中国人民解放军63870部队,陕西渭南714299
在可见光红外跟踪(RGB and Thermal Infrared Tracking,RGB-T)的研究中,为了在常规跟踪算法的基础上实现两个模态的有效融合,基于注意力机制提出了一种基于注意力交互的RGB-T跟踪算法。该算法引入注意力机制对可见光和红外两种模态的图像特征进行增强和融合,设计了自特征增强编码器对单一模态的特征进行增强,设计了互特征解码器对两个模态增强后的特征进行交互融合。编码器和解码器均采用两层注意力模块。为了减小算法模型的复杂度,对传统注意力模块进行简化,将全连接层改为1
![]()
![]()
1卷积。此外,该算法对多个卷积层的特征均进行分层融合,以充分挖掘各层卷积特征中的细节和语义信息。在GTOT,RGBT234和LasHeR三个数据集上进行对比测试。实验结果表明,所提算法性能优异,特别是在RGBT234和LasHeR这两个大规模数据集上取得了最优的跟踪结果,验证了注意力机制在RGB-T跟踪中的有效性。
1 北京理工大学光电学院,北京 100081
2 北京理工大学光电成像技术与系统教育部重点实验室,北京 100081
3 北京理工大学重庆创新中心,重庆 401135
近年来,随着深度传感器和三维激光扫描设备的普及,点云数据引起了广泛关注。相对于二维图像,点云数据不仅包含场景的深度信息,还不受光照等环境因素的影响,能够更精确地实现目标识别和三维定位。因此,基于点云的三维目标检测技术已经成为智能空间感知和场景理解的关键技术。本文首先介绍了点云数据的特点,并探讨了不同类型的点云特征提取方法;其次,详细阐述了基于体素、点、图以及体素与点混合的点云目标检测方法的原理和发展历程;然后,介绍了常见的室内外点云目标检测数据集和评价指标,并对各类点云目标检测方法在KITTI和Waymo数据集上的性能进行了详细的比较和分析;最后,对点云目标检测技术的研究进展进行了总结和展望。
点云 三维目标检测 单模态 多模态 光学学报
2023, 43(15): 1515001
广东工业大学 信息工程学院, 广东 广州 510006
为了增加融合图像的信息量, 结合非下采样剪切波变换(Non-Subsampled Shearlet Transform, NSST)和离散小波变换(Discrete Wavelet Transform, DWT)的互补优势, 提出了改进的多模态图像融合方法。采用NSST对两幅源图像进行多尺度、多方向的分解, 得到相应的高频子带和低频子带; 利用DWT将低频子带进一步分解为低频能量子带和低频细节子带, 并利用最大值选择规则融合能量子带; 采用改进连接强度的自适应脉冲耦合神经网络(Improved Connection Strength Adaptive Pulse Coupled Neural Network, ICSAPCNN)分别融合细节子带和高频子带, 并对能量子带和细节子带进行DWT逆变换, 得到融合的低频子带; 采用NSST逆变换重构出细节信息丰富的融合图像。实验证明, 提出的算法在主观视觉和客观评价方面均优于其他几种算法, 且能同时适用于红外与可见光源图像、医学源图像的融合。
多模态图像 图像融合 离散小波变换 自适应脉冲耦合神经网络 非下采样剪切波变换 multi-modality images, image fusion, discrete wave
1 清华大学深圳国际研究生院, 广东 深圳 518055
2 广东省偏振光学检测与成像工程技术研究中心, 广东 深圳 518055
海洋中各种微小颗粒物无处不在,它们与海洋物理过程、化学过程、生物和地质沉积等几乎都有关联,尤其在海洋碳循环中起着不可忽视的作用。但长期以来人们对海洋颗粒物的原位观测技术,以及对观测数据的细致分类仍不能满足需求。偏振光散射测量对散射颗粒的粒径、形态和亚细胞层次的微观结构特征十分敏感,测量结果可用于对复杂的海洋颗粒物结构特征甚至海洋生物的生理状态进行定量表征和细致分类。实现偏振光散射的原位动态监测已经在海洋环境监测领域展示出诱人的应用潜力。简单介绍海洋颗粒物的检测方法,重点介绍基于偏振光散射的颗粒物细致分类方法和初步应用,并对其未来的发展方向进行展望。
散射 偏振光 海洋颗粒物 细致分类 复合测量 海洋碳循环
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Namal Institute, Mianwali 42250, Pakistan
2 National University of Sciences & Technology (NUST), Islamabad 44000, Pakistan
3 Univ de Toulouse, INP, LAAS-CNRS, Toulouse F-31400, France
4 University of Engineering & Technology, Taxila 47080, Pakistan
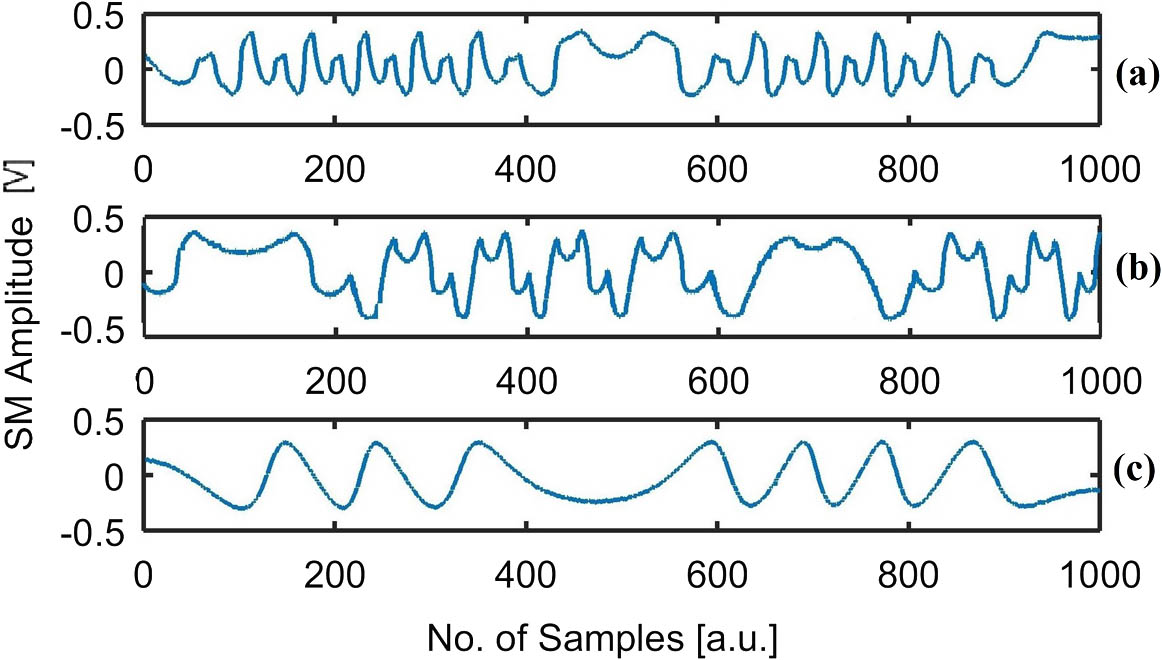
Self-mixing interferometry (SMI) is an attractive sensing scheme that typically relies on mono-modal operation of an employed laser diode. However, change in laser modality can occur due to change in operating conditions. So, detection of occurrence of multi-modality in SMI signals is necessary to avoid erroneous metric measurements. Typically, processing of multi-modal SMI signals is a difficult task due to the diverse and complex nature of such signals. However, the proposed techniques can significantly ease this task by identifying the modal state of SMI signals with 100% success rate so that interferometric fringes can be correctly interpreted for metric sensing applications.
