Abstract
In order to decrease the limit of detection of elements and improve signal-to-background ratio (SBR) and the stability of characteristic spectral lines of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) of heavy metals in soil, we study the polarization property of four characteristic discrete spectral lines of Fe, Pb, Ca, Mg elements and continuous background radiation of LIBS in soil, and analyze the limit of detection, SBR and relative standard deviation (RSD) of characteristic spectral lines of elements under the conditions of polarization and no-polarization. The results indicate that the polarization degree of four characteristic spectral lines Fe Ⅰ: 404.581 nm, Pb Ⅰ: 405.780 nm, Ca Ⅰ: 422.670 nm, Mg Ⅰ: 518.361 nm and corresponding continuous background radiation are 0.27, 0.17, 0.25, 0.23 and 0.70, 0.64, 0.69, 0.67, respectively. The polarization resolved LIBS (PRLIBS) technology makes RSD of four characteristic spectral lines Fe Ⅰ: 404.581 nm, Pb Ⅰ: 405.780 nm, Ca Ⅰ: 422.670 nm, Mg Ⅰ: 518.361 nm decrease by 3.28%, 2.2%, 3.24% and 1.34%, respectively. Continuous background radiation is effectively depressed by PRLIBS technology, and SBR of four characteristic spectral lines is increased by 5.59, 5.67, 5.30, 7.35 times, respectively. Under the conditions of polarization and no-polarization, the limits of detection of heavy metal Pb are 17.4×10-6 and 39.4×10-6, respectively, limit of detection under polarization is 44% that of non-polarization. Above results provide data support for further improving quantitative analysis ability of LIBS on heavy metal in soil.
1 引言
