
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Terahertz Science and Technology Research Center, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
2 National Key Laboratory of Application Specific Integrated Circuit, Hebei Semiconductor Research Institute, Shijiazhuang 050051, China
3 Center for Terahertz Waves, College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Technology, Ministry of Education, Tianjin 300072, China
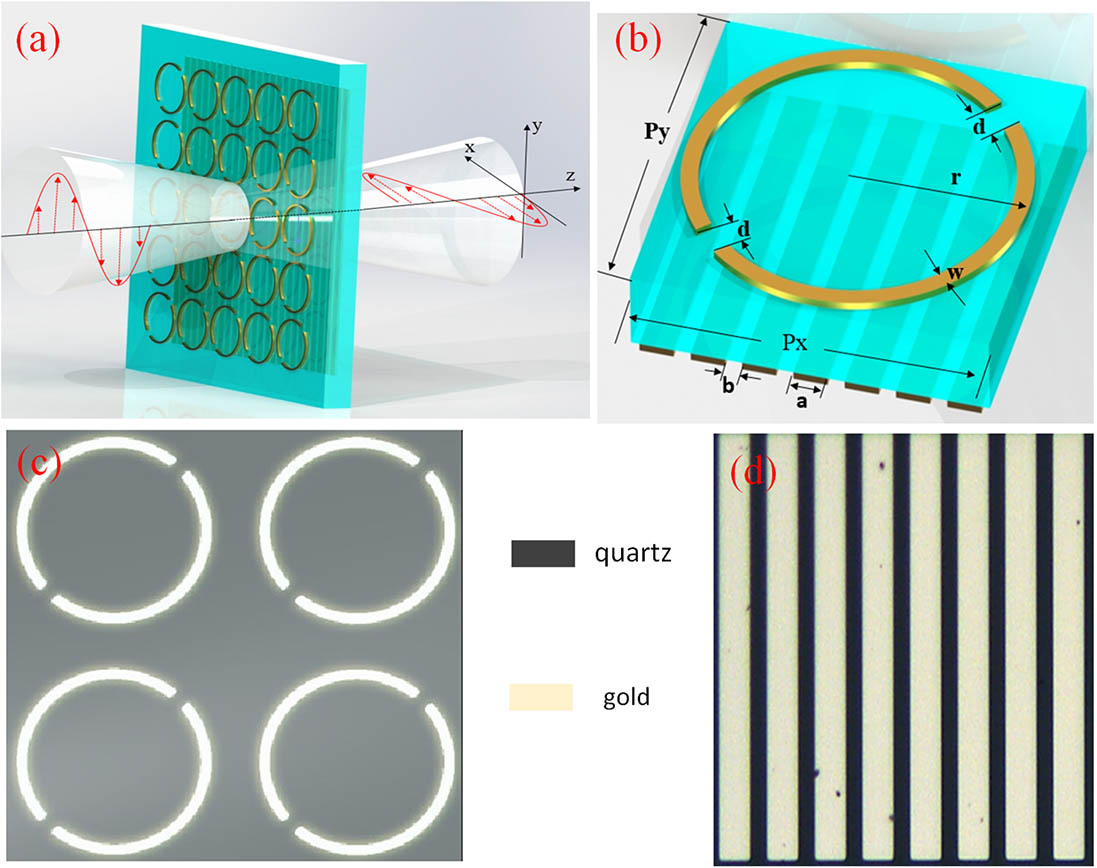
This Letter presents a double-layer structure combining a cracked cross meta-surface and grating surface to realize arbitrary incident linear terahertz (THz) wave polarization conversion. The arbitrary incident linear polarization THz wave will be induced with the same resonant modes in the unit cell, which results in polarization conversion insensitive to the linear polarization angle. Moreover, the zigzag-shaped resonant surface current leads to a strong magnetic resonance between the meta-surface and gratings, which enhances the conversion efficiency. The experimental results show that a more than 70% conversion rate can be achieved under arbitrary linear polarization within a wide frequency band. Moreover, around 0.89 THz nearly perfect polarization conversion is realized.
