1 上海大学材料科学与工程学院, 上海 200444
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所中科院强激光材料重点实验室, 上海 201800
3 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
采用时域有限差分法研究了硒化锌基底的抛物线型周期阵列仿生微结构的光学性质,重点分析了微结构阵列的周期、高度、占空比和形状轮廓等对反射率的影响,得到了有较好增透效果的结构参数。根据模拟参数进行两次干涉曝光制备掩模,采用反应离子刻蚀技术制备周期阵列微结构。通过场发射扫描电子显微镜对微结构的表面形貌进行表征,并采用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪在中红外波段分别对双面抛光、单面微结构的硒化锌片进行透过率测试。结果表明:单面微结构样品在2~5 μm范围内的整体平均透过率比双面抛光硒化锌基片提高了10%,在2.3 μm处的最大透过率为82%。
衍射 增透微结构 时域有限差分法 干涉曝光
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
2 CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200050, China
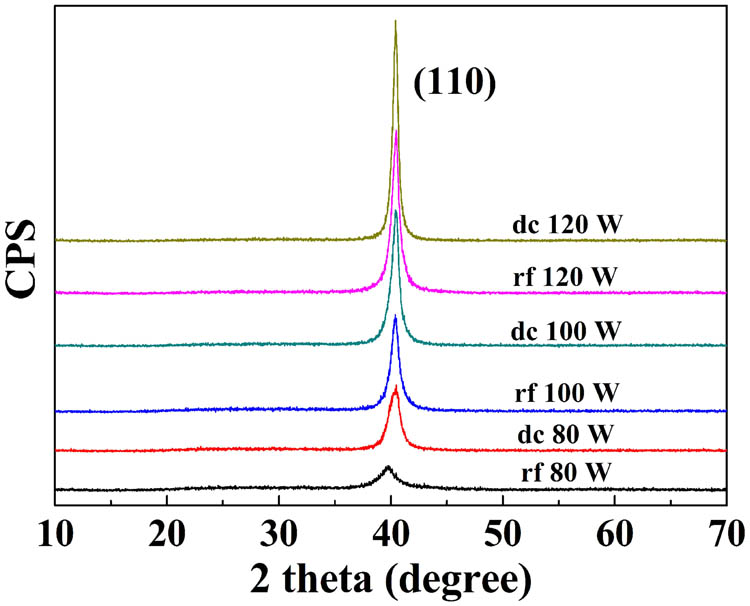
Molybdenum (Mo) thin films, most commonly used as electrical back contacts in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 (CIGS) solar cells, are deposited by rf and dc magnetron sputtering in identical systems to study the discrepancy and growth mechanisms of the two sputtering techniques. The results reveal that though different techniques generally deposit films with different characteristic properties, Mo films with similar structural and physical properties can be obtained at respective suitable deposition conditions. Highly adhesive and conductive Mo films on soda lime glass are further optimized, and the as-fabricated solar cells reach efficiencies as high as 9.4% and 9.1% without an antireflective layer.
310.1860 Deposition and fabrication 040.5350 Photovoltaic 350.6050 Solar energy Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(4): 043101