激光诱导击穿光谱(LIBS)技术通过经透镜会聚的激光脉冲作用在待测样品上,样品表面瞬间产生高温、高密度的等离子体,随后等离子体冷却过程中会辐射出与物质元素相对应的光谱信息,据此对物质元素进行定性以及定量分析。LIBS技术具有诸多优点,如:能对不同形态的样品进行分析、多元素同时检测、快速在线分析、样品无损检测等,并在诸多领域展开了相应的研究[1-14]。在土壤重金属检测方面:谷艳红等[1]采用元素粒子比方法对土壤中的重金属元素Cr的含量进行分析,结果表明,预测国家标准土壤中Cr含量的相对误差在7%以内;Yi等[2]采用小波变换背景去除算法结合标准加入法对土壤中的Pb元素进行了定量检测,该方法使得Pb含量的预测方均根误差由303×10-6减小到25.7×10-6;Fu等[3]提出了一种提高LIBS技术定量分析能力的快速变量选择方法,与传统方法相比,该方法预测的方均根误差和R2因子均有较好的结果。高功率密度的激光脉冲与物质相互作用的初期会产生较强的连续背景辐射,表征物质成分信息的元素特征分立谱线会叠加,甚至湮没在连续背景辐射之中。由于连续背景辐射的衰减寿命要小于特征分立谱线,目前一般通过时间分辨的方法来减弱或消除连续背景辐射对特征谱线测量和分析的影响,即通过数字脉冲延时发生器(如DG535)来严格控制激光脉冲发射与光谱信号采集之间的延迟时间。时间分辨LIBS技术的测量结果与诸多实验参数密切相关,且对操作人员的要求较高,因而限制了时间分辨LIBS方法的推广和应用。
偏振分辨LIBS(PRLIBS)近年来得到了较快发展。Liu等[15]利用飞秒双脉冲激光对Si材料进行烧蚀,首次发现了连续背景辐射的近全偏振现象,尤其是在紫外波段,连续谱的偏振度大于95%,而元素特征分立谱线的偏振度却很低;Penczak等[16]采用飞秒单脉冲对Al材料的偏振特性展开研究,分析了激光能量、激光聚焦位置、激光入射角、探测角度以及激光偏振态等参数对LIBS光谱偏振度的影响;Zhao等[17]利用飞秒单脉冲激光对Cu和石墨等离子体光谱的偏振特性进行分析;Liu等[18]利用纳秒单脉冲激光对Al材料进行烧蚀,分析了激光能量密度和激光聚焦位置等对光谱偏振特性的影响;Liu等[19]利用纳秒单脉冲激光对Al靶材的偏振特性进行分析,研究了偏振度随激光能量密度和探测角度的变化。目前的研究对象主要是针对Si、石墨以及金属材料Al、Cu等。土壤基体的特性复杂多变,目前对于土壤样品LIBS光谱偏振特性的研究工作尚未见报道。
本文重点针对土壤样品的LIBS连续背景辐射及元素特征分立谱线的偏振特性开展研究工作,通过对比分析有、无偏振条件下特征谱线的相对标准偏差(RSD)、信背比(SBR)以及元素检测限,期望能通过PRLIBS技术的相关研究在一定程度上提高土壤中重金属元素的LIBS定量分析能力。
2 实验装置
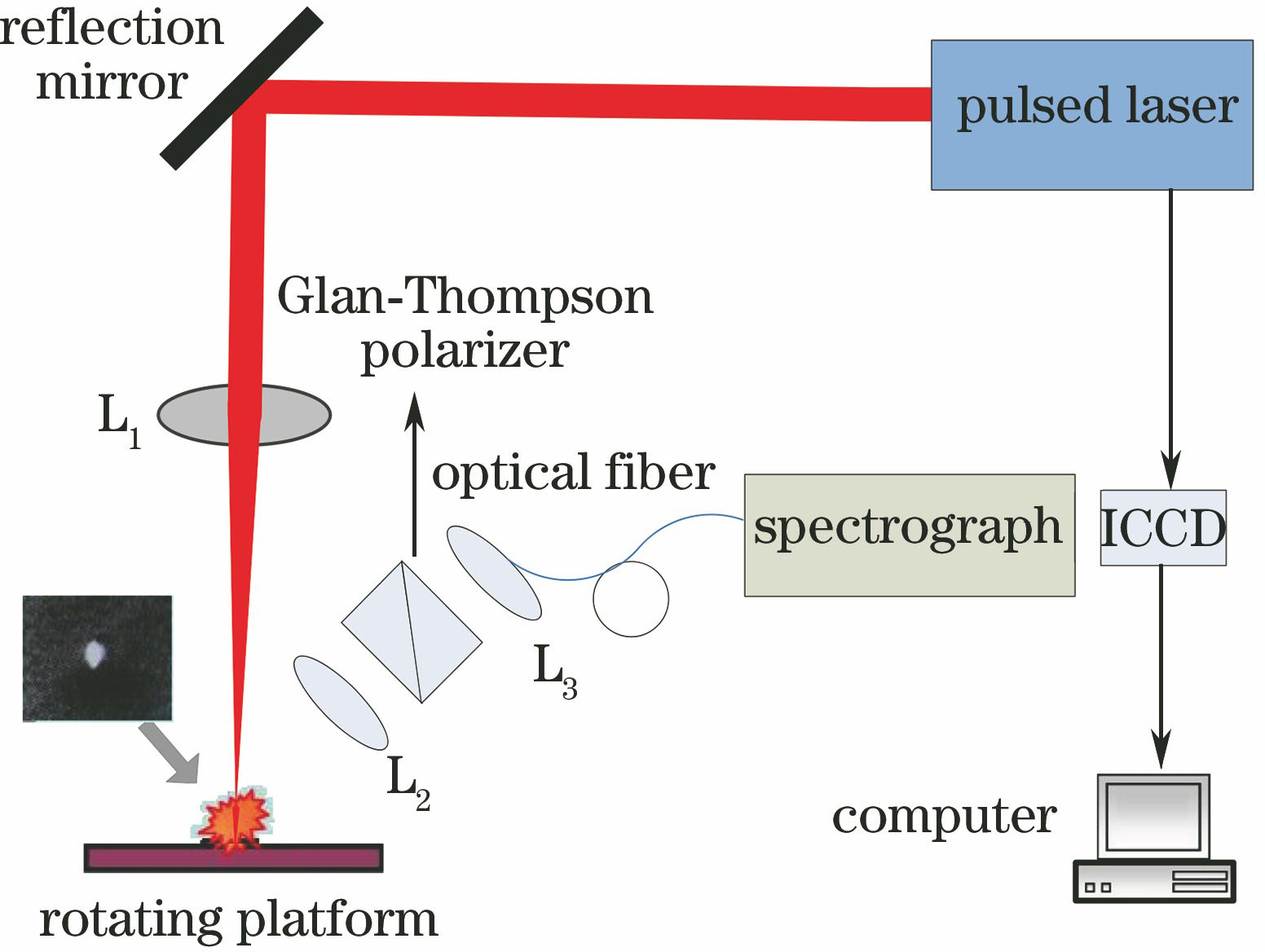
采用中心波长为1064 nm、脉冲宽度为6 ns的Nd∶YAG激光器(Ultra型,Quantel公司,法国)作为激发光源,激光脉冲经焦距f=50 mm的平凸透镜L1会聚后作用在样品上,高功率密度的脉冲激光使样品表面瞬间产生等离子体。等离子体光谱信号接收系统由两个焦距f=50 mm的平凸透镜L2和L3以及Glan-Thompson偏振棱镜(a-偏硼酸钡,通光波段为200~1100 nm)组成,光谱信号通过接收系统后耦合进光纤并传输至光谱仪(Mechelle 5000型,Andor公司,英国)进行分光,光谱仪的测量范围为200~850 nm,光谱分辨率λ/Δλ=5000,光谱信号最终由增强型电荷耦合器件(ICCD,i-STAR型,Andor公司,英国)进行探测。实验系统原理图如图1所示。
图 1. 偏振实验系统原理图
Fig. 1. Schematic of polarization experimental apparatus
下载图片 查看所有图片
