Photonics Research, 2021, 9 (2): 02000202, Published Online: Jan. 29, 2021
Adaptive optical focusing through perturbed scattering media with a dynamic mutation algorithm  Download: 627次
Download: 627次
Figures & Tables
Fig. 2. (a) Experimental setup. L 1 f = 60 mm L 2 L 3 f = 250 mm L 4 f = 50 mm 1920 × 1080 40 × = = =

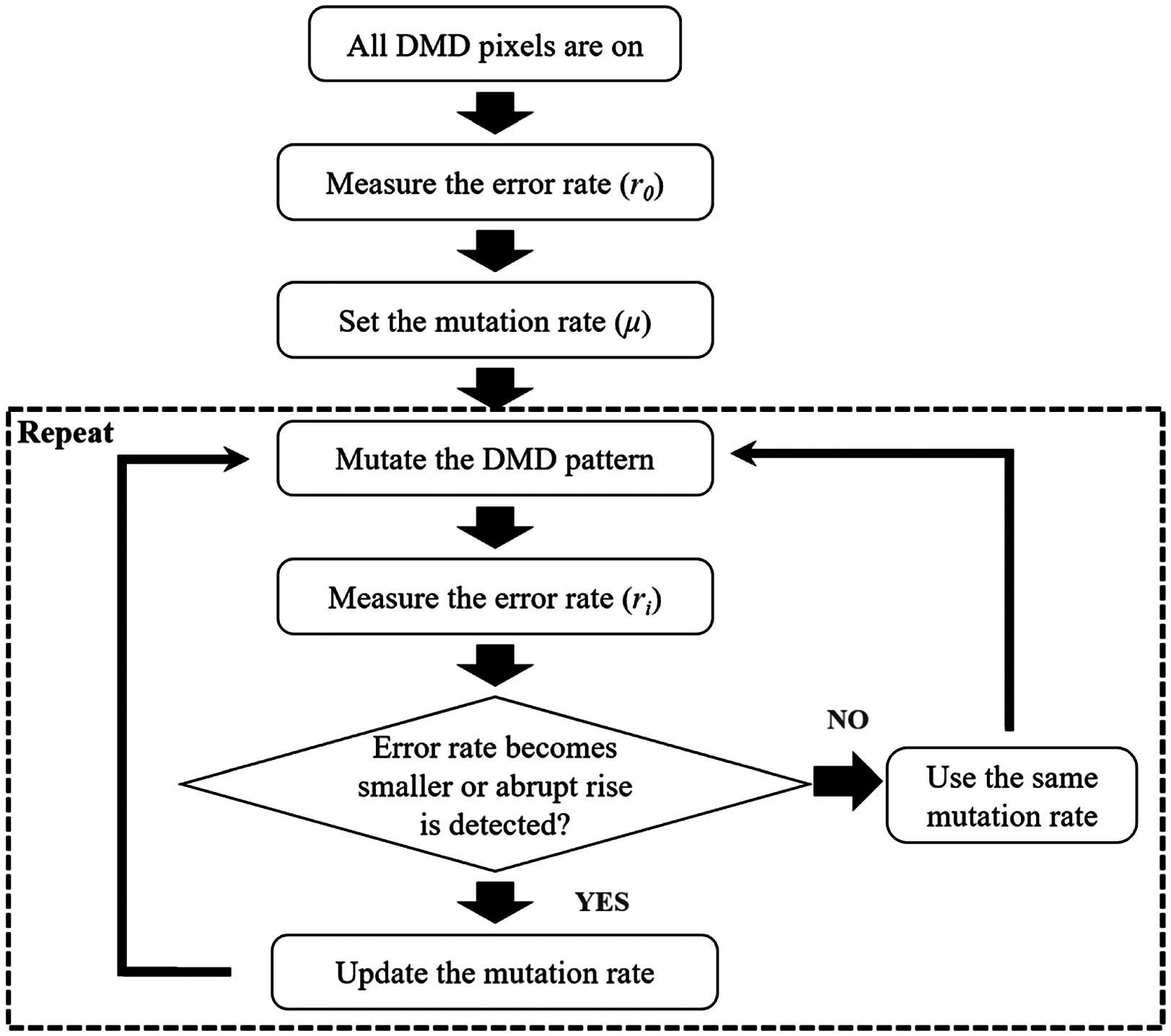
Fig. 3. Relative PBR error rate curves (η ′ − r r = 0 η ′ = ( 1 – 2 r ) 2

Fig. 4. Simulation results of the DMA, GA, and CSA under different conditions: (a) noise-free; (b) low-noise: 0.3 ⟨ I 0 ⟩ 0.6 ⟨ I 0 ⟩

Fig. 5. Experimental results of the DMA (red solid curve), GA (black dashed curve), and CSA (green dotted curve) focusing performance against strong noise.

Fig. 6. (a) Relationship between fiber rotation and PBR drop. (b) Measurement required to rebound for different degrees of fiber rotation. Each dot in (a) and (b) is averaged from five executions, and the error bars show the standard deviation of the measurements. The optimizations in (a) and (b) are realized by the DMA. (c) Experimental focusing performance of the DMA in response to 2.5°, 5°, and 7.5° fiber rotation.

Fig. 8. Focal spots at four different stages with different algorithms: before optimization (zeroth measurement), before fiber rotation (5000th measurement), right after 5° fiber rotation (5001st measurement), and after reoptimization (15,000th measurement). The 150 μm scale bar is applicable to all images in this figure.

Table1. Initial Parameters Set for the DMA, GA, and CSA
|
Huanhao Li, Chi Man Woo, Tianting Zhong, Zhipeng Yu, Yunqi Luo, Yuanjin Zheng, Xin Yang, Hui Hui, Puxiang Lai. Adaptive optical focusing through perturbed scattering media with a dynamic mutation algorithm[J]. Photonics Research, 2021, 9(2): 02000202.