160.3918 Metamaterials 050.2230 Fabry-Perot 260.5430 Polarization Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(4): 041602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Terahertz Science Cooperative Innovation Center, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
2 National Key Laboratory of Application Specific Integrated Circuit, Hebei Semiconductor Research Institute, Shijiazhuang 050051, China
3 Center for Terahertz Waves, College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Technology (Ministry of Education), Tianjin 300072, China
In this Letter, we demonstrate a linear polarization conversion of transmitted terahertz wave with double-layer meta-grating surfaces, which integrated the frequency selectivity of a split ring resonator metasurface and the polarization selectivity of a metallic grating surface. Since the double-layer can reduce the loss, and the Fabry–Perot like resonant effect between the two layers can improve the conversion efficiency, this converter can rotate the incident y-polarized terahertz wave into an x-polarized transmitted wave with relatively low loss and high efficiency. Experimental results show that an average conversion efficiency exceeding 75% from 0.25 to 0.65 THz with the highest efficiency of 90% at 0.43 THz with only 2 dB loss has been achieved.
160.3918 Metamaterials 050.2230 Fabry-Perot Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(8): 081601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physical Electronics, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
2 School of Information and Communication, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, Guilin 541004, China
A polarization-insensitive, square split-ring resonator (SSRR) is simulated and experimented. By investigating the influence of the asymmetrical arm width in typical SSRRs, we find that the variation of the arm width enables a blue shift of the resonance frequency for the 0° polarized wave and a red shift of the resonance frequency for the 90° polarized wave. Thus, the resonance frequency for the 0° polarized wave and the resonance frequency for the 90° polarized wave will be identical by asymmetrically adjusting the arm width of the SSRR. Two modified, split-ring resonators (MSRRs) that are insensitive to the polarization with asymmetrical arm widths are designed, fabricated, and tested. Excellent agreement between the simulations and experiments for the MSRRs demonstrates the polarization insensitivity with asymmetrical arm widths. This work opens new opportunities for the investigation of polarization-insensitive, split-ring resonator metamaterials and will broaden the applications of split-ring resonators in various terahertz devices.
350.2450 Filters, absorption 160.3918 Metamaterials 040.2235 Far infrared or terahertz Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(10): 101601
电子科技大学 物理电子学院 太赫兹研究中心,四川 成都610054
基于Smith-Purcell(SP)效应,采用粒子模拟的方法探讨了电子束团激发一维介质光子晶体中的SP辐射特性.模拟研究了单个束团激发一维介质圆柱光子晶体产生的SP辐射现象,并对周期束团激发的THz频段的相干SP辐射进行了模拟分析.研究表明,提高介质的相对介电常数和增加光子晶体的层数都可使辐射强度增加,选择合适的参数能够有效地增强THz频段的相干SP辐射强度.