实验所用土壤样品经自然风干、研磨、过100 目筛(100目=0.15 mm)后,用电子天平称量2.8 g的样品,将其压制成直径为30 mm、厚度为2.6 mm的圆饼状样品。用Pb(NO3)2和去离子水配制250 g/mL的标准溶液,利用此标准溶液与土壤进行混合配制。含Pb土壤样品的浓度梯度如表1所示。
表 1. 含不同浓度Pb的土壤样品
Table 1. Soil samples contained different concentrations of Pb
| Serial number of soil sample | Mass fraction /10-6 |
|---|
| 1 | 100 | | 2 | 200 | | 3 | 300 | | 4 | 400 | | 5 | 500 | | 6 | 600 | | 7 | 700 | | 8 | 800 | | 9 | 900 |
|
查看所有表
3 结果与讨论
3.1 光谱测量
在高功率密度的激光脉冲与物质相互作用产生等离子体的初始阶段,由于轫致辐射过程以及自由电子和离子间的复合过程,LIBS光谱中会产生较强的连续背景辐射,表征物质元素信息的特征分立谱线会叠加,甚至湮没在连续背景辐射中,这会严重影响LIBS光谱的测量和分析。当激光能量为100 mJ、延迟时间为0 μs和采集门宽为5 μs时,有、无偏振条件下样品在400~450 nm波长范围内的LIBS光谱图如图2所示。
图 2. 样品在400~450 nm波长范围内的光谱图
Fig. 2. Spectra of sample in the wavelength range of 400-450 nm
下载图片 查看所有图片
由图2可知:在无偏振条件下,元素特征分立谱线叠加在较强的连续背景辐射之上,这将会对LIBS定性和定量分析产生较大干扰;在有偏振条件下,PRLIBS较好地抑制了连续背景辐射,使得元素的特征分立谱线凸显出来。图3为重金属元素Pb的特征谱线Pb Ⅰ: 405.780 nm在有、无偏振条件下的LIBS光谱图。
图 3. 特征谱线Pb Ⅰ:405.780 nm在有、无偏振条件下的LIBS图
Fig. 3. LIBS spectra of characteristic spectral line Pb Ⅰ: 405.780 nm under the conditions of polarization and non-polarization
下载图片 查看所有图片
3.2 偏振特性分析
对于部分偏振光而言,用Imax来表示振动方向占优势的光矢量强度,用Imin表示振动方向处于劣势的光矢量强度。部分偏振光可以看作是由线偏振光与自然光混合而成的,假设线偏振光的强度和总的光强分别用Ip和It表示,偏振度用P表示,则有:
连续背景辐射和元素特征分立谱线的光谱强度I均满足马吕斯定律,则有:
式中:θ为偏振角;A和B均为常数。将(4)式代入(3)式中可得
在激光能量为100 mJ、延迟时间为0 μs和采集门宽为5 μs的条件下,在0~360°偏振角范围内,每隔20°旋转Glan-Thompson偏振棱镜。在各偏振角下测量3组实验数据,每组数据由10次激光脉冲累加而成,最终的光谱强度为3组实验数据的平均值。图4和图5分别示出特征谱线Pb Ⅰ:405.780 nm及其相应的连续背景辐射光谱强度随偏振角的变化。
图 4. 特征谱线Pb Ⅰ:405.780 nm光谱强度随偏振角的变化
Fig. 4. Variation of spectral intensity of characteristic spectral line Pb Ⅰ: 405.780 nm with polarization angle
下载图片 查看所有图片
图 5. 连续背景辐射光谱强度随偏振角的变化
Fig. 5. Variation of spectral intensity of continuous background radiation with polarization angle
