1 福建省超快激光技术及应用重点实验室(厦门大学),福建 厦门 361005
2 厦门大学深圳研究院,广东 深圳 518129
位于人眼可见波段(380~780 nm)的激光,在显示、生物医疗、精密加工、精密光谱、光通信等领域有着重要的应用价值。在众多可见光激光的产生方法中,可见光掺稀土光纤激光器因具有高效率、高光束质量、结构简单且免维护等优势,近年来受到国内外的广泛关注。对可见光掺稀土光纤激光器的研究进展进行了详细综述,介绍了可见光连续波光纤激光器、可见光调Q脉冲光纤激光器及可见光锁模脉冲光纤激光器的产生方式和特点。最新研究进展表明,其可覆盖蓝(~480 nm)、青(~491 nm)、绿(~520 nm)、黄(~573 nm)、橙(~605 nm)、红(~635 nm)及深红(~717 nm)等丰富的可见光波长,全光纤可见光输出功率已迈向10 W,而且可见光锁模超短脉冲宽度已窄至<200 fs。结合应用需求,简要展望了可见光波段光纤激光器的发展趋势。
激光器 可见光激光 掺稀土光纤激光器 连续波 调Q 锁模
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Fujian Key Laboratory of Ultrafast Laser Technology and Applications, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Innovation Laboratory for Sciences and Technologies of Energy Materials of Fujian Province (IKKEM), Xiamen 361005, China
3 Prokhorov General Physics Institute, Dianov Fiber Optics Research Center, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow 119333, Russia
4 Devyatykh Institute of Chemistry of High-Purity Substances, Russian Academy of Sciences, Nizhny Novgorod 603951, Russia
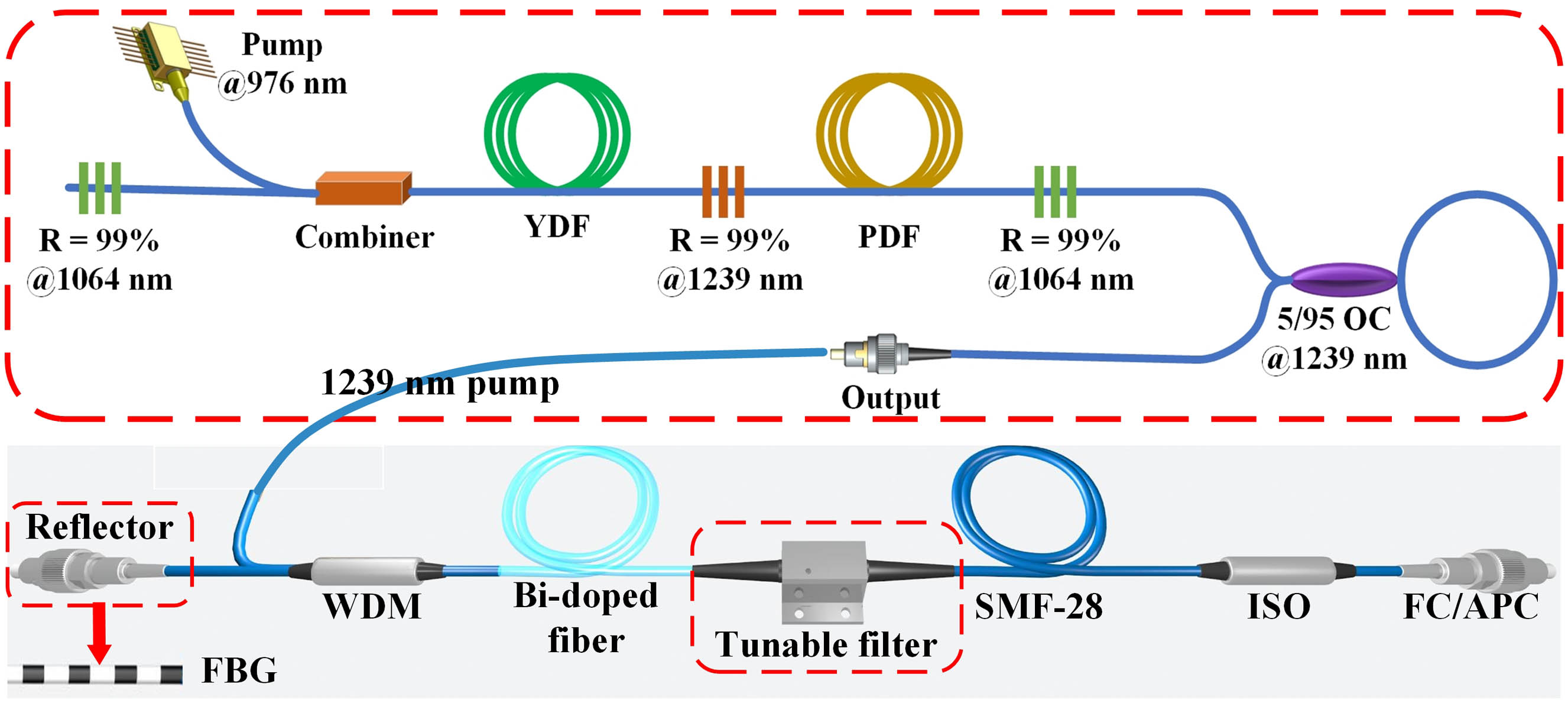
We have successfully generated a 1.3/1.4 µm random fiber laser (RFL) using bismuth (Bi)-doped phosphosilicate fiber. The Bi-doped RFL has shown excellent long-term operational stability with a standard deviation of approximately 0.34% over 1 h at a maximum output power of 549.30 mW, with a slope efficiency of approximately 29.21%. The Bi-doped phosphosilicate fiber offers an emission spectrum ranging from 1.28 to 1.57 µm, indicating that it can be tuned within this band. Here, we demonstrated a wavelength-tuning fiber laser with a wavelength of 1.3/1.4 µm, achieved through the using of a fiber Bragg grating or a tunable filter. Compared to traditional laser sources, the RFL reduces the speckle contrast of images by 11.16%. Due to its high stability, compact size, and high efficiency, this RFL is highly promising for use in biomedical imaging, communication, and sensor applications.
random fiber laser bismuth-doped fiber wavelength tuning fiber laser Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(7): 071401

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Electronic Engineering, School of Electronic Science and Engineering (National Model Microelectronics College), Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
