Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Information Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518000, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences-Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518000, China
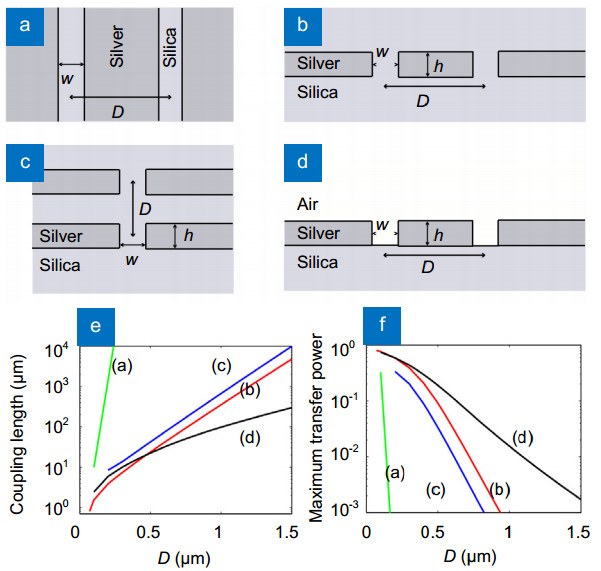
Plasmonic waveguides, as a competitive candidate, have been widely studied in rapid developing photonic integrated circuits (PICs) and optical interconnection fields. However, crosstalk between plasmonic waveguides is a critical issue that has to be considered in practice. Actually, crosstalk dominates the ultimate integration density of the planar photonic circuits. This paper reviews the recent research work on evaluation methods and crosstalk suppression approaches of plasmonic waveguides. Three crosstalk evaluation methods based on comparison of specific parameters of waveguides have been summarized. Furthermore, four specific approaches to reduce crosstalk have been illustrated as two categories according to their impacts on waveguide performances and the whole circuit. One means of crosstalk suppression is changing the placement of waveguides, which could maintain the transmission characteristics of the original waveguide. The other means is inserting medium, which has the advantage of occupying smaller space compared to the first method. Consequently, to suppress crosstalk between plasmonic waveguides, one should choose suitable approach.
crosstalk surface plasmons guided waves photonic integrated circuits optical interconnection Opto-Electronic Advances
2019, 2(4): 180022

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan
2 College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
We studied the near-field properties of localized surface plasmon resonances in finite linear gold nanochains using photoemission electron microscopy (PEEM). The localization of the electromagnetic field in the near-field region was mapped at high spatial resolution. By tuning the excitation laser wavelength, we can obtain the near-field spectra, from which the energy splitting between longitudinal (L) and transverse (T) plasmon modes can be revealed. In particular, the L-mode red shifts and the T-mode blue shifts with increasing chain length. The red shift of the L-mode is highly dependent on the gap distance. In contrast, the T-mode almost remains constant within the range of gap distance we investigated. This energy splitting between the L-mode and the T-mode of metallic chains is in agreement with previous far-field measurements, where it was explained by dipole-dipole near-field coupling. Here, we provide direct proof of this near-field plasmon coupling in nanochains via the above-described near-field measurements using PEEM. In addition, we explore the energy transport along the gold nanochains under excitation at oblique illumination via PEEM measurements together with numerical simulations.
surface plasmon resonance metallic nanochains near-field imaging photoemission electron microscopy Opto-Electronic Advances
2019, 2(4): 180030