下载图片 查看所有图片
图4和图5表明,元素的特征分立谱线和连续背景辐射的光谱强度均较好地符合马吕斯定律,特征谱线Fe Ⅰ:404.581 nm、Pb Ⅰ:405.780 nm、Ca Ⅰ:422.670 nm和Mg Ⅰ:518.361 nm及其相应的连续背景辐射的偏振度分别为0.27、0.17、0.25、0.23和0.70、0.64、0.69、0.67,连续背景辐射的偏振度高于元素特征分立谱线的偏振度。偏振条件下土壤LIBS光谱中的连续背景辐射得到有效抑制,而元素特征分立谱线所受影响相对较小。表2为4条特征谱线及其相应连续背景辐射的偏振度。
表 2. 4条特征谱线及其相应连续背景辐射的偏振度
Table 2. Polarization degree of four characteristic spectral lines and corresponding continuous background radiation
| Characteristicspectralline /nm | Polarizationdegree | Continuousbackgroundradiation /nm | Polarizationdegree |
|---|
| Fe Ⅰ: 404.581 | 0.27 | 403.5-404.0 | 0.70 | | Pb Ⅰ: 405.780 | 0.17 | 405.0-405.4 | 0.64 | | Ca Ⅰ: 422.670 | 0.25 | 421.0-421.4 | 0.69 | | Mg Ⅰ: 518.361 | 0.23 | 517.7-518.0 | 0.67 |
|
查看所有表
3.3 定量对比分析
3.3.1 光谱稳定性
光谱稳定性是光谱测量中一个十分重要的参数,一般用RSD来描述光谱稳定性。在有、无偏振条件下,均测量5组实验数据,每组数据由20次激光脉冲累加而成。对比分析了4条特征谱线Fe Ⅰ:404.581 nm、Pb Ⅰ:405.780 nm、Ca Ⅰ:422.670 nm和Mg Ⅰ:518.361 nm的RSD,具体结果如图6所示。
图 6. 有、无偏振条件下的RSD
Fig. 6. RSD under the conditions of polarization and non-polarization
下载图片 查看所有图片
由图6的结果可知:无偏振条件下,Fe Ⅰ:404.581 nm、Pb Ⅰ:405.780 nm、Ca Ⅰ:422.670 nm和Mg Ⅰ:518.361 nm的RSD分别为9.22%、7.73%、9.27%和7.15%;有偏振条件下,Fe Ⅰ:404.581 nm、Pb Ⅰ:405.780 nm、Ca Ⅰ:422.670 nm和Mg Ⅰ:518.361 nm的RSD分别为5.94%、5.53%、6.03%和5.81%。由于连续背景辐射具有一定的随机性和波动性,PRLIBS有效抑制了连续背景辐射,提高了光谱的稳定性和重复性。与无偏振条件相比,有偏振条件下4条特征谱线的RSD分别下降了3.28%、2.20%、3.24%和1.34%。
3.3.2 光谱的SBR
对4条特征谱线Fe Ⅰ:404.581 nm、Pb Ⅰ:405.780 nm、Ca Ⅰ:422.670 nm和Mg Ⅰ:518.361 nm的SBR做进一步分析。表3为有、无偏振条件下样品中4条特征谱线的SBR。
表3的结果表明,与无偏振条件下的LIBS光谱相比,PRLIBS使得4条特征谱线Fe Ⅰ:404.581 nm、Pb Ⅰ:405.780 nm、Ca Ⅰ:422.670 nm和Mg Ⅰ:518.361 nm的SBR分别提高了5.59、5.67、5.30和7.35倍。
3.3.3 元素检测限
