Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Beijing Institute of Tracking and Telecommunications Technology, Beijing 100094, China
2 School of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
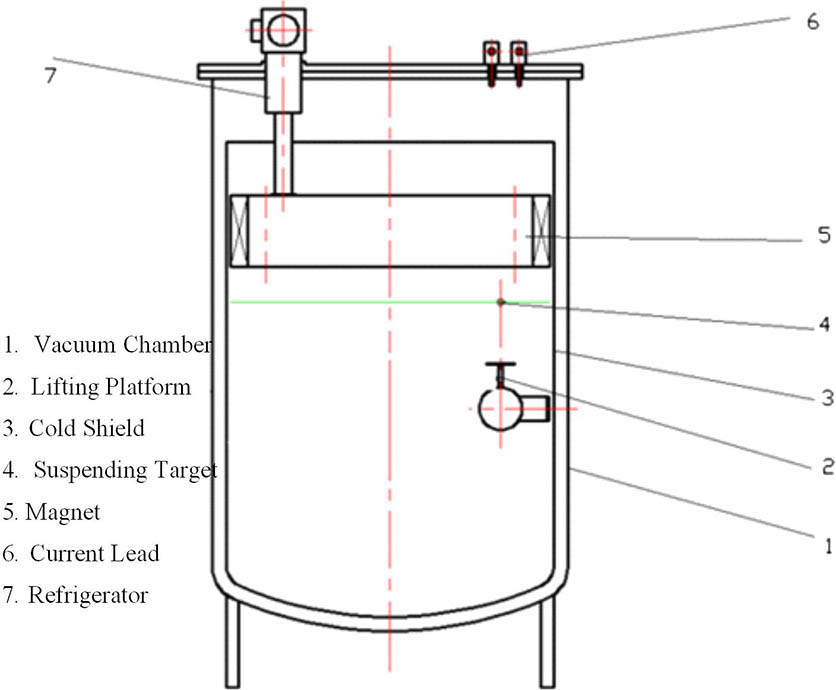
Impact and torsion pendulums are applied in impulse coupling experiments of high-energy laser irradiation of space debris. It is difficult to achieve a multi-pulse experiment and thus hard to analyze the multi-pulse impulse coupling effect. Here, we designed a new recoil impulse experimental measurement system of non-contact, multi-degrees of freedom, and multi-pulse irradiation. The system used a low-pressure and low-temperature vacuum chamber to simulate the space environment, the pinning effect of magnetic levitation to achieve aluminum target suspension, and high-speed cameras to record the displacement over time to calculate the impulse of the target. Then the impulse coupling experiment of multi-pulse laser irradiation on the aluminum target was performed. The result shows that the multi-pulse impulse coupling effect is not the linear accumulation of coupling results by every single-pulse and multi-pulse coefficient that decreases with the increase of the number of pulses, and eventually stabilizes as the decrease gets smaller.
140.3325 Laser coupling 140.3390 Laser materials processing Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(12): 121401
为了精确地研究全覆盖条件下高能脉冲激光辐照空间碎片的冲量矢量的特性, 在假设烧蚀阈值系数、激光入射能量密度和冲量耦合系数随到靶能量密度线性变化的基础上, 提出了精细描述冲量耦合系数的处理方法, 进一步完善了冲量矢量的数值计算方法。以圆柱体碎片为例, 通过仿真实验, 从不同角度分析了冲量耦合系数对冲量矢量的影响, 并指出适当提高激光入射能量密度能够显著增大冲量矢量。
激光技术 激光烧蚀 高能脉冲激光 冲量耦合系数 空间碎片 激光与光电子学进展
2016, 53(12): 121404





