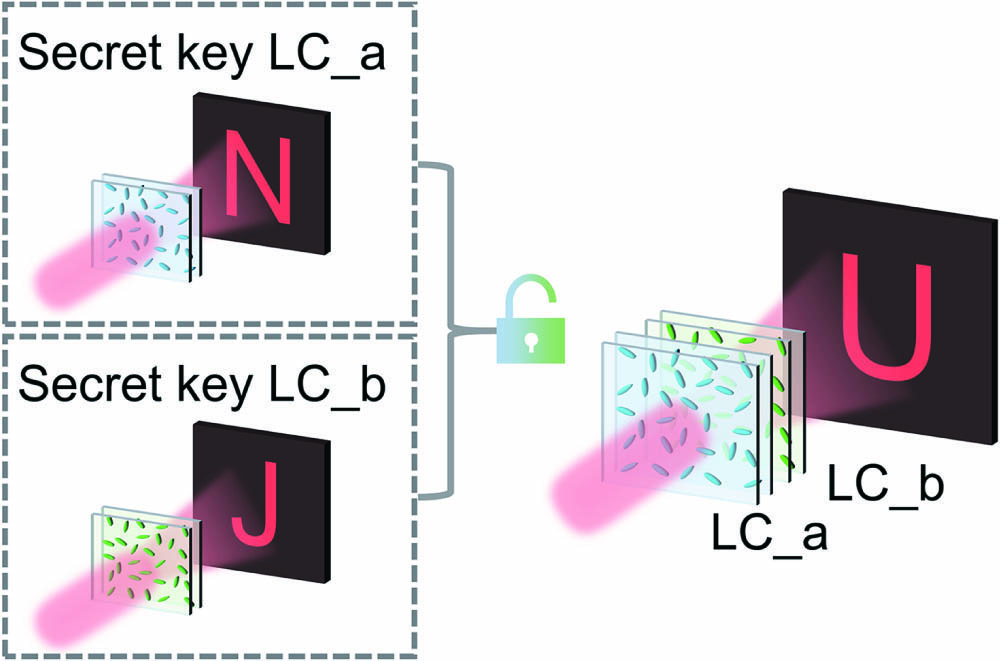
Cascaded holography coupled with the secret-sharing scheme has recently gained considerable attention due to its enhanced information processing and encryption capabilities. Here, we propose a new holographic iterative algorithm and present the implementation of cascaded liquid crystal (LC) holography for optical encryption. Each LC layer acts as the secret key and can generate a distinct holographic image. By cascading two LC elements, a new holographic image is formed. Additionally, we showcase the dynamic optical encryption achieved by electrically switching LCs with combined electric keys. This work may offer promising applications in optical cryptography, all-optical computing, and data storage.
liquid crystals holography optical encryption Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(12): 120003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shandong Provincial Engineering and Technical Center of Light Manipulations & Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
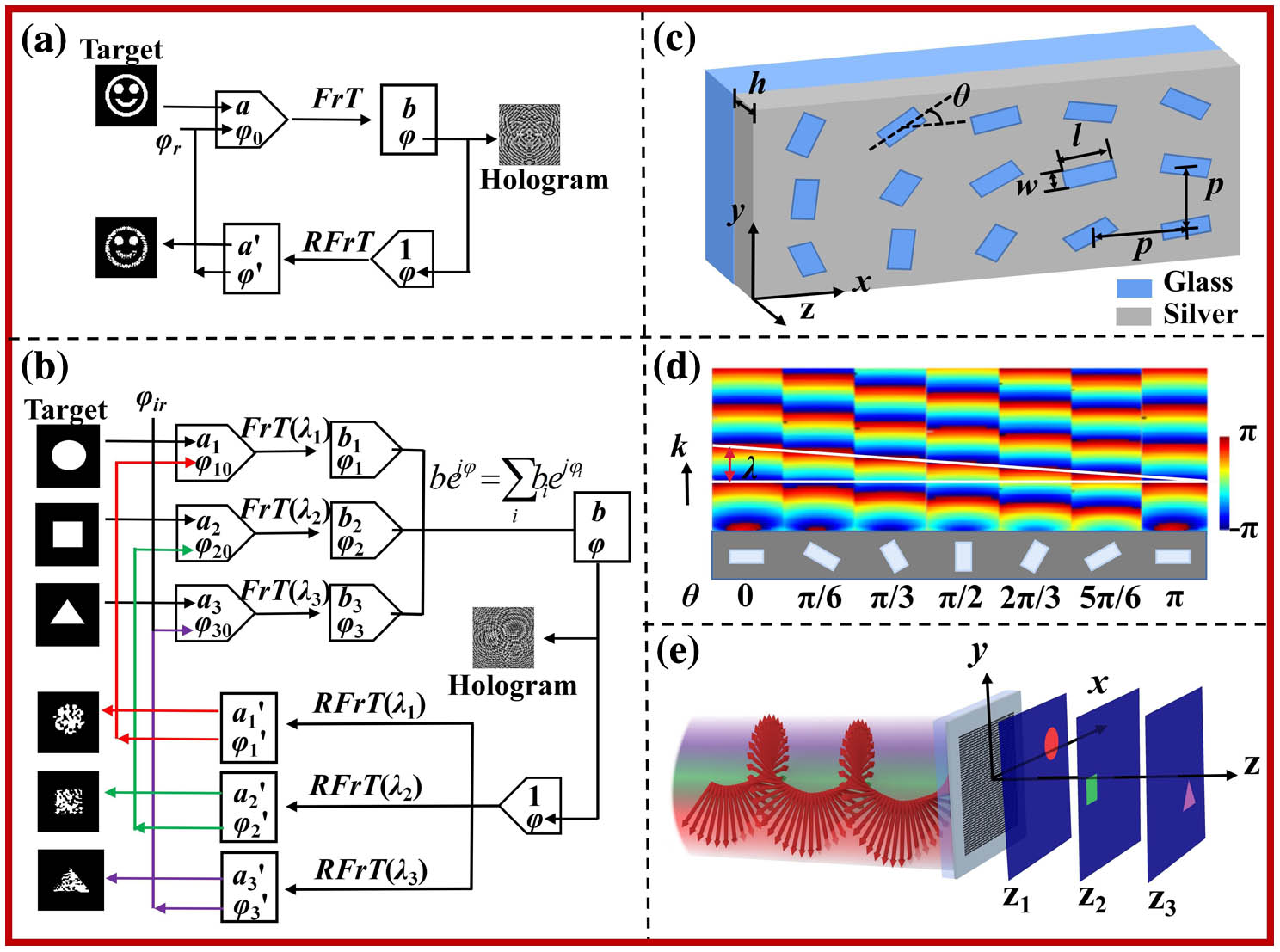
In light of the powerful light manipulation ability of holographic metasurfaces, optical imaging with wavelength multiplexing and polarization multiplexing is performed in this paper. The metasurface is composed of identical rectangular nanoholes etched in silver film. Three imaging effects, including the in-plane color imaging, three-dimensional wavelength-encrypted imaging, and polarization-multiplexing wavelength-encrypted imaging, are realized. The designed metasurface has compact