以土壤中的Pb元素为例,在有、无偏振条件下对比分析LIBS元素检测限。在激光能量为100 mJ、延迟时间为1 μs和采集门宽为5 μs的条件下,每个浓度的土壤样品均测量5组实验数据,每组数据由20次激光脉冲累加而成,最终Pb元素的光谱强度为5组实验数据的平均值。图7和图8分
表 3. 有、无偏振条件下4条特征谱线的SBR
Table 3. SBR of four characteristic spectral lines under the conditions of polarization and non-polarization
| Condition | SBR |
|---|
| Fe Ⅰ: 404.581 nm | Pb Ⅰ: 405.780 nm | Ca Ⅰ: 422.670 nm | Mg Ⅰ: 518.361 nm |
|---|
| Polarization | 3.28 | 3.88 | 9.33 | 2.62 | | Non-polarization | 18.33 | 21.99 | 49.43 | 19.25 |
|
查看所有表
别示出了无偏振和有偏振条件下LIBS光谱强度与Pb元素浓度之间的关系。
图 7. 无偏振条件下元素Pb的定标曲线
Fig. 7. Calibration curve of Pb without polarization
下载图片 查看所有图片
图 8. 有偏振条件下元素Pb的定标曲线
Fig. 8. Calibration curve of Pb with polarization
下载图片 查看所有图片
元素的检测限为
式中:cL为元素的检测限;SB为空白背景的标准偏差;k为定标曲线的斜率。
有、无偏振条件下Pb元素检测限的对比结果如表4所示。
表 4. 有、无偏振条件下Pb的检测限
Table 4. Limit of detection of Pb under the conditions of polarization and non-polarization
| Condition | k | SB | cL /10-6 |
|---|
| Polarization | 1.43 | 18.8 | 39.4 | | Non-polarization | 1.93 | 11.2 | 17.4 |
|
查看所有表
由表4可知,偏振条件下Pb元素的检测限得以降低,约为无偏振条件下的44%。
4 结论
土壤LIBS光谱中连续背景辐射和元素特征谱线均具有偏振特性,并且连续背景辐射的偏振度大于特征分立谱线。PRLIBS技术提高了光谱的稳定性和SBR,降低了重金属元素的检测限。在土壤重金属LIBS测量中,利用PRLIBS技术能够有效地抑制土壤LIBS光谱中的连续背景辐射,可在一定程度上提高LIBS技术对元素检测的定量分析能力。
参考文献
[1] 谷艳红, 赵南京, 马明俊, 等. 基于元素粒子比的土壤重金属元素快速分析方法研究[J]. 中国激光, 2015, 42(11): 1115002.
谷艳红, 赵南京, 马明俊, 等. 基于元素粒子比的土壤重金属元素快速分析方法研究[J]. 中国激光, 2015, 42(11): 1115002.
Gu Y H, Zhao N J, Ma M J, et al. Rapid measurement of particle ratio in soil by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(11): 1115002.
Gu Y H, Zhao N J, Ma M J, et al. Rapid measurement of particle ratio in soil by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(11): 1115002.
