Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Radio Frequency Heterogeneous Integration (Shenzhen University), Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Guangdong Province & Ministry of Education, College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
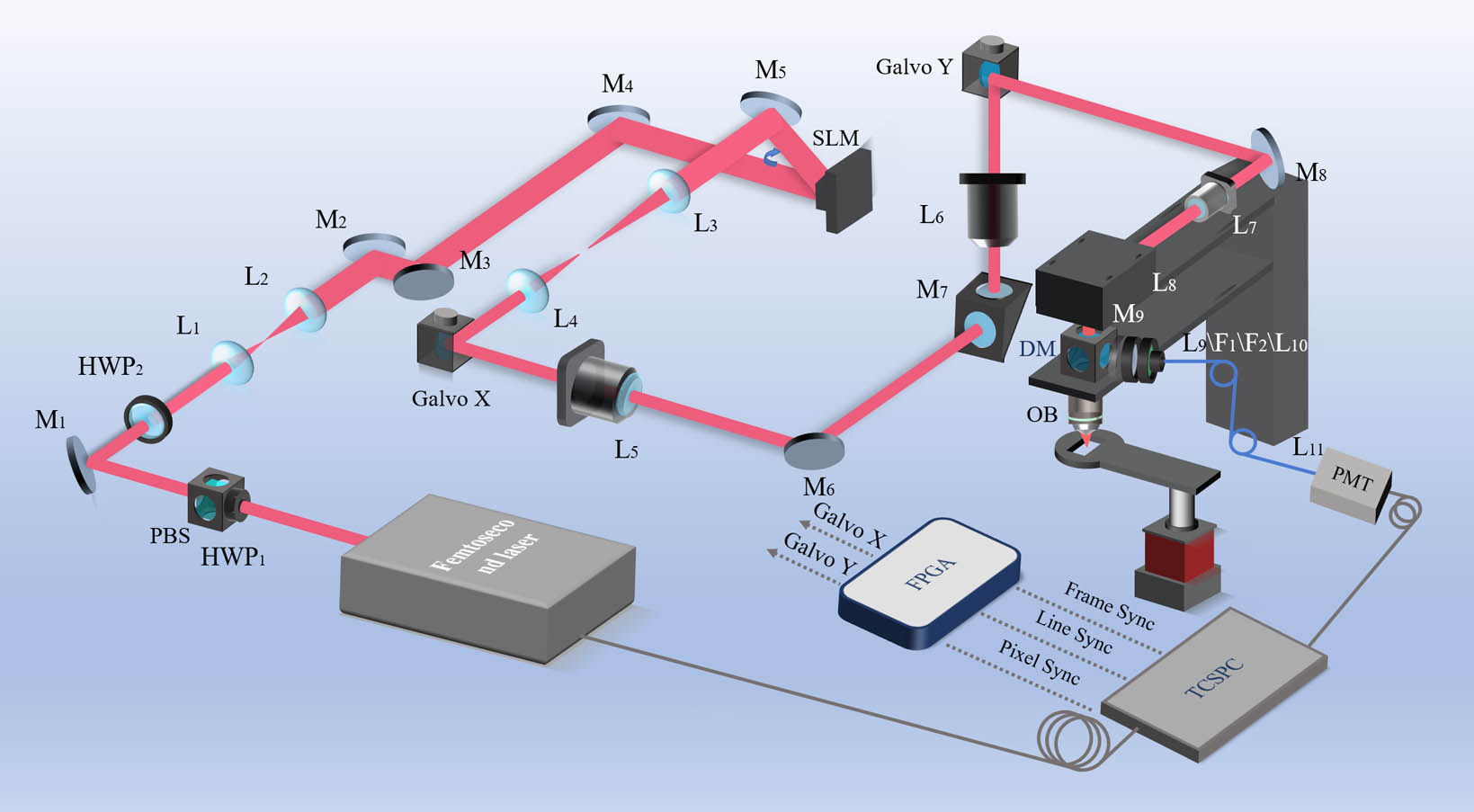
Fluorescence lifetime imaging can reveal the high-resolution structure of various biophysical and chemical parameters in a microenvironment quantitatively. However, the depth of imaging is generally limited to hundreds of micrometers due to aberration and light scattering in biological tissues. This paper introduces an iterative multi-photon adaptive compensation technique (IMPACT) into a two-photon fluorescence lifetime microscopy system to successfully overcome aberrations and multiple scattering problems in deep tissues. It shows that 400 correction modes can be achieved within 5 min, which was mainly limited by the frame rate of a spatial light modulator. This system was used for high-resolution imaging of mice brain tissue and live zebrafish, further verifying its superior performance in imaging quality and photon accumulation speed.
