2014, 2(6) Column
Photonics Research 第2卷 第6期
Effect of spatial hole burning on a dual-wavelength mode-locked laser based on compactly combined dual gain media Download:626次
Download:626次
 Download:626次
Download:626次The effect of spatial hole burning (SHB) on dual-wavelength self-mode-locked lasers based on physically combined Nd:YVO4∕Nd:LuVO4 and Nd:YVO4∕Nd:KGW composite active medium is comparatively investigated. The length of the first Nd:YVO4 crystal is optimized to realize a highly compact and efficient TEM00-mode picosecond laser at 1.06 μm with optical conversion efficiency greater than 20%. When the SHB effect is enhanced by decreasing the separation between the input end mirror and the composite gain medium, it is experimentally found that not only the pulse duration monotonically decreases, but also the temporal behavior gradually displays a narrow-peak-on-a-pedestal shape for the Nd:YVO4∕Nd:LuVO4 scheme, while the multipulse operation can be obtained for the Nd:YVO4∕Nd:KGW configuration. These phenomena are further explored by numerically simulating mode-locked pulses from the experimentally measured optical spectra.
Lasers diode-pumped Lasers neodymium Lasers solidstate Mode-locked lasers A blind deconvolution algorithm with modified Tikhonov regularization is introduced. To improve the spectral resolution, spectral structure information is incorporated into regularization by using the adaptive term to distinguish the spectral structure from other regions. The proposed algorithm can effectively suppress Poisson noise as well as preserve the spectral structure and detailed information. Moreover, it becomes more robust with the change of the regularization parameter. Comparative results on simulated and real degraded Raman spectra are reported. The recovered Raman spectra can easily extract the spectral features and interpret the unknown chemical mixture.
Spectroscopy Raman Inverse problems Spectroscopy high-resolution We present a compact Tm-doped fiber laser (TDFL) to generate pulse bursts at 1.92 μm based on phase and intensity modulations. A phase modulator (PM) and an intensity modulator (IM) were included in the linear TDFL cavity to perform the simultaneous active intracavity phase and intensity modulation. Stable pulse bursts have been achieved with tunable repetition rate in the range of 36–44 kHz (modulated by the PM) and duration of about 9.6 μs. The repetition rate of the individual pulse in a burst is about 9 MHz (modulated by the IM), and the pulse width is about 6 ns. By changing the IM signal’s repetition rate and duty cycle, different individual pulse shapes are obtained with pulse durations between 6 and 34 ns.
Lasers fiber Infrared and far-infrared lasers Mode-locked lasers Fiber optics infrared Modulation characteristics and microwave generation for AlGaInAs/InP microring lasers under four-wave mixing Download:1021次
Download:1021次
 Download:1021次
Download:1021次The dynamic characteristics are investigated for a microring laser with an external radius of 12 μm subject to external optical injection. Single-mode operation with a side mode suppression ratio of 33.4 dB is realized at a biasing current of 25 mA and a temperature of 290 K, and the corresponding small-signal modulation response is obtained with a resonance peak frequency of 7.5 GHz. Under the optical injection from a tunable laser, the improvements of the small-signal modulation response induced by four-wave mixing are observed for the microring laser, which shows an additional resonance peak around the frequency of the beat frequency between the lasing mode and the injecting light. Furthermore, optical generation of a microwave signal is realized by the light beating between the lasing mode and the injecting light measured by a high-speed photodetector and a spectrum analyzer.
