2022, 20(5) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第20卷 第5期
Machine learning can effectively accelerate the runtime of a computer-generated hologram. However, the angular spectrum method and single fast Fresnel transform-based machine learning acceleration algorithms are still limited in the field-of-view angle of projection. In this paper, we propose an efficient method for the fast generation of large field-of-view holograms combining stochastic gradient descent (SGD), neural networks, and double-sampling Fresnel diffraction (DSFD). Compared with the traditional Gerchberg–Saxton (GS) algorithm, the DSFD-SGD algorithm has better reconstruction quality. Our neural network can be automatically trained in an unsupervised manner with a training set of target images without labels, and its combination with the DSFD can improve the optimization speed significantly. The proposed DSFD-Net method can generate 2000-resolution holograms in 0.05 s. The feasibility of the proposed method is demonstrated with simulations and experiments.
computer-generated hologram holographic display machine learning In this Letter, we have experimentally verified a low-complexity subcarrier pairwise-averaging (SPA)-enhanced channel estimation (CE) method for small-size fast Fourier transform (FFT) non-Hermitian symmetric orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (NHS-OFDM) transceivers. Compared with intra-symbol frequency averaging (ISFA), more than 20% look-up tables and 10% logic power consumption can be saved. The least-square (LS), ISFA, and SPA CE methods are compared by offline and real-time digital signal processing approaches. The results show that the receiver sensitivity of the SPA NHS-OFDM transmission system with 64/128-point FFT can be improved by more than 1 dB at the bit error rate of 3.8 × 10-3 compared to the LS.
NHS-OFDM least-square intra-symbol frequency-averaging subcarrier pairwise-averaging The spectral linewidth of a transversely excited pulsed
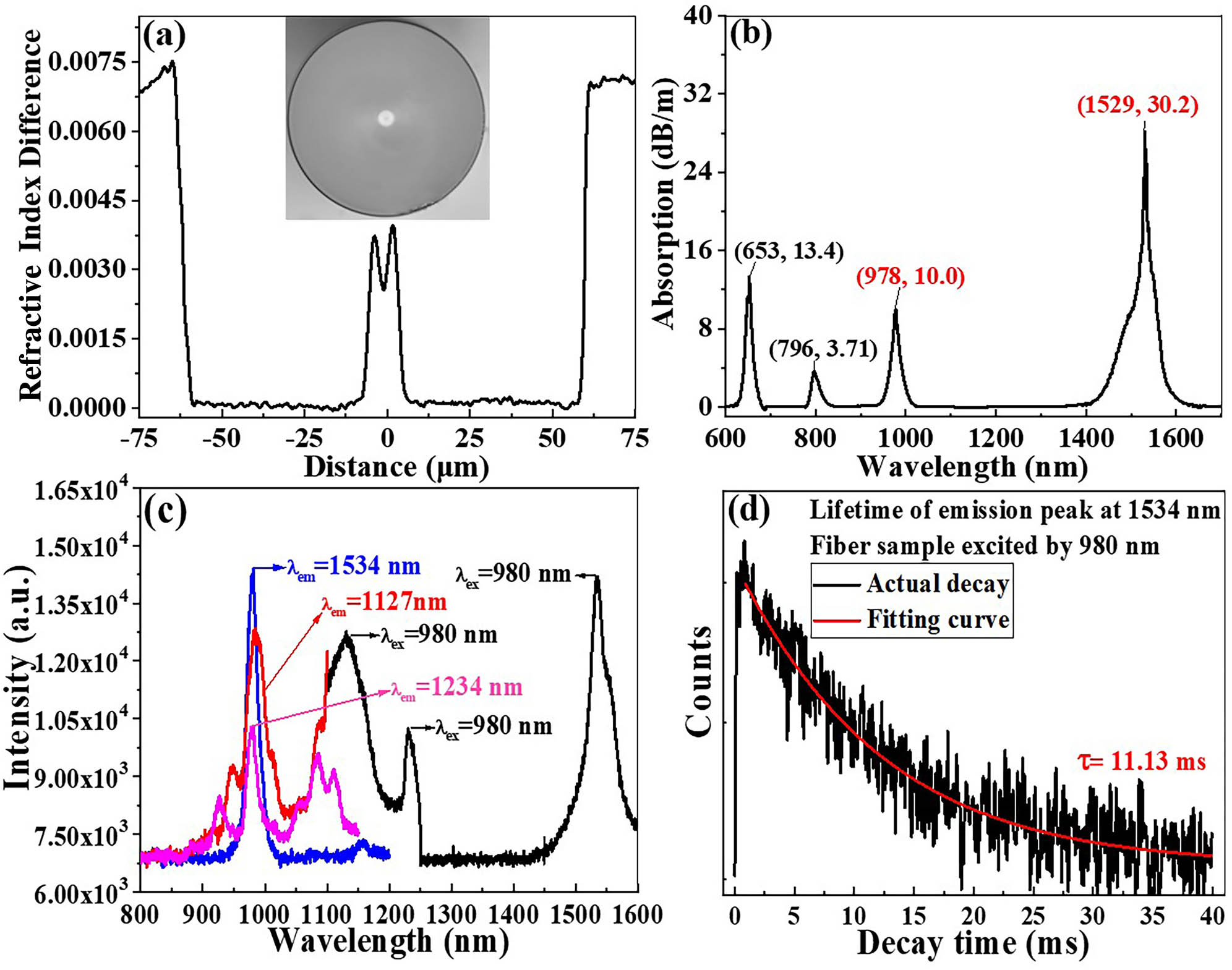
short pulse continuous tuning pulse compression High signal-to-noise ratio fiber laser at 1596 nm based on a Bi/Er/La co-doped silica fiber Download:506次
Download:506次
 Download:506次
Download:506次We fabricate a high-performance Bi/Er/La co-doped silica fiber with a fluorescence intensity of
Bi/Er/La co-doped silica fiber high signal-to-noise ratio laser narrow linewidth We report VOx x
nonlinear optical properties saturable absorber VOx/NaVO3 composite Q-switching In this study, an excellent polarization optical crystal
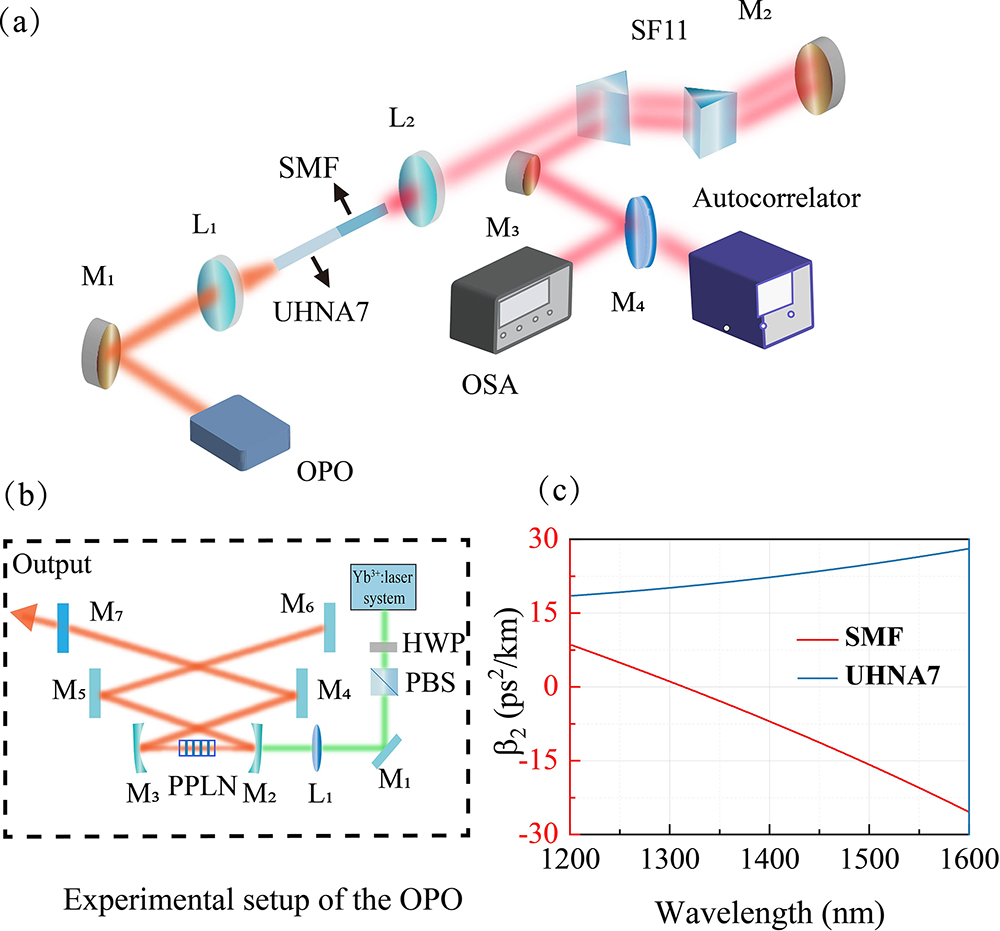