structure, and the obtained image has lower noise. The simulation and experiment results give the verification. Multiple images, including spatial multiplexing, wavelength multiplexing, and polarization multiplexing, exhibit immense potentialities of metasurfaces, and this work is helpful for expanding the applications of metasurfaces.
metasurface holography optical encryption color imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 100501
1 重庆邮电大学通信与信息工程学院,重庆 400065
2 东北大学计算机科学与工程学院,辽宁 沈阳 110819
为了实现直接检测(DD)光正交频分复用(OOFDM)系统安全可靠通信,在发送端利用混沌加密技术来提高DD-OOFDM系统的安全性,在接收端采用Kramers-Kronig(KK)接收机来解决OFDM信号子载波拍频干扰的问题。利用混沌加密前后的图像像素值分布对系统的安全性进行分析验证。此外,分析了KK接收机的结构和其实现的条件,仿真测试了基于混沌加密和KK接收机的DD-OOFDM系统的误码率性能。
直接检测 光正交频分复用 子载波拍频干扰 混沌加密 Kramers-Kronig接收机 光学学报
2023, 43(19): 1906004
暨南大学光子技术研究院广东省光纤与通信技术重点实验室,广东 广州 511443
超表面在光偏振调控方面具有卓越的能力,利用超表面结构的偏振控制实现信息编码与加密成为一种新兴的光学编码技术。本文旨在介绍超表面偏振光学及其在信息加密领域的最新进展。首先介绍对光束偏振态进行整体调控的各类超表面偏振光学元件,包括超表面波片、偏振器和偏振分束器,强调了超表面在偏振操控方面的卓越性能;接着深入介绍基于不同微型超表面偏振光学元件进行的像素化偏振信息编码,包括对近场偏振态空间分布进行逐点编码的马吕斯超表面,以及对远场偏振态进行空间编码的偏振全息和矢量全息超表面;然后阐述近场与远场像素化偏振空间编码超表面在信息隐藏与加密领域的应用示范;最后进行简要总结,并展望超表面偏振信息编码技术的未来发展趋势与应用潜力。
表面光学 偏振调控 超表面偏振光学元件 马吕斯超表面 矢量全息 信息加密 中国激光
2023, 50(18): 1813010
1 福建师范大学光电与信息工程学院医学光电科学与技术教育部重点实验室,福建 福州 350117
2 福建师范大学光电与信息工程学院福建省光子技术重点实验室,福建 福州 350117
通过调制具有不同编码单元的参考光,对信息光进行分页式加密存储。提出两种参考光编码加密模式,即扇形参考光编码模式和随机位置参考光编码模式,并对这两种方法进行验证。实验结果表明,这两种方式都通过正交相位编码完成加密解密的过程。对两种方法的加密性进行评估,不同密钥对应的加密信息之间的相似度均值分别为0.57和0.02,均方误差的平均值分别为537和1872。随机位置参考光编码模式下的同轴系统安全性更高。正交相位加密技术可以有效地防止存储数据被非法访问和窃取,保证了数据的安全性。
全息 全息数据存储 同轴系统 正交相位 加密 中国激光
2023, 50(18): 1813017





