中国激光, 2021, 48 (2): 0202008, 网络出版: 2021-01-06
面向电解水的激光制备微纳米结构催化电极  下载: 1544次特邀综述
下载: 1544次特邀综述
Laser Fabricated Electrodes with Micro-Nano Structures for Electrocatalytic Water Splitting
图 & 表
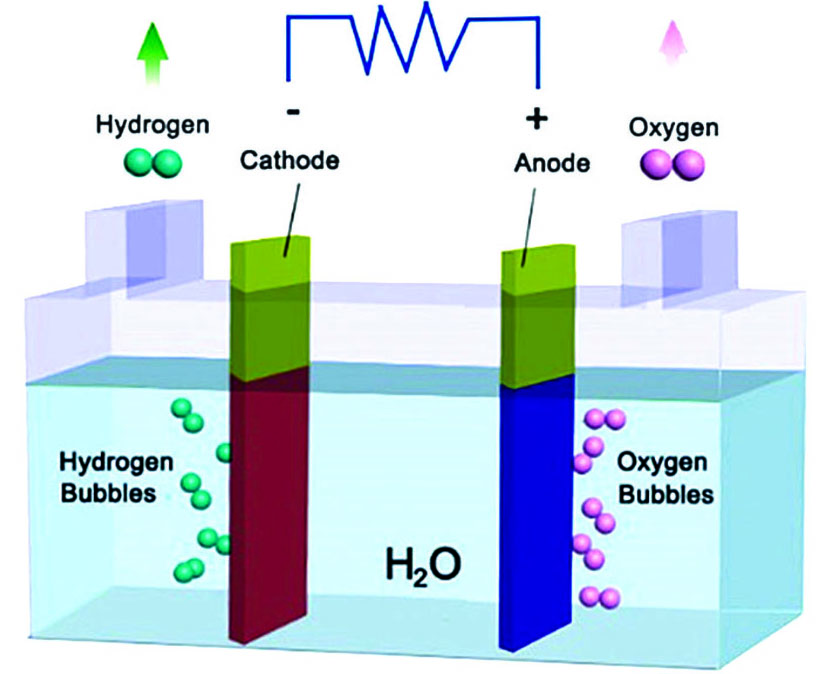
图 2. 催化活性的评估。(a)极化曲线示意图;(b)Tafel斜率示意图
Fig. 2. Evaluation of catalytic activity. (a) Schematic illustration of polarization curve; (b) schematic illustration of Tafel slope

图 3. 激光与溶液作用的几个典型实例。(a)过渡金属氢氧化物的合成示意图[22];(b)(c)过渡金属氢氧化物的SEM图片[22];(d)过渡金属氢氧化物初始状态与2h后过电压的比较[22];(e)无定型MoSx的合成示意图、分子结构以及析氢催化机理[65];(f)无定型MoSx的TEM图片(插图为相应的SAED花样)[65]
Fig. 3. Several typical examples of the interaction between laser and solution. (a) Schematic illustration of the preparation process of transition metal hydroxides[22]; (b)(c) SEM images of transition metal hydroxides[22]; (d) overpotential values of transition metal hydroxides at time =0 and time =2h[22]; (e) schematic illustration of the preparation pro

图 4. 激光与颗粒作用的几个典型实例。(a)激光破碎Co3O4的合成示意图[24];(b)激光破碎Co3O4的DFT计算模型[24];(c)激光破碎Co3O4的析氧极化曲线[24];(d)激光辐照MoS2的合成示意图[66];(e)激光辐照MoS2的析氢极化曲线[66];(f)激光液相辐照制备氮掺杂GO的实验装置示意图[
Fig. 4. Several typical examples of the interaction between laser and particles. (a) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of laser-fragmentated Co3O4; (b) structural modes for DFT calculation of laser-fragmentated Co3O4; (c) OER polarization curves of laser-fragmentated Co3
图 5. 激光与块体靶材作用的几个典型实例。(a) NiFe LDH的析氧反应过程示意图[86];(b) NiO/NiFe LDH的透射电镜(TEM)图片[40];(c) NiO/NiFe LDH的析氧极化曲线[40];(d) NiO/NiFe LDH的DFT计算模型[40];(e) RuAu单原子合金的合成示意图[71];(f)(g) RuAu单原子合金的HAADF-STEM图片[71];(h) RuAu
Fig. 5. Several typical examples of the interaction between laser and bulk targets. (a) Schematic illustration of the OER process of NiFe LDH[86]; (b) TEM image of NiO/NiFe LDH[40]; (c) OER polarization curves of NiO/NiFe LDH[40]; (d) structural models for DFT calculation of NiO/NiFe LDH[40]; (e) schematic

