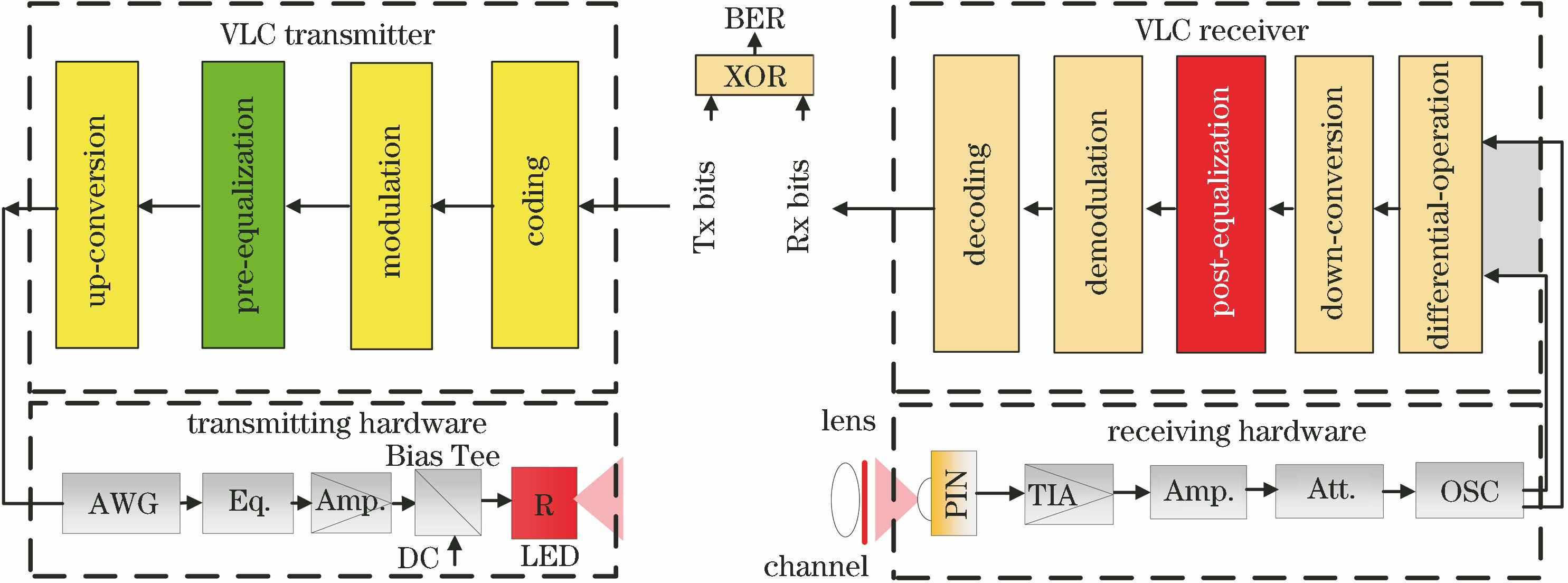
基于机器学习的可见光通信信号处理研究现状  下载: 3526次封面文章
下载: 3526次封面文章
邹鹏, 赵一衡, 胡昉辰, 迟楠. 基于机器学习的可见光通信信号处理研究现状[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(1): 010001.
Peng Zou, Yiheng Zhao, Fangchen Hu, Nan Chi. Research Status of Machine Learning Based Signal Processing in Visible Light Communication[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(1): 010001.
[1] Chi N, Haas H, Kavehrad M, et al. Visible light communications: demand factors, benefits and opportunities[Guest Editorial][J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2015, 22(2): 5-7.
[2] TanakaY, HaruyamaS, NakagawaM. Wireless optical transmissions with white colored LED for wireless home links[C]∥11th IEEE International Symposium on Personal Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications. PIMRC 2000. Proceedings (Cat. No.00TH8525), September 18-21, 2000, London, UK. New York: IEEE, 2000: 1325- 1329.
[3] Haas H, Yin L, Wang Y L, et al. What is LiFi?[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2016, 34(6): 1533-1544.
[4] O'Brien D. Minh H L, Zeng L B, et al. Indoor visible light communications: challenges and prospects[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7091: 709106.
[5] 贾科军, 靳斌, 郝莉. 室内可见光通信OFDM自适应比特功率加载算法性能分析[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(3): 030603.
[6] 杨玉峰, 蒋明争, 张颖, 等. 基于单光源的全双工可见光通信系统设计[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(1): 010603.
[7] Neokosmidis I, Kamalakis T, Walewski J W, et al. Impact of nonlinear LED transfer function on discrete multitone modulation: analytical approach[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2009, 27(22): 4970-4978.
[8] Ying K, Yu Z H, Baxley R J, et al. Nonlinear distortion mitigation in visible light communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2015, 22(2): 36-45.
[9] Inan B. Jeffrey Lee S C, Randel S, et al. Impact of LED nonlinearity on discrete multitone modulation[J]. Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 2009, 1(5): 439-451.
[10] Wang Y G, Tao L, Huang X X, et al. 8-Gb/s RGBY LED-based WDM VLC system employing high-order CAP modulation and hybrid post equalizer[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2015, 7(6): 7904507.
[11] Bishop CM. Pattern recognition and machine learning[M]. New York: Springer, 2006: 103- 107.
[12] 卓刘, 陈晓琪, 谢振平, 等. 基于深度神经网络的迷彩目标发现仿真学习方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(7): 071102.
[13] 曲磊, 王康如, 陈利利, 等. 基于RGBD图像和卷积神经网络的快速道路检测[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(10): 101003.