adaptive optics iterative optimization two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy wavefront correction Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 041702
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院,光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室,广东 深圳 518060
荧光寿命显微成像(FLIM)已经广泛应用于生命科学研究领域,具有高灵敏和高特异性的特点,在对组织微环境进行定量表征方面具有独特优势,但由于成像速度相对较慢,限制了FLIM的活体应用。近年来,随着光电子器件和人工智能等技术的发展,开启了FLIM活体成像新篇章。介绍通过优化硬件和算法两方面提升时域和频域FLIM技术的成像速度,以及其在生物医学基础研究和临床疾病诊断中的应用研究进展。最后,对活体FLIM成像的未来发展进行展望。
荧光寿命显微成像 人工智能 活体成像 癌症诊断 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(6): 0618005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentations, Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, College of Optical, Science and Engineering, International Research Center for Advanced Photonics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, P. R. China
2 Dr. Li Dak Sum & Yip Yio Chin Center for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, P. R. China
3 College of Biomedical Engineering and Instrument Science, Interdisciplinary Institute of Neuroscience and Technology (ZIINT), Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, P. R. China
Fluorescence imaging in the second near-infrared window (NIR-II, 900–1880nm) with less scattering background in biological tissues has been combined with the confocal microscopic system for achieving deep in vivo imaging with high spatial resolution. However, the traditional NIR-II fluorescence confocal microscope with separate excitation focus and detection pinhole makes it possess low confocal efficiency, as well as difficultly to adjust. Two types of upgraded NIR-II fluorescence confocal microscopes, sharing the same pinhole by excitation and emission focus, leading to higher confocal efficiency, are built in this work. One type is fiber-pinhole-based confocal microscope applicable to CW laser excitation. It is constructed for fluorescence intensity imaging with large depth, high stabilization and low cost, which could replace multiphoton fluorescence microscopy in some applications (e.g., cerebrovascular and hepatocellular imaging). The other type is air-pinhole-based confocal microscope applicable to femtosecond (fs) laser excitation. It can be employed not only for NIR-II fluorescence intensity imaging, but also for multi-channel fluorescence lifetime imaging to recognize different structures with similar fluorescence spectrum. Moreover, it can be facilely combined with multiphoton fluorescence microscopy. A single fs pulsed laser is utilized to achieve up-conversion (visible multiphoton fluorescence) and down-conversion (NIR-II one-photon fluorescence) excitation simultaneously, extending imaging spectral channels, and thus facilitates multi-structure and multi-functional observation.
Self-confocal fiber-pinhole air-pinhole multi-channel fluorescence lifetime imaging multi-color imaging Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2024, 17(1): 2350025
1 赋同量子科技(浙江)有限公司,浙江 嘉兴 314100
2 集成电路材料全国重点实验室,中国科学院上海微系统与信息技术研究所,上海 200050
自2001年被发明以来,超导纳米线单光子探测器(SNSPD)迅速成长为近红外波段的明星光子探测器,其在近红外波段如1550 nm处系统探测效率超过95%,暗计数率低于1 cps(counts per second),时间抖动优于10 ps,探测速率高于1 GHz,并广泛应用在量子信息领域。近年来,研究人员开始将SNSPD引入到生物领域,以替代在近红外波段具有低信噪比、多后脉冲的半导体单光子探测器。本文将介绍SNSPD的探测原理和性能指标,并系统地阐述SNSPD在生物领域中的应用现状和发展前景。
超导纳米线单光子探测器 共聚焦显微镜 单线态氧检测 漫反射光谱 荧光寿命成像 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(1): 0104002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Guangdong, Province & Ministry of Education, College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, P. R. China
Apoptosis is very important for the maintenance of cellular homeostasis and is closely related to the occurrence and treatment of many diseases. Mitochondria in cells play a crucial role in programmed cell death and redox processes. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD(P)H) is the primary producer of energy in mitochondria, changing NAD(P)H can directly reflect the physiological state of mitochondria. Therefore, NAD(P)H can be used to evaluate metabolic response. In this paper, we propose a noninvasive detection method that uses two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (TP-FLIM) to characterize apoptosis by observing the binding kinetics of cellular endogenous NAD(P)H. The result shows that the average fluorescence lifetime of NAD(P)H and the fluorescence lifetime of protein-bound NAD(P)H will be affected by the changing pH, serum content, and oxygen concentration in the cell culture environment, and by the treatment with reagents such as H2O2 and paclitaxel. Taxol (PTX). This noninvasive detection method realized the dynamic detection of cellular endogenous substances and the assessment of apoptosis.