Smith-Purcell辐射 电子束团 相干辐射 photonic crystal SP radiation electron bunch THz THz coherent radiation
设计了等离子体填充的二维金属光子晶体特殊开放腔体结构,并采用粒子模拟技术(PIC)建立了基于等离子体填充腔体结构物理模型,分析了等离子体填充下二维腔体的各模式场分布特性,以及等离子体的引入对腔体内各模式工作频率、电场幅值的影响。结果表明: 腔体内各模式的电场强度随等离子体密度的增加而减弱,模式频率随背景等离子体归一化频率的提高而增加,工作模式的产生与激励方式密切相关。
等离子体填充 金属光子晶体 腔体 慢波系统 plasma-filled metallic photonic crystal cavity slow wave system 强激光与粒子束
2014, 26(4): 043001
1 曲阜师范大学物理工程学院, 山东 曲阜 273165
2 电子科技大学物理电子学院, 四川 成都 610054
等离子体光子晶体是等离子体学科和光子晶体学科交叉的产物,它不仅具有一般光子晶体的性质, 而且还体现等离子体的特性,通过改变等离子体参数或外加磁场可有效控制其带隙。若在可调带隙的等 离子体光子晶体中构造适当缺陷,则可形成可调滤波器和波导等器件,在工程方面具有重要应用。 结合本课题组工作,综述了等离子体光子晶体的研究进展,在此基础上,展望了等离子体光子晶体的发 展前景,为人们进一步研究等离子体光子晶体的特性和应用提供参考。
量子光学 可调带隙 等离子体参数 等离子体光子晶体 quantum optics tunable photonic band gap plasma parameters plasma photonic crystals
1 电子科技大学 物理电子学院, 成都 610054
2 四川教育学院 物理与电子技术系, 成都 610041
采用基于场匹配理论的数值计算和仿真技术对中心频率为0.225 THz的两路波导功率合成器的场分布特性及合成效率进行了研究。数值计算结果表明:随着两路输入波相位差的增大,合成波束的峰值场的幅值逐步减小;增加输入波导间隔板厚度,合成波束峰值场的位置逐步远离输入端口,使合成波导的长度增加;仿真和数值计算得到了基于一致的结果。仿真结果表明:当两路输入信号的相位差小于35°时,合成效率大于90%,带宽为10.000 GHz。
波导不连续性 场匹配方法 波束合成 功率合成 waveguide discontinuity field-matched method wave beam combining power combining
电子科技大学,物理电子学院高能所,四川,成都,610054
采用理论分析和粒子模拟相结合的方法,对连续电子注通过平板矩形光栅产生毫米波段史密斯-帕塞尔(SP)超辐射机理进行了研究.研究结果表明:选择恰当的电子注与光栅尺寸参数,光栅表面慢波将与电子注互作用,使电子注产生群聚,群聚的电子束团将在光栅表面产生史密斯-帕塞尔超辐射,其辐射频率为电子注与光栅表面慢波互作用同步点频率的整数倍,其辐射角度方向与史密斯-帕塞尔公式所预期的基本一致, 表面慢波由于光栅的有限长度也能在其端头以一定的形式辐射出去.
色散方程 史密斯-帕塞尔效应 超辐射 粒子模拟
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Physical Electronics, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054
The relative band gap for a rhombus lattice photonic crystal is studied by plane wave expansion method and high frequency structure simulator (HFSS) simulation. General wave vectors in the first Briliouin zone are derived. The relative band gap as a function of air-filling factor and background material is investigated, respectively, and the nature of photonic band gap for different lattice angles is analyzed by the distribution of electric energy. These results would provide theoretical instruction for designing optical integrated devices using photonic crystal with a rhombus lattice.
光子晶体 菱形晶格 相对带隙宽度 空气填充率 相对介电常数 填充率 160.4670 Optical materials 230.0230 Optical devices 230.3120 Integrated optics devices 220.0220 Optical design and fabrication Chinese Optics Letters
2008, 6(4): 279
电子科技大学物理电子学院,四川 成都 610054
近年来,随着国际上掀起的太赫兹(Terahertz,THz)研究热,太赫兹科学技术的发展更为迅速。但是,对于THz的各种功能器件,利用基于经典电磁理论的微波技术手段或者利用基于量子理论方法的光学技术手段都遇到了很大的困难。90年代末,随着频率禁带处在THz波段的光子晶体(Photonic crystal,PC)制作方法和技术的提高,基于光子晶体的THz器件应运而生。为此,就国际上在光子晶体THz滤波器,光子晶体THz波导,光子晶体THz光纤和光子晶体THz谐振腔方面所做的主要工作和研究成果进行了较详细的论述分析及归纳总结,并对光子晶体THz器件未来的发展提出了几点看法。
太赫兹 光子晶体 光子晶体THz器件 Terahertz photonic crystal photonic crystal Terahertz devices





