1 苏州大学电子信息学院,江苏 苏州 215006
2 苏州市先进光通信网络技术重点实验室,江苏 苏州 215006
随着智能网联汽车的发展,车载网络作为汽车内传感器、处理器和执行器间的信息共享平台,逐步向简化架构和更高带宽方向发展。通过对智能网联汽车上几种主要新型车载传感器的工作原理介绍和带宽需求分析,分析了车载网络的带宽需求趋势。同时,本文根据对传统车载网络的网络架构和主流协议的回顾,以及对当前车载网络发展的追踪,指出了车载网络在汽车智能化趋势下面临的带宽瓶颈,光纤传输是未来车载网络的发展方向。最后,通过车载网络对光纤要求的分析和对塑料光纤传输技术的行业现状和最新研究进展的调研,说明了车载光纤传输技术亟须进一步研究。
光纤通信 摄像头 激光雷达 雷达 智能网联汽车 车载网络 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(5): 0500005
1 北京交通大学全光网络与现代通信网教育部重点实验室, 北京 100044
2 北京交通大学光波技术研究所, 北京 100044
少模掺铒光纤放大器(FM-EDFA)是长距离模分复用(MDM)光纤通信系统中必不可少的中继器件,其模间增益差(DMG)直接影响系统的通信质量。为实现FM-EDFA中不同模式的增益均衡,在包层泵浦条件下,提出了一种支持4模式组的铒离子分层掺杂环芯光纤,且无需考虑泵浦模式。对环芯光纤进行了设计,通过控制纤芯中心凹陷和外部凹槽折射率引起的模式分布变化,结合合理设计的铒离子掺杂半径及浓度来减小DMG。结果表明,当铒离子在环芯内分双层掺杂时,最大 DMG从0.8 dB(单层均匀掺杂)降低至0.44 dB(环芯双层)。在全C波段(1530~1565 nm)中,4模式组增益超过22 dB,最大DMG低于0.45 dB,噪声系数小于5.3 dB。包层泵浦结构有利于实现FM-EDFA的全光纤连接,易于与MDM通信系统集成,并发挥掺铒光纤放大器的全光补偿优势。
光通信 光纤通信 少模掺铒光纤放大器 环芯光纤 增益均衡 包层泵浦
1 广东工业大学信息工程学院,先进光子技术研究院,广东 广州 510006
2 广东省信息光子技术重点实验室,广东 广州 510006
3 河源广工大协同创新研究院,广东 河源 517000
为了进一步增加光纤通信容量,作为空分复用实现方案之一的多芯光纤技术吸引了人们越来越多的研究兴趣。与此同时,基于多芯光纤的各种新型有源、无源光器件也不断涌现。其中,多芯光纤光栅,由于结合了多芯光纤与光纤光栅的独特优势,为新型全光纤器件的设计和应用提供了多种可能,在光纤通信、光纤传感、光纤激光器等领域具有广泛的应用空间。本文分别从多芯光纤选择性刻写和全芯刻写出发,详细介绍了多种基于不同光源、不同写入方式的多芯光纤光栅刻写方案,并结合不同应用场景,分析了不同方案的技术特点。
光纤光栅 光纤通信 光纤传感器 多芯光纤 光栅刻写 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(3): 0300004
1 华中科技大学武汉国家光电研究中心, 湖北 武汉 430074
2 武汉长进激光技术有限公司, 湖北 武汉 430206
为了保证掺铒光纤在辐照环境下的工作性能与寿命,采用改进的化学气相沉积(MCVD)方法制备了C波段抗辐照掺铒光纤。在常温下使用 60Co辐射源对自研掺铒光纤进行累积剂量为1500 Gy、平均剂量率为0.2 Gy/s的辐照,结果发现,该光纤在980 nm和1550 nm处的辐致损耗(RIA)分别为1.4 dB/m和0.8 dB/m。搭建了掺铒光纤放大器(EDFA)进行增益测试,测试过程中采用输入功率为-20 dBm的1550 nm信号与波长为980 nm的泵浦源。测试结果表明,在100 mW和500 mW泵浦功率下,1550 nm处的辐致增益变化(RIGV)分别为0.8 dB和0.2 dB。
光纤光学 掺铒光纤 抗辐照 光纤通信 掺铒光纤放大器 中国激光
2021, 48(20): 2015001
1 国防科技大学前沿交叉学科学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
2 脉冲功率激光技术国家重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410073
3 高能激光技术湖南省重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410073
光纤光栅具有抗电磁干扰、耐腐蚀、可塑性强、体积小、质量轻、与光纤系统天然兼容等特点,已被广泛应用于光纤传感、光纤通信、光纤激光器等领域,并发挥了重要作用。目前,常见的光纤光栅制作方法主要有紫外曝光法、CO2激光刻写和飞秒激光刻写。飞秒激光刻写技术的出现大大简化了光纤光栅制作流程,由于其成栅机理不同于常见的紫外曝光法,无需对光纤进行载氢处理,非常有利于在超大芯径光纤上制备高性能光栅。根据是否使用相位模板,基于飞秒的光栅制备总体分为直写和相位模板辅助刻写两种方式。本文从刻写方式的角度对国内外基于飞秒激光的光纤光栅研制情况进行了全面综述,详细总结分析了各种刻写方式的特点与光栅的应用场合,指出其在分布式光纤传感、光纤通信波分复用、多波长激光器、大功率光纤激光器等方面具有潜在的重要应用价值和广泛应用前景。
激光器 光纤光栅 光纤传感器 光纤激光器 光纤通信 飞秒激光 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(11): 111420

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures and College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
Photonic waveguide arrays provide a simple and versatile platform for simulating conventional topological systems. Here, we investigate a novel one-dimensional (1D) topological band structure, a dimer chain, consisting of silicon waveguides with alternating self-coupling and inter-coupling. Coupled mode theory is used to study topological features of such a model. It is found that topological invariants of our proposed model are described by the global Berry phase instead of the Berry phase of the upper or lower energy band, which is commonly used in the 1D topological models such as the Su–Schrieffer–Heeger model. Next, we design an array configuration composed of two dimer patterns with different global Berry phases to realize the topologically protected waveguiding. The topologically protected propagation feature is simulated based on the finite-difference time-domain method and then observed in the experiment. Our results provide an in-depth understanding of the dynamics of the topological defect state in a 1D silicon waveguide array, and may provide different routes for on-chip lightwave shaping and routing.
