Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Light Field Manipulation and Information Acquisition, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, School of Physical Science and Technology, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710129, China
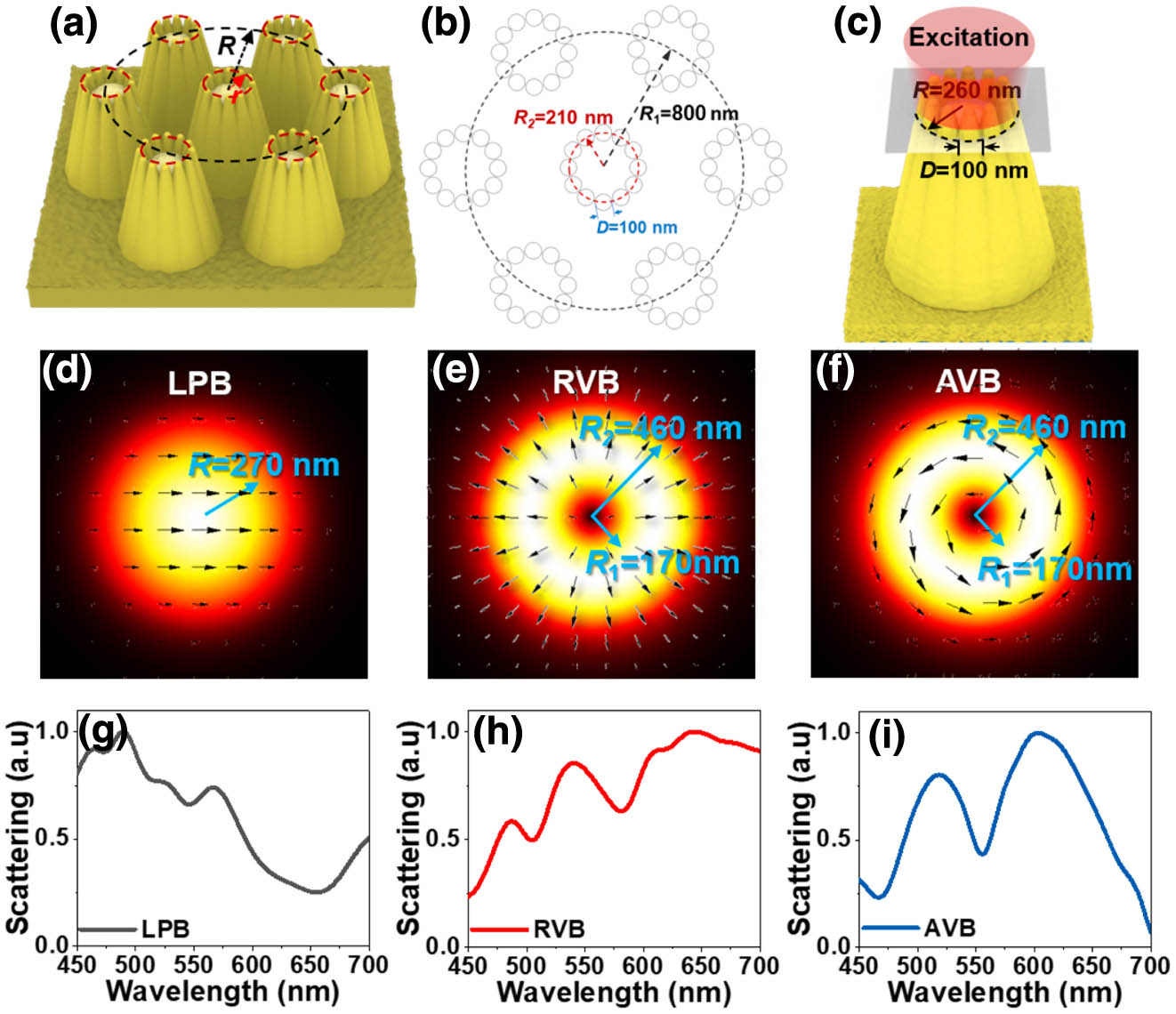
Noble metallic nanostructures with strong electric near-field enhancement can significantly improve nanoscale light–matter interactions and are critical for high-sensitivity surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Here, we use an azimuthal vector beam (AVB) to illuminate the plasmonic tips circular cluster (PTCC) array to enhance the electric near-field intensity of the PTCC array, and then use it to improve SERS sensitivity. The PTCC array was prepared based on the self-assembled and inductive coupled plasmon (ICP) etching methods. The calculation results show that, compared with the linearly polarized beam (LPB) and radial vector beam excitations, the AVB excitation can obtain stronger electric near-field enhancement due to the strong resonant responses formed in the nanogap between adjacent plasmonic tips. Subsequently, our experimental results proved that AVB excitation increased SERS sensitivity to 10-13 mol/L, which is two orders of magnitude higher than that of LPB excitation. Meanwhile, the PTCC array had excellent uniformity with the Raman enhancement factor calculated to be . This kind of vector light field enhancing Raman spectroscopy may be applied in the field of sensing technologies, such as the trace amount detection.
surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy plasmonic tips circular cluster array azimuthal vector beam surface plasmon polaritons Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(3): 033603

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, School of Physics Science and Technology, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China
2 MOE Key Laboratory of Weak-Light Nonlinear Photonics, TEDA Applied Physics Institute and School of Physics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300457, China
We present the generation of the nanosecond cylindrical vector beams (CVBs) in a two-mode fiber (TMF) and its applications of stimulated Raman scattering. The nanosecond (1064 nm, 10 ns, 10 Hz) CVBs have been directly produced with mode conversion efficiency of ~18 dB (98.4%) via an acoustically induced fiber grating, and then the stimulated Raman scattering signal is generated based on the transmission of the nanosecond CVBs in a 100-m-long TMF. The transverse mode intensity and polarization distributions of the first-order Stokes shift component (1116.8 nm) are consistent with the nanosecond CVBs pump pulse.
vector beam stimulated Raman scattering fiber grating Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(1): 010603

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Space Applied Physics and Chemistry, Ministry of Education, and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, School of Science, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China
2 Université Polytechnique Hauts de France, IEMN DOAE CNRS, Campus Le Mont Houy, 59309, Valenciennes Cedex, France
Goodness of fit is demonstrated for theoretical calculation of z-scan data based on beams propagating in the nonlinear medium and the Fresnel–Kirchhoff diffraction integral in experiments with high nonlinear refraction and absorption. The constancy of nonlinear optical parameters is achieved regardless of sample thickness and laser intensity, which clarifies the physical significance of optical parameters. We have obtained = 2.0 × 10?19 m2/W and = 5.0 × 10?13 m/W for carbon disulfide excited by a pulsed laser at 800 nm with pulse duration of 35 fs, which are independent of sample thickness and laser intensity. Affirming constancy of the extracted parameters to the incident light intensity may become a practice to verify the goodness of the z-scan experiment.
z-scan technique nonlinear refraction and absorption nonlinear optical coefficient carbon disulfide Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(7): 071903

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Space Applied Physics and Chemistry, Ministry of Education, and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, School of Science, North Western Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China
2 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117583, Singapore
3 LEES Program, Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research & Technology (SMART), Singapore 138602, Singapore
A polarization-insensitive plasmonic absorber is designed consisting of Au fishnet structures on a TiO2 spacer/Ag mirror. The fishnet structures excite localized surface plasmon and generate hot electrons from the absorbed photons, while the TiO2 layer induces Fabry–Perot resonance, and the Ag mirror acts as a back reflector. Through optimizing the TiO2 layer thickness, numerical simulation shows that 97% of the incident light is absorbed in the Au layer. The maximum responsivity and external quantum efficiency of the device can approach 5 mA/W and ~1%, respectively, at the wavelength of 700 nm.