[2] Yi R X, Guo L B, Zou X H, et al. Background removal in soil analysis using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with standard addition method[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(3): 2607-2618.
Yi R X, Guo L B, Zou X H, et al. Background removal in soil analysis using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with standard addition method[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(3): 2607-2618.
[3] Fu X, Duan F J, Huang T T, et al. A fast variable selection method for quantitative analysis of soils using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2017, 32(6): 1166-1176.
Fu X, Duan F J, Huang T T, et al. A fast variable selection method for quantitative analysis of soils using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2017, 32(6): 1166-1176.
[4] 胡丽, 赵南京, 刘文清, 等. 基于多元校正的水体Pb元素LIBS定量分析[J]. 光学学报, 2015, 35(6): 0630001.
胡丽, 赵南京, 刘文清, 等. 基于多元校正的水体Pb元素LIBS定量分析[J]. 光学学报, 2015, 35(6): 0630001.
Hu L, Zhao N J, Liu W Q, et al. Quantitative analysis of Pb in water based on multivariate calibration with LIBS[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(6): 0630001.
Hu L, Zhao N J, Liu W Q, et al. Quantitative analysis of Pb in water based on multivariate calibration with LIBS[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(6): 0630001.
[5] 朱光正, 郭连波, 郝中骐, 等. 气雾化辅助激光诱导击穿光谱检测水中的痕量金属元素[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(2): 024212.
朱光正, 郭连波, 郝中骐, 等. 气雾化辅助激光诱导击穿光谱检测水中的痕量金属元素[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(2): 024212.
Zhu G Z, Guo L B, Hao Z Q, et al. Detection of metal element in water using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy assisted by nebulizer[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(2): 024212.
Zhu G Z, Guo L B, Hao Z Q, et al. Detection of metal element in water using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy assisted by nebulizer[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(2): 024212.
[6] Díaz Pace D M, Miguel R E, Di Rocco H O, et al. . Quantitative analysis of metals in waste foundry sands by calibration free-laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2017, 131: 58-65.
Díaz Pace D M, Miguel R E, Di Rocco H O, et al. . Quantitative analysis of metals in waste foundry sands by calibration free-laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2017, 131: 58-65.
[7] Gottlieb C, Millar S, Günther T, et al. Revealing hidden spectral information of chlorine and sulfer in data of a mobile laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system using chemometrics[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2017, 132: 43-49.
Gottlieb C, Millar S, Günther T, et al. Revealing hidden spectral information of chlorine and sulfer in data of a mobile laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system using chemometrics[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2017, 132: 43-49.
[8] 辛勇, 孙兰香, 杨志家, 等. 基于一种远程双脉冲激光诱导击穿光谱系统原位分析钢样成分[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(7): 2255-2259.
辛勇, 孙兰香, 杨志家, 等. 基于一种远程双脉冲激光诱导击穿光谱系统原位分析钢样成分[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(7): 2255-2259.
Xin Y, Sun L X, Yang Z J, et al. In-situ analysis of solid steel samples with remote double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(7): 2255-2259.
Xin Y, Sun L X, Yang Z J, et al. In-situ analysis of solid steel samples with remote double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(7): 2255-2259.
[9] Zhou W D, Li K X, Shen Q M, et al. Optical emission enhancement using laser ablation combined with fast pulse discharge[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(3): 2573-2578.
Zhou W D, Li K X, Shen Q M, et al. Optical emission enhancement using laser ablation combined with fast pulse discharge[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(3): 2573-2578.
[10] Wang Z, Feng J, Li L Z, et al. A non-linearized PLS model based on multivariate dominant factor for laser induced breakdown spectroscopy measurements[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2011, 26(11): 2175-2182.
Wang Z, Feng J, Li L Z, et al. A non-linearized PLS model based on multivariate dominant factor for laser induced breakdown spectroscopy measurements[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2011, 26(11): 2175-2182.
[11] 王金梅, 颜海英, 郑培超, 等. 基于激光诱导击穿光谱定量检测土壤中营养元素的研究[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(11): 1111002.
