Author Affiliations
Abstract
CAS Key Laboratory of Wireless-Optical Communications, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230027, China
The received signal intensity fluctuation and communication performance of an underwater optical wireless communication (UOWC) system under the air bubble effects are experimentally investigated. For different bubble density and size, lognormal, gamma, Weibull, and generalized extreme value distributions are tested to fit the fluctuation of the signal intensity at the receiving end. The best fitting distribution is found to vary with bubble parameters. The communication system performance with on–off keying and pulse position modulation is further studied.
060.4510 Optical communications 010.0010 Atmospheric and oceanic optics 270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 100008

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 College of Materials Science and Opto-Electronic Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A high-performance transportable fountain clock is attractive for use in laboratories with high-precision time-frequency measurement requirements. This Letter reports the improvement of the stability of a transportable rubidium-87 fountain clock because of an optimization of temperature characteristics. This clock integrates its physical packaging, optical benches, microwave frequency synthesizers, and electronic controls onto an easily movable wheeled plate. Two optical benches with a high-vibration resistance are realized in this work. No additional adjustment is required after moving them several times. The Allan deviation of the fountain clock frequency was measured by comparing it with that of the hydrogen maser. The fountain clock got a short-term stability of at 1 s and long-term stability on the order of 10 16 at 100,000 s.
020.3320 Laser cooling 120.3940 Metrology 270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise 270.5570 Quantum detectors Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 080201
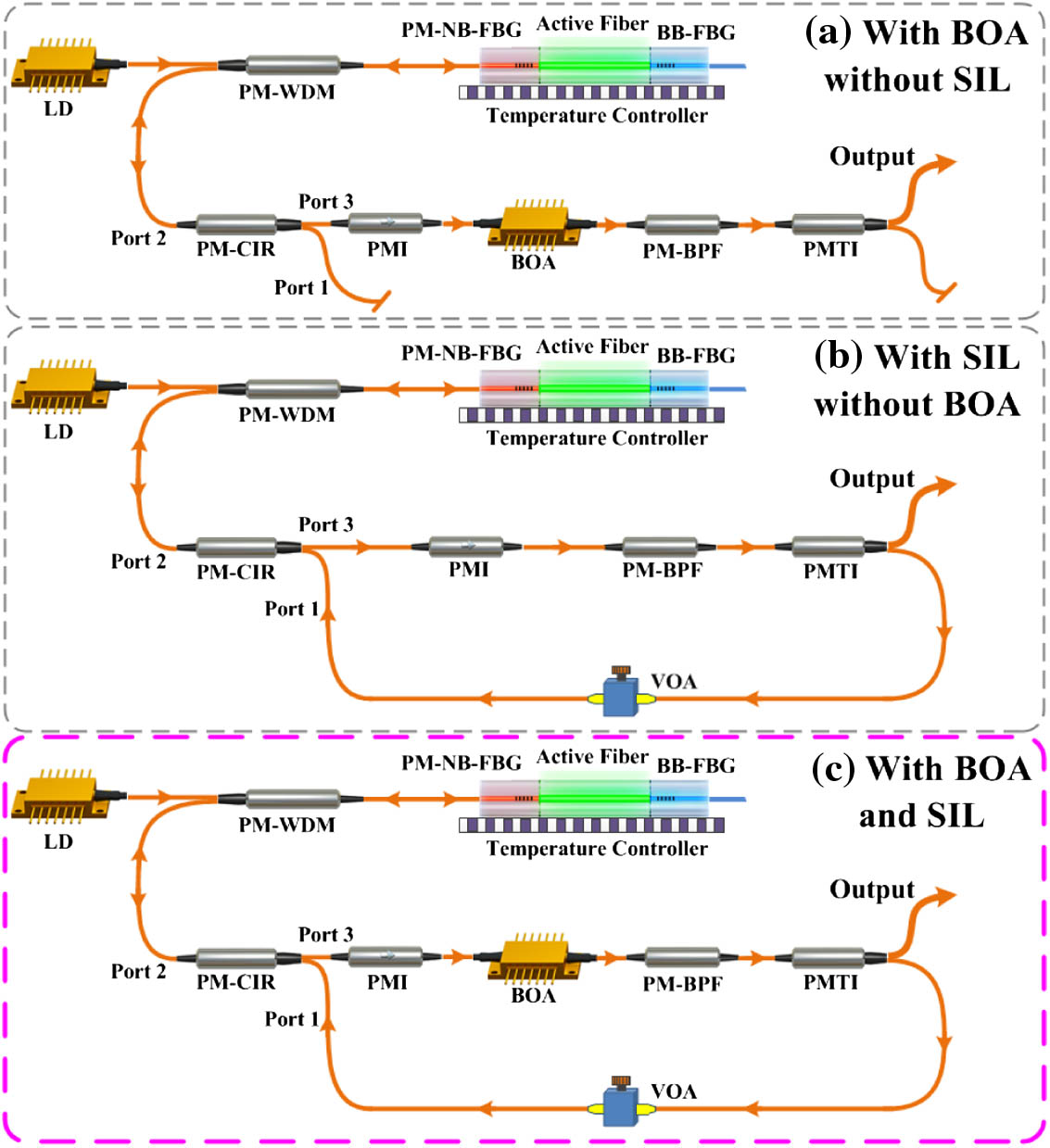
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices and Institute of Optical Communication Materials, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
2 College of Optoelectronic Technology, Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu 610225, China
3 Guangdong Engineering Technology Research and Development Center of High-Performance Fiber Laser Techniques and Equipments, Zhuhai 519031, China
4 Guangdong Engineering Technology Research and Development Center of Special Optical Fiber Materials and Devices, Guangzhou 510640, China
5 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fiber Laser Materials and Applied Techniques, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
A noise-sidebands-free and ultra-low relative intensity noise (RIN) 1.5 μm single-frequency fiber laser is demonstrated for the first time to our best knowledge. Utilizing a self-injection locking framework and a booster optical amplifier, the noise sidebands with relative amplitudes as high as 20 dB are completely suppressed. The RIN is remarkably reduced by more than 64 dB at the relaxation oscillation peak to retain below 150 dB/Hz in a frequency range from 75 kHz to 50 MHz, while the quantum noise limit is 152.9 dB/Hz. Furthermore, a laser linewidth narrower than 600 Hz, a polarization-extinction ratio of more than 23 dB, and an optical signal-to-noise ratio of more than 73 dB are acquired simultaneously. This noise-sidebands-free and ultra-low-RIN single-frequency fiber laser is highly competitive in advanced coherent light detection fields including coherent Doppler wind lidar, high-speed coherent optical communication, and precise absolute distance coherent measurement.
Lasers, fiber Lasers, single-mode Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise Photonics Research
2018, 6(4): 04000326