图 6. 结构和电化学特征示意图[14]。(a)传统的粉末催化剂;(b)自支撑微纳米结构催化电极
Fig. 6. Schematic illustration of the structural and electrochemical features[14]. (a) Conventional powdery catalysts; (b) self-supported micro-nano electrode

图 7. 脉冲激光制备的自支撑微纳米结构。(a)分散纳米颗粒[90];(b)纳米波纹[91];(c)绒毛状团簇[45];(d)菜花状团聚体[94];(e)分层级微纳米结构[95];(f)纳米线[98];(g)纳米片[98];(h)纳米草[Fig. 7. Self-supported micro-nano structures fabricated by pulse laser. (a) Dispersive nanoparticles[90]; (b) nanoripples[91]; (c) fluff-like clusters[45]; (d) cauliflower-like aggregates[94]; (e) hierarchical micro-nano structures[95]; (f) nanowires[
Fig. 7. Self-supported micro-nano structures fabricated by pulse laser. (a) Dispersive nanoparticles[90]; (b) nanoripples[91]; (c) fluff-like clusters[45]; (d) cauliflower-like aggregates[94]; (e) hierarchical micro-nano structures[95]; (f) nanowires[

图 8. 激光直接制备自支撑微纳米结构催化电极的几个典型实例。(a)激光烧蚀镍片的全解水极化曲线[45];(b)激光烧蚀镍片的稳定性测试结果[45];(c)全解水装置照片[45];(d)三维分布的Fe3O4纳米颗粒团簇的SEM图片[47];(e)三维分布的Fe3O4纳米颗粒团簇的稳定性测试结果[47];(f)NiS2/MoS2异质结的合成示意图[Fig. 8. Several typical examples of self-supported catalytic electrodes with micro-nano structures directly fabricated by laser. (a) Polarization curves for overall water splitting of laser-ablated Ni plates[45]; (b) stability test of laser-ablated Ni plates[45]; (c) digital photograph of the overall water splitting device[45]; (d) SEM image of three-dimen

Fig. 8. Several typical examples of self-supported catalytic electrodes with micro-nano structures directly fabricated by laser. (a) Polarization curves for overall water splitting of laser-ablated Ni plates[45]; (b) stability test of laser-ablated Ni plates[45]; (c) digital photograph of the overall water splitting device[45]; (d) SEM image of three-dimen

图 9. 激光复合其他化学法制备自支撑微纳米结构催化电极的几个典型实例。(a)(b)CoS2/WS2纳米复合物的SEM图片和TEM图片[77];(c)(d)NiO/CoFe LDH分层级纳米结构的合成示意图和全解水极化曲线[50]
Fig. 9. Several typical examples of self-supported catalytic electrodes with micro-nano structures fabricated by laser hybrid with other chemical methods. (a)(b) SEM image and TEM image of CoS2/WS2 hybrid catalysts[77]; (c)(d) schematic illustration of the preparation process of NiO/CoFe LDH hierarchical nanostructures and polarization curves for overall water splitting[50]

图 10. 大面积制备的可行性验证。(a)(b)低碳钢催化电极的大面积样品照片和稳定性测试结果[46];(c)~(f)不锈钢丝网电极的大面积样品照片、SEM图片和两电极极化曲线[47]
Fig. 10. Feasibility verification of large-area preparation. (a)(b) Digital photograph of large-area sample and stability test of the mild steel electrode[46]; (c)--(f) digital photograph and SEM images of large-area sample, and two-electrode polarization curves[47]

表 1基于激光微纳制造技术制备的电解水催化剂的性能总结
Table1. Summary of the catalytic activity of various catalysts based on laser micro-nano fabrication
|
蔡明勇, 江国琛, 钟敏霖. 面向电解水的激光制备微纳米结构催化电极[J]. 中国激光, 2021, 48(2): 0202008. Cai Mingyong, Jiang Guochen, Zhong Minlin. Laser Fabricated Electrodes with Micro-Nano Structures for Electrocatalytic Water Splitting[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48(2): 0202008.