Qu L, Wang K R, Chen L L, et al. Fast road detection based on RGBD images and convolutional neural network[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(10): 101003.
[14] 朱玥, 覃尧, 董岚, 等. 人工智能在移动通信网络中的应用: 基于机器学习理论的信道估计与信号检测算法[J]. 信息通信技术, 2019, 13(1): 19-25.
Zhu Y, Qin Y, Dong L, et al. Application cases of artificial intelligence in mobile communication networks: machine-learning-based channel estimator and signal detector[J]. Information and Communications Technologies, 2019, 13(1): 19-25.
[15] Khan FN, LuC, Lau A P T. Machine learning methods for optical communication systems[C]∥Advanced Photonics 2017 (IPR, NOMA, Sensors, Networks, SPPCom, PS), July 24-27, 2017, New Orleans, Louisiana, United States. Washington, D.C.: OSA, 2017: SpW2F. 3.
[17] TanimuraT, HoshidaT, Rasmussen JC, et al. OSNR monitoring by deep neural networks trained with asynchronously sampled data[C]∥2016 21st OptoElectronics and Communications Conference (OECC) held jointly with 2016 International Conference on Photonics in Switching (PS), July 3-7, 2016, Niigata, Japan. New York: IEEE, 2016: 16424746.
[18] Skoog R A, Banwell T C, Gannett J W, et al. Automatic identification of impairments using support vector machine pattern classification on eye diagrams[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2006, 18(22): 2398-2400.
[20] Gonzalez NG, ZibarD, Monroy IT. Cognitive digital receiver for burst mode phase modulated radio over fiber links[C]∥36th European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication, September 19-23, 2010, Torino, Italy. New York: IEEE, 2010: 11636818.
[22] Khan F N, Yu Y, Tan M C, et al. Experimental demonstration of joint OSNR monitoring and modulation format identification using asynchronous single channel sampling[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(23): 30337-30346.
[23] Khan F N, Zhong K P. Al-Arashi W H, et al. Modulation format identification in coherent receivers using deep machine learning[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2016, 28(17): 1886-1889.
[24] He H T, Wen C K, Jin S, et al. Deep learning-based channel estimation for beamspace mmWave massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(5): 852-855.
[25] Ye H, Li G Y, Juang B H. Power of deep learning for channel estimation and signal detection in OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(1): 114-117.
[26] Ha Y, Niu W Q, Chi N. Frequency reshaping and compensation scheme based on deep neural network for a FTN CAP 9QAM signal in visible light communication system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11048: 110482F.
[27] Chi N, Zhao Y H, Shi M, et al. Gaussian kernel-aided deep neural network equalizer utilized in underwater PAM8 visible light communication system[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(20): 26700-26712.
[28] Lu X Y, Lu C, Yu W X, et al. Memory-controlled deep LSTM neural network post-equalizer used in high-speed PAM VLC system[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(5): 7822-7833.
[29] Yu W X, Lu X Y, Chi N. Signal decision employing density-based spatial clustering of machine learning in PAM-4 VLC system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10849: 108491D.
[30] Lu X Y, Qiao L, Zhou Y J, et al. An I-Q-Time 3-dimensional post-equalization algorithm based on DBSCAN of machine learning in CAP VLC system[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 430: 299-303.
[31] Lu X Y, Wang K H, Qiao L, et al. Nonlinear compensation of multi-CAP VLC system employing clustering algorithm based perception decision[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2017, 9(5): 7906509.
[32] Lu XY, Zhao MM, QiaoL, et al. Non-linear compensation of multi-CAP VLC system employing pre-distortion base on clustering of machine learning[C]∥Optical Fiber Communication Conference, March 11-15, 2018, San Diego, California, United States. Washington, D.C.: OSA, 2018: M2K. 1.
[33] Lu X, Zhou Y, Qiao L, et al. Amplitude jitter compensation of PAM-8 VLC system employing time-amplitude two-dimensional re-estimation base on density clustering of machine learning[J]. Physica Scripta, 2019, 94(5): 055506.
[34] Niu WQ, HaY, ChiN. Novel phase estimation scheme based on support vector machine for multiband-CAP visible light communication system[C]∥2018 Asia Communications and Photonics Conference (ACP), October 26-29, 2018, Hangzhou, China. New York: IEEE, 2018: 18382490.
[35] Suykens J A K, Vandewalle J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 1999, 9(3): 293-300.
[36] ScholkopfB, Smola AJ. Learning with kernels: support vector machines, regularization, optimization, and beyond[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2001: 133- 145.
[37] Haigh P A, Ghassemlooy Z, Rajbhandari S, et al. Visible light communications: 170 Mb/s using an artificial neural network equalizer in a low bandwidth white light configuration[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2014, 32(9): 1807-1813.
[38] Guan W P, Wu Y X, Xie C Y, et al. High-precision approach to localization scheme of visible light communication based on artificial neural networks and modified genetic algorithms[J]. Optical Engineering, 2017, 56(10): 106103.
[39] Haigh PA, GhassemlooyZ, PapakonstantinouI, et al. A MIMO-ANN system for increasing data rates in organic visible light communications systems[C]∥2013 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), June 9-13, 2013, Budapest, Hungary. New York: IEEE, 2013: 5322- 5327.
邹鹏, 赵一衡, 胡昉辰, 迟楠. 基于机器学习的可见光通信信号处理研究现状[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(1): 010001. Peng Zou, Yiheng Zhao, Fangchen Hu, Nan Chi. Research Status of Machine Learning Based Signal Processing in Visible Light Communication[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(1): 010001.