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, Institute of Semiconductors & Institute of Material Science and Optoelectronic Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
Relative intensity noise (RIN) and high-speed modulation characteristics are investigated for an AlGaInAs/InP hybrid square-rectangular laser (HSRL) with square side length, rectangular length, and width of 15,300, and 2 μm, respectively. Single-mode operation with side-mode suppression larger than 40 dB has been realized for the HSRL over wide variation of the injection currents. In addition, the HSRL exhibits a 3 dB modulation bandwidth of 15.5 GHz, and an RIN nearly approaches standard quantum shot-noise limit 2hv/P= 164 dB/Hz at high bias currents due to the strong mode selection of the square microcavity. With the increase of the DC bias current of the Fabry–Perot section, significantly enhanced modulation bandwidth and decreased RIN are observed. Furthermore, intrinsic parameters such as resonance frequency, damping factor, and modified Schawlow–Townes linewidth are extracted from the noise spectra.
Microcavity devices Semiconductor lasers Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise Photonics Research
2018, 6(3): 03000193
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Laser Polarization and Information Technology, Department of Physics, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, China
2 Department of Physics and Information Engineering, Jining University, Qufu 273155, China
We show how to optimally protect quantum states and freeze coherence under incoherent channels using a quantum weak measurement and quantum measurement reversal. In particular, we present explicit formulas for the conditions for freezing quantum coherence in a given quantum state.
270.1670 Coherent optical effects 270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(5): 052701

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Physics, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
Based on the standard angular momentum theory, we create an experiment on preparing maximally path-entangled (|N,0 +|0,N )2 (NOON) states of triphotons. In order to explain the error between the theoretical and experimental data, we consider the background events during the experiment, and observe their effect on the uncertainty in S^1. Afterwards, we calculate the quantum Fisher information (QFI) of the states to evaluate their potential applications in quantum metrology. Our results show that by adding the appropriate background terms, the theoretical data of the produced states matches well with the experimental data. In this case, the QFI of the states is lower than maximally entangled NOON states, but still higher than a classical state.
270.5585 Quantum information and processing 120.5050 Phase measurement 270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise 000.4430 Numerical approximation and analysis Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(3): 032701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Physics, The University of Burdwan, Burdwan 713104, West Bengal, India
Squeezed state of light explores a new era in noiseless communication and data processing recently breaking the quantum limit of noise. We propose a new mechanism of modulating an amplitude-squeezed signal with the instantaneous intensity variation of a coherent signal. The modulating signal is a coherent light where the amplitude-squeezed light takes the role of a carrier signal.
270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise 270.6570 Squeezed states Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(1): 012702
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Applied Physics, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305, USA
2 Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305, USA
We develop a formulation of few-photon Fock-space waveguide transport that includes dissipation in the form of reservoir coupling. We develop the formalism for the case of a two-level atom and then show that our formalism leads to a simple rule that allows one to obtain the dissipative description of a system from the nondissipative case.
Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise Multiphoton processes Quantum electrodynamics Scattering, particles Quantum information and processing Quantum optics Photonics Research
2013, 1(3): 03000110
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Contrary to expectations, a measurement of the random walk in the ring laser gyro (RLG) as a function of laser power P shows that it is not consistent with the P^{-1/2} rule. In the experiment, the random walk and laser power are tested and recorded at different discharge currents. The random walk decreases with increasing power, but with a rate much less than the theoretical value according to current literature. In order to solve the inconsistency above, we derive the expression for the random walk in RLGs based on laser theory. Theoretical analysis shows that, accumulating effects of lower energy level due to its limited lifetime lead to additional quantum noise from spontaneous emission. Results show that the random walk in the RLGs consists of two components. The former decreases with increasing power according to the P^{-1/2} rule, whereas the other is power-independent. Thus far, the power-independent quantum limit has not appeared in the literature; therefore, the expressions for RLGs should be modified to describe the low-loss RLGs exactly, where the power-independent term takes a relatively larger proportion. The findings are significant to the further reduction of quantum limit in low-loss RLGs.
140.3560 Lasers, ring 140.3370 Laser gyroscopes 270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(6): 061404
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Physics and Information Engineering, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350002, China
The Bell-nonlocality of two initially entangled macroscopic fields in the double Jaynes-Cummings model is investigated. Moreover, the process by which detuning between the atomic transition frequency and the field frequency affects the evolution of the Bell-nonlocality of two macroscopic fields is studied. The effect of the disparity between the two coupling strengths is discussed.
贝尔非定域性 宏观场 失谐量 270.1670 Coherent optical effects 270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(7): 072702