Glan prism laser damage threshold birefringence polarized optical crystal We report an experimental generation of few-cycle pulses at 53 MHz repetition rate. Femtosecond pulses with pulse duration of 181 fs are firstly generated from an optical parametric oscillator (OPO). Then, the pulses are compressed to sub-three-cycle with a hybrid compressor composed of a commercial single-mode fiber and a pair of prisms, taking advantage of the tunability of the OPO and the numerical simulating of the nonlinear compression system. Our compressed optical pulses possess an ultrabroadband spectrum covering over 470 nm bandwidth (at
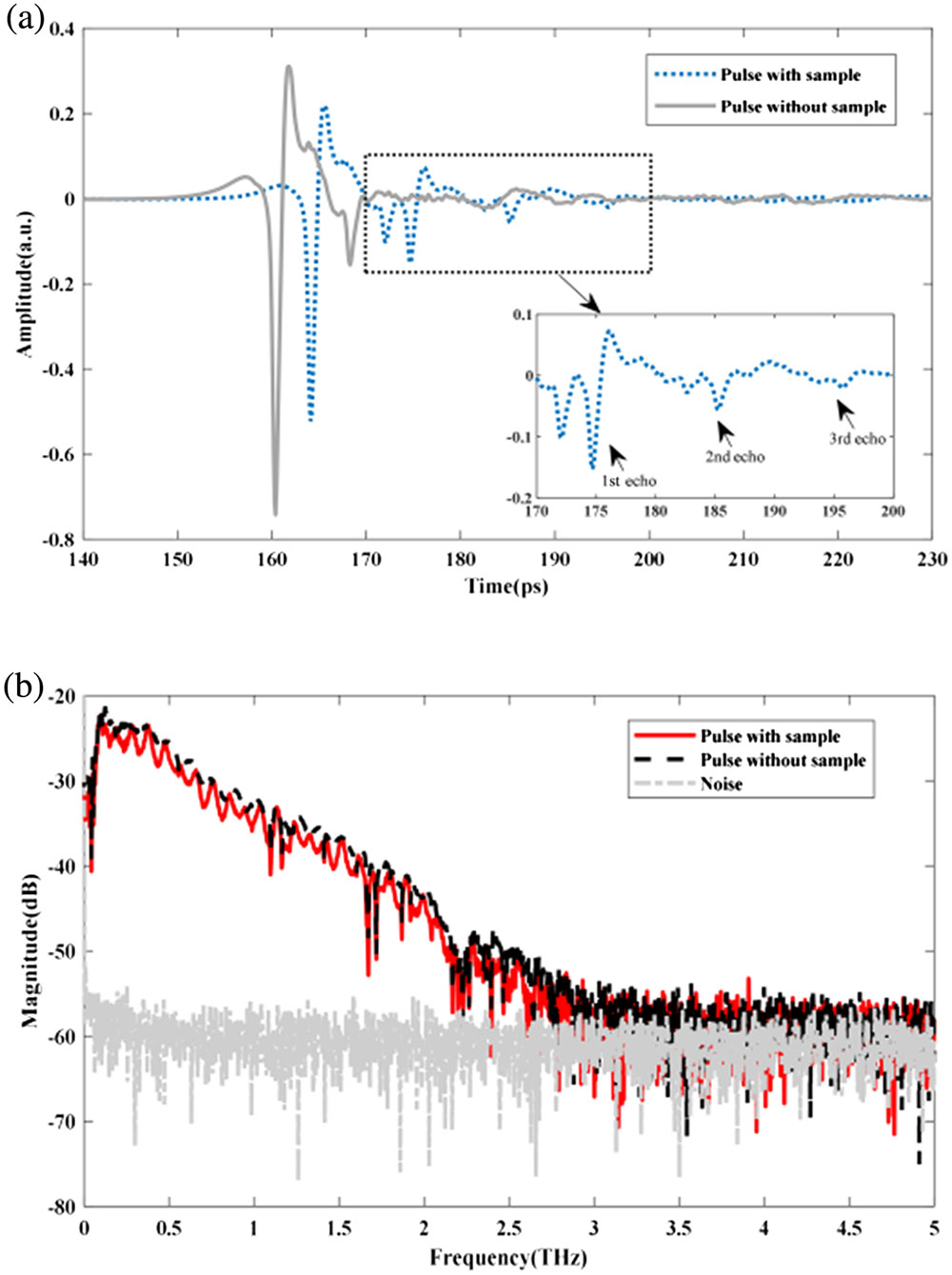
nonlinear compression few cycle pulse optical parametric oscillator This study proposes a method based on material dispersion models to computationally simulate terahertz (THz) time-domain spectroscopy signals. The proposed method can accurately extract the refractive indices and extinction coefficients of optically thin samples and high-absorption materials in the THz band. This method was successfully used to extract the optical constants of a 470-μm-thick monocrystalline silicon sample and eliminate all errors associated with the Fabry–Pérot oscillation. When used to extract the optical constants of a 16.29-mm-thick polycarbonate sample, our method succeeded in minimizing errors caused by the low signal-to-noise ratio in the extracted optical constants.