In this paper, we propose a temperature-sensing scheme utilizing a passively mode-locked fiber laser combined with the beat frequency demodulation system. The erbium-doped fiber is used in the laser ring cavity to provide the gain and different lengths of single-mode fibers inserted into the fiber ring cavity operate as the sensing element. Different temperature sensitivities have been acquired in the experiment by monitoring the beat frequency signals at different frequencies. The experimental results indicate that the beat frequency shift has a good linear response to the temperature change. The sensitivity of the proposed sensor is about -44 kHz/°C when the monitored beat frequency signal is about 10 GHz and the ratio of the sensing fiber to the overall length of the laser cavity is 10 m/17.5 m, while the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the monitored signal is approximately 30 dB. The proposed temperature-sensing scheme enjoys attractive features such as tailorable high sensitivity, good reliability, high SNR, and low cost, and is considered to have great potential in practical sensing applications.
temperature sensing mode-locking fiber laser beat frequency Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(2): 020603

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Science and Technology on Electro-Optical Information Security Control Laboratory, Tianjin 300308, China
Conventional ultrashort pulsewidth measurement technology is autocorrelation based on second-harmonic generation; however, nonlinear crystals and bulky components are required, which usually leads to the limited wavelength range and the difficult adjustment with free-space light alignment. Here, we proposed a compact all-fiber pulsewidth measurement technology based on the interference jitter (IJ) and field-programmable gate array (FPGA) platform, without requiring a nonlinear optical device (e.g., nonlinear crystal/detector). Such a technology shows a wide measurement waveband from 1 to 2.15 µm at least, a pulsewidth range from femtoseconds to 100 ps, and a small relative error of 0.15%–3.8%. In particular, a minimum pulse energy of 219 fJ is experimentally detected with an average-power-peak-power product of . The IJ-FPGA technology may offer a new route for miniaturized, user-friendly, and broadband pulsewidth measurement.