Apoptosis nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging microscop microenvironment Hep G2 Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2022, 15(3): 2250014
1 复旦大学工程与应用技术研究院生物医学工程技术研究所,上海 200433
2 复旦大学信息科学与工程学院光科学与工程系,上海 200433
酿酒酵母是最具有吸引力的微生物之一,监测其在不同生长时期的新陈代谢状态变化对基础生物学和工业研究都具有重要意义。依据酵母的生成曲线规律培养了不同时间的酵母细胞,基于荧光寿命显微成像(FLIM)进行自体荧光寿命图像的采集,并提出了一种基于机器学习的自动分析方法,可无标记快速鉴别年轻和衰老的酵母细胞。首先,采用深度监督U-Net实现酵母细胞的自动分割;然后,提取每个酵母细胞的荧光寿命特征和形态特征;最后,采用无监督聚类方法实现分类。实验结果表明,酵母的衰老伴随着新陈代谢的变化。FLIM作为一种无标记成像技术可应用于酵母细胞的代谢分析中,结合自动化分析流程可快速准确地区分具有不同代谢差异的细胞,为后续单细胞的筛选奠定了基础。
激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(6): 0617019
光子学报
2021, 50(10): 1017001
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院 光电器件与系统重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518000
有机-无机卤化铅钙钛矿多晶薄膜太阳能电池在近几年的研究中实现了光电转换效率的快速增长。然而,其多晶结构的活性层导致器件仍然遭受到表面和晶界位置缺陷引起的性能衰减。本研究借助两种有机氢碘酸盐,即苯乙基碘化胺(Phenethylammonium iodide,PEAI)和邻氟苯乙胺碘(2-Fluorophenylethylammonium iodide,o-F-PEAI),在CH3NH3PbI3钙钛矿多晶薄膜表面形成钝化层。扫描电子显微镜和原子力显微镜分析结果显示,PEAI和o-F-PEAI处理后的钙钛矿薄膜晶界被钝化层明显填充,表面粗糙度也显著下降。另外,荧光寿命成像分析结果显示钝化后的钙钛矿薄膜具有更多的光子数和更长的荧光寿命。上述结果表明,PEAI和o-F-PEAI诱导的钝化层可以有效抑制多晶薄膜表面和晶界位置的缺陷复合行为。因此,钝化后的倒置结构钙钛矿太阳能电池器件功率转换效率(Power conversion efficiency,PCE)可以达到21%。此外,o-F-PEAI钝化处理后的器件由于氟离子的作用表现出更好的器件稳定性。
荧光寿命显微成像 倒置钙钛矿太阳能电池 表面钝化 fluorescence-lifetime imaging microscopy inverted perovskite solar cell surface passivation PEAI PEAI o-F-PEAI o-F-PEAI
1 深圳大学生命与海洋科学学院, 广东省植物表观遗传学重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
2 深圳大学龙华生物产业创新研究院, 广东 深圳 518060
3 深圳大学物理与光电工程学院, 广东 深圳 518060
细胞是动植物结构和生命活动的基本单位。 细胞过程的一个重要特点就是其生化组分在时空调控上的相互作用关系。 然而, 利用传统的生化方法(如酵母双杂交系统、 pull-down系统等)很难在空间上评估活细胞内分子间的相互作用。 光学技术的快速发展, 为研究活细胞中生物分子的时空动态提供了新的遗传研究工具, 其中荧光共振能量转移-荧光寿命显微成像(FRET-FLIM)技术在实时探测分析活细胞中生物大分子构象变化和分子间动态相互作用过程具有独特的优势, 如: 实现对活细胞的实时“可视化”研究, 同时具有高时空分辨率; 检测更加灵敏、 结果可信度高; 且基于简易的数学运算完成简单快捷的分析程序。 介绍FRET-FLIM技术的理论背景知识, 对比了该技术与传统蛋白相互作用技术研究的利弊, 同时归纳了其在蛋白相互作用、 细胞生物学和疾病诊断等方面的最新应用研究进展, 最后总结和讨论了FRET-FLIM技术的未来发展趋势, 以期能够为揭示活细胞的结构和细胞过程相关研究提供新的见解。
荧光共振能量转移 荧光寿命显微成像 蛋白相互作用 疾病诊断 Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) Protein interaction Disease diagnosis 光谱学与光谱分析
2021, 41(4): 1023