王金梅, 颜海英, 郑培超, 等. 基于激光诱导击穿光谱定量检测土壤中营养元素的研究[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(11): 1111002.
Wang J M, Yan H Y, Zheng P C, et al. Quantitative detection of nutrient elements in soil based on laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(11): 1111002.
Wang J M, Yan H Y, Zheng P C, et al. Quantitative detection of nutrient elements in soil based on laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(11): 1111002.
[12] 杨文斌, 李斌成, 韩艳玲, 等. 激光诱导击穿光谱技术定量分析氩气和氮气中的痕量氧含量[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(10): 1011001.
杨文斌, 李斌成, 韩艳玲, 等. 激光诱导击穿光谱技术定量分析氩气和氮气中的痕量氧含量[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(10): 1011001.
Yang W B, Li B C, Han Y L, et al. Quantitative analysis of trace oxygen concentration in argon and nitrogen based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(10): 1011001.
Yang W B, Li B C, Han Y L, et al. Quantitative analysis of trace oxygen concentration in argon and nitrogen based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(10): 1011001.
[13] 朱元硕, 李颖, 卢渊, 等. 基于向量空间模型的岩屑LIBS光谱分类识别方法[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(9): 2891-2895.
朱元硕, 李颖, 卢渊, 等. 基于向量空间模型的岩屑LIBS光谱分类识别方法[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(9): 2891-2895.
Zhu Y S, Li Y, Lu Y, et al. Study on identification method based on vector space model for geological cuttings using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(9): 2891-2895.
Zhu Y S, Li Y, Lu Y, et al. Study on identification method based on vector space model for geological cuttings using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(9): 2891-2895.
[14] 杨晖, 黄林, 刘木华, 等. 激光诱导击穿光谱结合移动窗口偏最小二乘对脐橙中重金属Cd的检测[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2017, 54(8): 083002.
杨晖, 黄林, 刘木华, 等. 激光诱导击穿光谱结合移动窗口偏最小二乘对脐橙中重金属Cd的检测[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2017, 54(8): 083002.
Yang H, Huang L, Liu M H, et al. Detection of cadmium in navel orange by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with moving window partial least square[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2017, 54(8): 083002.
Yang H, Huang L, Liu M H, et al. Detection of cadmium in navel orange by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with moving window partial least square[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2017, 54(8): 083002.
[15] Liu Y M, Singha S, Witt T E, et al. Observation of near total polarization in the ultrafast laser ablation of Si[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(16): 161502.
Liu Y M, Singha S, Witt T E, et al. Observation of near total polarization in the ultrafast laser ablation of Si[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(16): 161502.
[16] Penczak J S, Liu Y M, Gordon R J. Polarization resolved laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of Al[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2009, 113: 13310-13317.
Penczak J S, Liu Y M, Gordon R J. Polarization resolved laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of Al[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2009, 113: 13310-13317.
[17] Zhao Y B, Singha S, Liu Y M, et al. Polarization resolved laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 2009, 34(4): 494-496.
Zhao Y B, Singha S, Liu Y M, et al. Polarization resolved laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 2009, 34(4): 494-496.
[18] Liu Y M, Penczak J S, Gordon R J. Nanosecond polarization resolved laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(2): 112-114.
Liu Y M, Penczak J S, Gordon R J. Nanosecond polarization resolved laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(2): 112-114.
[19] Liu J, Tao H Y, Gao X, et al. The polarization characteristics of single shot nanosecond laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of Al[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2013, 22(4): 044206.
Liu J, Tao H Y, Gao X, et al. The polarization characteristics of single shot nanosecond laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of Al[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2013, 22(4): 044206.
余洋, 赵南京, 孟德硕, 马明俊, 兰智高. 基于偏振分辨LIBS技术的土壤重金属检测研究[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(8): 0811001. Yu Yang, Zhao Nanjing, Meng Deshuo, Ma Mingjun, Lan Zhigao. Detection of Heavy Metals in Soil Based on Polarization Resovled LIBS Technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45(8): 0811001.
 下载: 843次
下载: 843次