Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2020, 5 (6): 065201, Published Online: Nov. 24, 2020
Development of low-coherence high-power laser drivers for inertial confinement fusion  Download: 554次
Download: 554次
Figures & Tables
Fig. 3. Phase-matching curve for frequency tripling of chirp pulses. Reprinted with permission from Raoult et al. , Opt. Lett. 24 (5), 354-356 (1999). Copyright 1999 Optical Society of America.

Fig. 5. Schematic of the ISI method. Reprinted with permission from Zhao et al. , Appl. Opt. 58 (8), 2121–2126 (2019). Copyright 2019 Optical Society of America.

Fig. 6. (a) Demonstration of the echelon-free ISI method. Reprinted with permission from Lehmberg et al. , J. Appl. Phys. 62 (7), 2680–2701 (1987). Copyright 1987 AIP Publishing LLC. (b) Spatial mode dispersion in the optical fiber smoothing method. Reprinted with permission from Veron et al. , Opt. Commun. 65 , 42–46 (1988). Copyright 1988 Elsevier.

Fig. 7. Optical frequency as a function of time for different light sources: (a1) high-coherence pulse; (b1) chirped pulse and transform-limited pulse; (c1) phase-modulated pulse; (d1) instantaneous broadband pulse. (a2), (b2), (c2), and (d2) are the corresponding frequency–phase diagrams.

Fig. 8. Schematic of the low-coherence front-end system. AWG, arbitrary waveform generator; AM, amplitude modulator; OC, optical circulator; SM LD, single-mode laser diode; WDM, wavelength division multiplexer; AOM, acoustic optical modulator; FC, fiber collimator; M, mirror; HWP, half-wave plate; P, polarizer; BC, birefringent crystal; MMLD, multimode laser diode. Reprinted with permission from Rao et al. , Opt. Laser Technol. 122 , 105850 (2020). Copyright 2020 Elsevier.

Fig. 9. Illustration of the pulse shapes that can be generated by our system: (a) square pulse; (b) high-contrast pulse; (c) exponential pulse; (d) spectra of different pulse shapes. Reprinted with permission from Rao et al. , Opt. Laser Technol. 122 , 105850 (2020). Copyright 2020 Elsevier.

Fig. 10. (a) Spectrum without spectral control. (b) Spectrum with a nearly flat top. (c) Saddle-type spectrum for a Nd:glass amplifier. (d) Temporal profiles of the spectra in (a)–(c). Reprinted with permission from Rao et al. , Opt. Laser Technol. 122 , 105850 (2020). Copyright 2020 Elsevier.

Fig. 11. Schematic of the high-gain preamplifier: FE, front end; RA, repetitive amplifier; SA, single-shot amplifier; FA, fiber amplifier; HWP, half-wave plate; FR, Faraday rotator; PC, Pockels cell; PBS, polarizing beam splitter; BF, birefringent filter; P, polarizer; M, mirror; BE, beam expander; LCSM, liquid crystal spatial modulator; PSF, spatial filter; Φ, Nd:glass rod (diameter, mm); EOS, electro-optical switch. Reprinted with permission from Cui et al. , Opt. Lett. 44 (11), 2859–2862 (2019). Copyright 2019 Optical Society of America.

Fig. 12. (a) Temporal and (b) spectral profiles of the light in the single-shot amplifier. The “sa” label indicates the saddle-shaped spectrum. Reprinted with permission from Cui et al. , Opt. Lett. 44 (11), 2859–2862 (2019). Copyright 2019 Optical Society of America.

Fig. 13. Visibility of interference fringes at different locations. The dots are experimental results, and the curves are fitting results. FE, front end, RA, repetitive amplifier, SA, single-shot amplifier. Reprinted with permission from Cui et al. , Opt. Lett. 44 (11), 2859–2862 (2019). Copyright 2019 Optical Society of America.

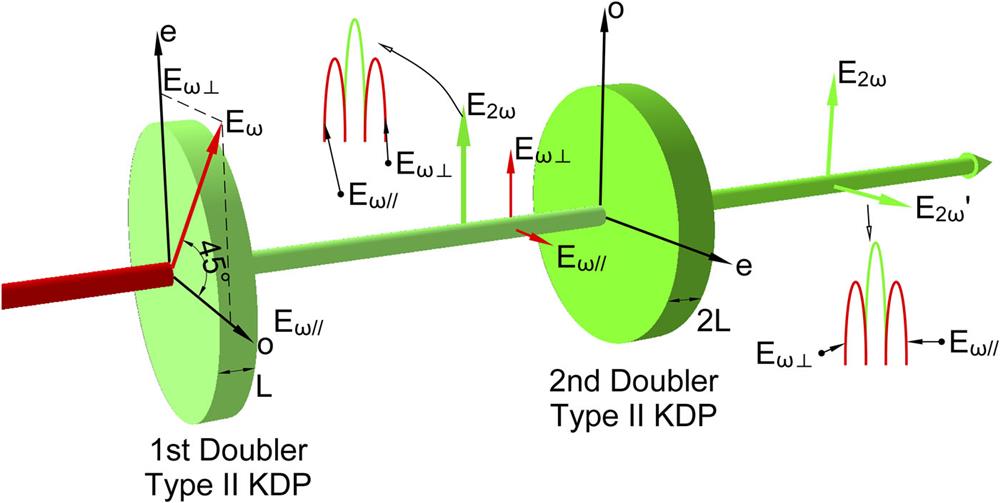
Fig. 18. Results of SHG in the low-coherence laser facility. Reprinted with permission from Ji et al. , Opt. Lett. 44 (17), 4359–4362 (2019). Copyright 2019 Optical Society of America.

Fig. 19. Near fields of the fundamental wave (a) and the second harmonic (b), and the corresponding far fields of the fundamental wave (c) and the second harmonic (d). (a) and (c) are reprinted with permission from Cui et al. , Opt. Lett. 44 (11), 2859–2862 (2019). Copyright 2019 Optical Society of America. (b) and (d) are reprinted with permission from Ji et al. , Opt. Lett. 44 (17), 4359–4362 (2019). Copyright 2019 Optical Society of America.

Fig. 20. Experimental and simulation results for second-harmonic efficiency vs fundamental wave energy when a KDP crystal is used.

Fig. 21. Temporal intensity distribution of second-harmonic conversion measured by a streak camera with a resolution of 11 ps.

Fig. 23. Focal spots obtained using ISI + LA with smoothing times (a) T = τ , (b) T = 10τ , (c) T = 100τ , and (d) T = 1000τ . (e)–(h) show the corresponding x -axis intensity distributions. Reprinted with permission from Zhao et al. , Appl. Opt. 58 (8), 2121–2126 (2019). Copyright 2019 Optical Society of America.

Fig. 24. (a) Experimental focal spot using partial ISI + LA with broadband light. (b) Theoretical result. Reprinted with permission from Li et al. , Appl. Opt. 59 (10), 2976–2982 (2020). Copyright 2020 Optical Society of America.

Yanqi Gao, Yong Cui, Lailin Ji, Daxing Rao, Xiaohui Zhao, Fujian Li, Dong Liu, Wei Feng, Lan Xia, Jiani Liu, Haitao Shi, Pengyuan Du, Jia Liu, Xiaoli Li, Tao Wang, Tianxiong Zhang, Chong Shan, Yilin Hua, Weixin Ma, Xun Sun, Xianfeng Chen, Xiuguang Huang, Jian Zhu, Wenbing Pei, Zhan Sui, Sizu Fu. Development of low-coherence high-power laser drivers for inertial confinement fusion[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2020, 5(6): 065201.