pulse width measurement interference jitter FPGA platform optical device Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(3): 031404
1 国网福建省电力有限公司漳州供电公司,福建 漳州 363000
2 厦门大学电子科学与技术学院(国家示范性微电子学院),福建 厦门 361005
报道了全光纤耗散孤子被动锁模掺铒光纤激光器,通过调节泵浦功率和偏振态可以进一步获得2孤子和3孤子的束缚态耗散孤子。利用反常色散光纤对宽带2孤子束缚态耗散孤子进行脉宽压缩,压缩后的脉宽用双曲正割拟合为96 fs,计算得时间带宽积为0.324,表明其为近转换极限脉冲。宽带光谱的获得得益于腔内的色散管理和碳纳米管可饱和吸收体的大调制深度(20%)。在此基础上,获得了光谱宽度达35 nm的耗散孤子(中心波长为1.57 μm),这也是基于碳纳米管产生耗散孤子的最宽光谱。
激光光学 超快非线性光学 脉冲压缩 锁模激光器 束缚态孤子 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(11): 1114003
介绍了3 μm光纤激光器常用的光纤基质和稀土增益离子,分析了3 μm稀土掺杂光纤激光器的工作原理,并且从不同研究视角回顾了3 μm稀土掺杂光纤激光器的研究进展。其中,锁模中红外光纤激光器、小型化全光纤中红外激光器和3~4 μm更长波长的中红外光纤激光器是目前研究的主要趋势和热点。随着3 μm中红外光纤激光相关技术的迅速发展,结构更紧凑、性能更优异的3 μm光纤激光器不断涌现,必将大大推动其商业化和实用化的进程,更好地满足不同领域的应用需求。
激光器 光纤激光器 中红外 稀土离子 氟化物光纤 小型化 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(17): 170605
厦门大学电子科学与技术学院(国家示范性微电子学院), 福建 厦门 361005
以被动锁模正色散掺镱(Yb)光纤激光器为研究对象,实验比较研究了激光腔内滤波带宽对产生正色散束缚态孤子的影响。采用高掺Yb光纤作为增益介质,半导体饱和吸收镜作为锁模部件,获得1064 nm全光纤线型腔锁模激光器。当腔内带通滤波器选用不同带宽(0.2,1.0,1.2,2.3 nm)时,观察到不同的皮秒锁模脉冲状态。在滤波带宽较小(0.2 nm)或较大(2.3 nm)时,仅产生稳定的单脉冲耗散孤子;相反地,在滤波带宽适中(1.0 nm或1.2 nm)时,分别观察到典型的相位差为π和-π/2束缚态耗散孤子,脉宽和脉冲间隔均分别为3 ps和14 ps。将束缚态耗散孤子激光通过主控振荡功率放大技术放大至1.4 W后,将其注入到光子晶体光纤中,获得了750~1600 nm超连续谱(10 dB谱宽),输出功率约为0.7 W,相比传统耗散孤子抽运具有更好的光谱平坦性。
激光器 束缚态孤子 滤波带宽 超连续谱

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Information and Communication Branch, State Grid Jiangxi Electric Power Corporation Ltd., Nanchang 330077, China
2 Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
We demonstrate a 2080 nm long-wavelength mode-locked thulium (Tm)-doped fiber laser operating in the dissipative soliton resonance (DSR) regime. The compact all-fiber dumbbell-shaped laser is simply constructed by a 50/50 fiber loop mirror (FLM), a 10/90 FLM, and a piece of large-gain Tm-doped double-clad fiber pumped by a 793 nm laser diode. The 10/90 FLM is not only used as an output mirror, but also acts as a periodical saturable absorber for initiating DSR mode locking. The stable DSR pulses are generated at the center wavelength as long as 2080.4 nm, and the pulse duration can be tunable from 780 to 3240 ps as the pump power is increased. The maximum average output power is 1.27 W, corresponding to a pulse energy of 290 nJ and a nearly constant peak power of 93 W. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the longest wavelength for DSR operation in a mode-locked fiber laser.
060.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(3): 030602
厦门大学电子科学与技术学院电子工程系,福建 厦门 361005
为了提升MoS2可饱和吸收体在脉冲激光器中的稳定性和工作性能,本论文采用氧化石墨烯(GO)作为胶体表面活性剂,通过LPE 的方法剥离出少层MoS2,并进一步开展了少层GO-MoS2用于掺铒光纤激光器(EDFL)锁模的实验研究。在实验中获得了中心波长为1558 nm,重复频率为7.86 MHz,脉宽为1.9 ps 的稳定锁模脉冲激光。当泵浦功率为60.5 mW 时,输出功率为0.48 mW,脉冲峰值功率为32.1 W。研究证明,采用这种方法制备的新型复合二维材料有利于保持少层MoS2的稳定性,并且能提高MoS2可饱和吸收体的损伤阈值,以获取更大脉冲能量的超快激光。
被动锁模 光纤激光器 复合二维材料 passive mode-locking fiber laser composite two-dimensional material GO-MoS2 GO-MoS2

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Key Laboratory of Materials for High-Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Shenzhen Research Institute of Xiamen University, Shenzhen 518057, China
The direct generation of passively Q-switched lasers at a green wavelength has rarely been investigated in the past. In this Letter, we demonstrate a passively Q-switched praseodymium-doped yttrium lithium fluoride green laser at 522 nm using CdTe/CdS quantum dots as a saturable absorber. A maximum average output power of 33.6 mW is achieved with the shortest pulse width of 840 ns. The corresponding pulse energy and peak power reached 0.18 μJ and 0.21 W, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first demonstration in regard to a quantum dots saturable absorber operating in the green spectral region.
140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(2): 020005