terahertz time-domain spectrum material optical constant Debye dispersion model Palladium-based hydrogen sensors have been typically studied due to the dielectric function that changes with the hydrogen concentration. However, the development of a reliable, integral, and widely applicable hydrogen sensor requires a simple readout mechanism and an optimization of the fast detection of hydrogen. In this work, optical fiber hydrogen sensing platforms are developed using an optimized metasurface, which consists of a layer of palladium nanoantennas array suspended above a gold mirror layer. Since the optical properties of these palladium nanoantennas differ from the traditional palladium films, a high reflectance difference can be achieved when the sensor based on the metasurface is exposed to the hydrogen atmosphere. Finally, the optimized reflectance difference
hydrogen detection metasurface palladium optical fiber sensor Photon nanosieves, as amplitude-type metasurfaces, have been demonstrated usually in a transmission mode for optical super-focusing, display, and holography, but the sieves with subwavelength size constrain optical transmission, thus leading to low efficiency. Here, we report reflective photon nanosieves that consist of metallic meta-mirrors sitting on a transparent quartz substrate. Upon illumination, these meta-mirrors offer the reflectance of
metasurfaces nanosieves holograms reflective mirrors Optical line tweezers have been an efficient tool for the manipulation of large micron particles. In this paper, we propose to create line traps with transformable configurations by using the transverse electromagnetic mode-like laser source. We designed an optical path to simulate the generation of the astigmatic beams and line traps with a series of lenses to realize the rotational transformation with respect to the rotation angle of cylindrical lenses. It is shown that the spherical particles with diameters ranging from 5 μm to 20 μm could be trapped, aligned, and revolved in experiment. The periodical trapping forces generated by transformable line traps might open an alternative way to investigate the mechanical properties of soft particles and biological cells.
optical line tweezers transformable line traps optical manipulation Unidirectional electromagnetic windmill scattering in a magnetized gyromagnetic cylinder Download:635次
Download:635次
 Download:635次
Download:635次We present a discovery of an unusual unidirectionally rotating windmill scattering of electromagnetic waves by a magnetized gyromagnetic cylinder via an analytical theory for rigorous solution to fields and charges and an understanding of the underlying mathematical and physical mechanisms. Mathematically, the generation of nonzero off-diagonal components can break the symmetry of forward and backward scattering coefficients, producing unidirectional windmill scattering. Physically, this windmill scattering originates from the nonreciprocal unidirectional rotation of polarized magnetic charges on the surface of a magnetized gyromagnetic cylinder, which drives the scattering field to radiate outward in the radial direction and unidirectionally emit in the tangential direction. Interestingly, the unidirectional electromagnetic windmill scattering is insensitive to the excitation direction. Moreover, we also discuss the size dependence of unidirectional windmill scattering by calculating the scattering spectra of the gyromagnetic cylinder. These results are helpful for exploring and understanding novel interactions between electromagnetic waves and gyromagnetic materials or structures and offer deep insights for comprehending topological photonic states in gyromagnetic systems from the aspect of fundamental classical electrodynamics and electromagnetics.
unidirectional electromagnetic windmill scattering magnetized gyromagnetic cylinder topological photonics 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