Nonlinear optical devices Nonlinear optics four-wave mixing Semiconductor lasers Optical mode study of III–V-nanowire-based nanophotonic crystals for an integrated infrared band microlaser Download:810次
Download:810次
 Download:810次
Download:810次In this paper, we study an original strategy to generate an infrared waveband microlaser by an integrated III–V-nanowire (NW)-based photonic array for on-chip interconnects. The optical modes of the III–V-NW-based photonic array are investigated for utilization as an all-in-one gain medium, waveguide, and cavity. Adequate designs of periodic arrays of InP NWs with different polarization TM and TE modes are studied by 3D electromagnetic simulation finite difference time domain to optimize the resonant active photonic crystal (hybrid Bloch modes) in the infrared band at 1.3 μm. According to our calculations, NWs larger than 0.2 μm in diameter are needed to conceive optic modes inside NW photonics in TM polarization. However, smaller NW photonics, such as 0.1 μm in diameter, can obtain only the TE mode inside the NWs. This phenomenon is theoretically illustrated by the dispersive curves of NW-based photonics. It aims at demonstrating that the slow velocity mode inside the NW photonics will cause amplification of lightwaves and generate microlasers in the infrared band at 1.3 μm. These studies are of prime importance for further microlaser integration to silicon-on-insulator (SOI) waveguides for on-chip optical interconnects.
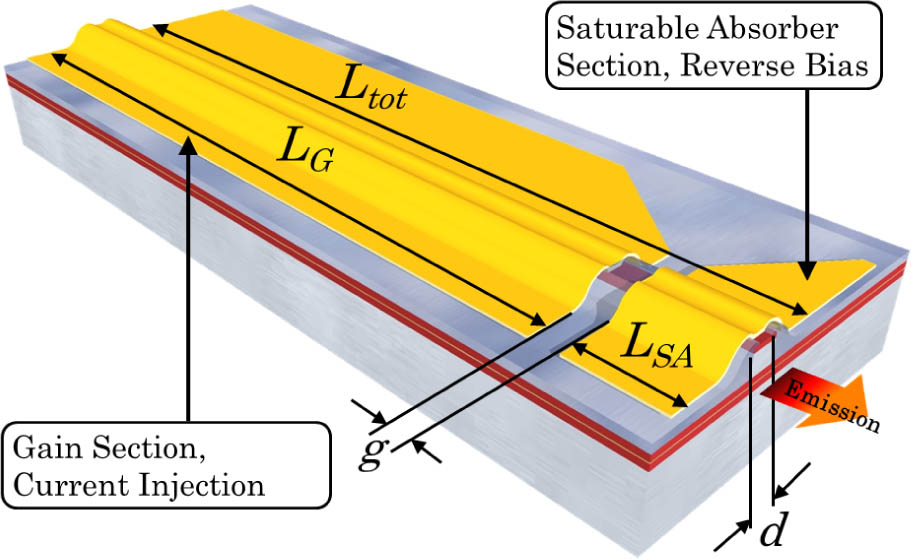
Infrared and far-infrared lasers Optical resonators Semiconductor lasers Microcavities Photonic crystals Passive mode-locking in semiconductor lasers in a Fabry–Perot configuration with a bandgap blueshift applied to the saturable absorber (SA) section has been experimentally characterized. For the first time a fully post-growth technique, quantum well intermixing, was adopted to modify the material bandgap in the SA section. The measurements showed not only an expected narrowing of the pulse width but also a significant expansion of the range of bias conditions generating a stable train of optical pulses. Moreover, the pulses from lasers with bandgap shifted absorbers presented reduced chirp and increased peak power with respect to the nonshifted case.
Mode-locked lasers Semiconductor lasers Integrated optics devices 公告
动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-25
PR Highlight (Vol. 12, Iss. 2): 封面|超紧凑片上偏振控制器动态信息 丨 2024-04-11
PR Highlight (Vol. 11, Iss. 12): 亮点 | 十亿像素级、高通量的无透镜偏振编码叠层成像技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
PR 封面故事 (Vol. 12, Iss. 3): 封面 | 基于时空编码神经网络的像差感知超分辨成像动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
PR 封面故事 (Vol. 12, Iss. 1) 光涡旋与手性器件微纳3D打印动态信息 丨 2024-03-14
PR Highlight (Vol. 12, Iss. 1): 同步双脉冲激光烧蚀中的气泡相互作用效应激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