plasmonic absorber Fabry–Perot resonance internal photoemission surface plasmon Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(5): 052402
1 西北工业大学理学院陕西省光信息技术重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710072
2 西北工业大学理学院超常条件材料物理与化学教育部重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710072
光纤结构光场作为光场调控的一个重要分支,逐渐引起了研究者们的广泛关注。首先基于光纤矢量模式理论,讨论了光纤中具有空间偏振/相位奇异特性的结构光场的产生机理;然后,介绍了光纤结构光场的产生方法,如长周期光纤光栅耦合法、光纤端面微结构法和轨道角动量转换法等;最后,介绍了光纤结构光场在超分辨成像、涡旋光通信、等离子针尖纳米聚焦和非线性频率转换等方面的一些典型应用。
物理光学 光场调控 矢量光场 涡旋光场 模式耦合
1 厦门理工学院光电与通信工程学院福建省光电技术与器件重点实验室, 厦门市LED照明应用工程技术研究中心, 福建 厦门 361024
2 西北工业大学理学院空间应用物理化学教育部重点实验室, 陕西省光信息技术重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710072
使用含镁摩尔分数为5%的掺镁铌酸锂晶体对57.4 fs脉冲在1550 nm通信波段进行了Ⅰ型(o+o-e)和0型(e+e-e)的倍频对比实验。对于Ⅰ型倍频, 在4.3 GW/cm2的峰值功率密度下得到了谱宽为28 nm、脉宽为79 fs的谐波脉冲, 转换效率最高达54%; 对于0型倍频, 在3.7 GW/cm2的峰值功率密度下得到了谱宽为2.1 nm的谐波脉冲, 转换效率最高为40%。分别从飞秒脉冲多波长成分的相位匹配(频域)和基波与谐波脉冲的群速度匹配(时域)两个角度, 对倍频过程中基波脉冲和谐波脉冲的演变进行了详细分析。发现同时满足多波长成分相位匹配时, 传播中谐波的谱宽能维持不变; 而仅满足中心波长相位匹配时, 谐波光谱则随着传播长度的增加而逐渐变窄。
超快光学 Ⅰ型倍频 飞秒脉冲 群速度匹配 掺镁铌酸锂
1 西安交通大学激光红外研究所,西安,710049
2 西安华腾光电有限责任公司,西安,710043
本文提出了一种高精度激光电子二维倾角测量技术,该技术利用液体表面多次光反射,将倾角变化转换成激光光斑的位移,并通过多次光学反射实现光学放大,从而实现了倾角和倾角变化的高精度测量.利用本技术实现的倾角测量仪器具有测量精度高、体积小等优点,经过标定试验系统测量精度达到2.5″.高精度激光电子二维倾角测量系统可广泛应用于水坝安全监测工程、各种建筑和检测领域.
倾角测量 大坝安全监测 PSD
1 西安交通大学激光红外研究所,西安,710049
2 西安华腾光电有限责任公司,西安,710049
详细阐述了电子散斑时间平均法振动测量技术的原理,通过对影响测量精度的诸因素进行理论和实验分析,提出通过应用连续相位扫描技术克服相移系统相移不准确所带来的误差.通过散斑平均技术的实施,消除散斑对测量精度的影响.在实验中得到了满意的测量结果.通过线性近似法,解决了振幅低于30 nm的振动测量问题,从而使系统分辨率达到亚纳米级,测量精度达到纳米级.
振动模态 散斑平均 相移
1 西安交通大学激光红外研究所,西安,710049
2 西安华腾光电有限责任公司,西安,710043
3 湖南省电力试验研究所,湖南,410007
采用软硬件滤波技术来消除振动和空气扰动的影响,通过现场仪器标定技术来增强测量系统的适应性,非线性补偿技术、温度控制等技术的实施,使得研制出的发电机组标高测量系统具有测量动态范围大、测量精度高、实时快速、现场适应性好等特点.
标高测量 中值滤波 线性拟合