self-mixing interferometry laser diode multi-modality optical feedback Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(1): 011201
华东师范大学化学与分子工程学院 上海市绿色化学与化工过程绿色化重点实验室, 上海 200062
上转换发光纳米颗粒是一类遵循反斯托克斯原理的新型发光材料, 具有发光强度高、发光稳定、无组织背景荧光、无光漂白、低毒性以及较好的生物相容性等优点, 其激发光为红外或者近红外光, 活体组织穿透深度高, 在生物医学检测、诊断以及疾病治疗等方面均具有潜在的应用价值。磁共振成像是目前医学临床常用的影像检测手段之一, 具有软组织成像质量高、空间分辨率高、无辐射、无损伤等优点, 在心脑血管、肿瘤等疾病的影像诊断方面具有重要作用。本文将聚焦于近年来稀土上转换发光纳米材料在磁共振影像方面的研究进展, 通过介绍磁共振成像机理、磁共振造影剂的构建、上转换发光纳米材料的设计及在磁共振医学影像、疾病治疗等方面的应用, 并结合我们课题组基于UCNP医学磁共振多模态影像的相关研究进展, 对上转换发光纳米颗粒在磁共振成像方面的应用研究进行探讨和展望。
上转换发光纳米颗粒 磁共振成像 多模态影像 疾病治疗 upconversion nanoparticle magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) multi-modality imaging disease therapy
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics-Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, P. R. China
2 MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics Department of Biomedical Engineering Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wuhan 430074, P. R. China
3 Campbell Family Cancer Research Institute and Ontario Cancer Institute University Health Network, Toronto, P. R. Canada
The development of experimental animal models for head and neck tumors generally rely on the bioluminescence imaging to achieve the dynamic monitoring of the tumor growth and metastasis due to the complicated anatomical structures. Since the bioluminescence imaging is largely affected by the intracellular luciferase expression level and external D-luciferin concentrations, its imaging accuracy requires further confirmation. Here, a new triple fusion reporter gene, which consists of a herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase (TK) gene for radioactive imaging, a far-red fluorescent protein (mLumin) gene for fluorescent imaging, and a firefly luciferase gene for bioluminescence imaging, was introduced for in vivo observation of the head and neck tumors through multi-modality imaging. Results show that fluorescence and bioluminescence signals from mLumin and luciferase, respectively, were clearly observed in tumor cells, and TK could activate suicide pathway of the cells in the presence of nucleotide analog-ganciclovir (GCV), demonstrating the effectiveness of individual functions of each gene. Moreover, subcutaneous and metastasis animal models for head and neck tumors using the fusion reporter gene-expressing cell lines were established, allowing multi-modality imaging in vivo. Together, the established tumor models of head and neck cancer based on the newly developed triple fusion reporter gene are ideal for monitoring tumor growth, assessing the drug therapeutic efficacy and verifying the effectiveness of new treatments.
Head and neck cancer tumor metastasis model three fusion reporter gene far-red fluorescent protein firefly luciferase multi-modality imaging Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2012, 5(4): 1250028