fiber optics fiber optics communications fiber optics imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(5): 051301

Xin Tian 1,2,3Hao Li 1,2,3Le Liu 1,2,3Meng Wang 1,2,3[ ... ]Zefeng Wang 1,2,3,*
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Pulsed Power Laser Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of High Energy Laser Technology, Changsha 410073, China
We report here an ultra-broadband linearly polarized (LP) LP01 LP11 mode converter operating at 1 μm based on a long period fiber grating (LPFG) fabricated in a conventional two-mode fiber (TMF) by a line-focused CO2 laser. The measured 3 dB bandwidth is about 240 nm, which is the broadest bandwidth for such fiber mode converters. The maximum conversion efficiency between the LP01 and LP11 modes is >99% over the range of 1000 nm to 1085 nm, almost covering the whole emission band of Yb3+, which is useful for further power scaling of high-power fiber lasers operating at the 1 μm band.
060.2340 Fiber optics components 060.3735 Fiber Bragg gratings 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 140.3510 Lasers, fiber Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(12): 120602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures and College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
Inspired by recent rapid deep learning development, we present a convolutional-neural-network (CNN)-based algorithm to predict orbital angular momentum (OAM) mode purity in optical fibers using far-field patterns. It is found that this image-processing-based technique has an excellent ability in predicting the OAM mode purity, potentially eliminating the need of using bulk optic devices to project light into different polarization states in traditional methods. The excellent performance of our algorithm can be characterized by a prediction accuracy of 99.8% and correlation coefficient of 0.99994. Furthermore, the robustness of this technique against different sizes of testing sets and different phases between different fiber modes is also verified. Hence, such a technique has a great potential in simplifying the measuring process of OAM purity.
060.2310 Fiber optics 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.2350 Fiber optics imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 100603
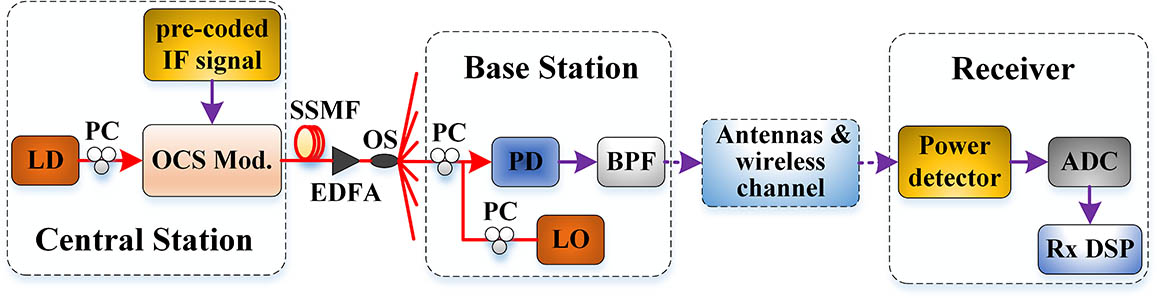
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Ministry of Education, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 611731, China
A pre-coding-assisted power detection scheme for radio over fiber downlink is presented. This scheme can eliminate laser phase noise while avoiding high energy-consuming electrical carrier required in conventional power and/or envelope detection schemes. Theoretical analysis and experimental verification are performed. 0.625 Gbaud pre-coded quadrature phase-shift keying or 16 quadrature amplitude modulation signals can both be recovered by power detection without electrical carrier assistance at the receiver after 75 km fiber transmission. Not only robust against the laser phase noise, an improvement of about 5 dB in receiver sensitivity can also be achieved, as compared with the conventional power detection scheme.
060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 060.2840 Heterodyne Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(11): 110602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Opto-electronic Information Technical Science of Ministry of Education, College of Precision Instruments and Opto-electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 Fiberhome & Fujikura Optics Co., Ltd., Wuhan 430074, China
Using the few-mode erbium-doped fiber (FM-EDF) with a simple two-layer erbium-doped structure, we demonstrate an all-fiber FM-EDF amplifier. The gain equalization among the six spatial modes supported by the FM-EDF is achieved when only the pump in the fundamental mode (LP01) is applied. When the signals in six spatial modes are simultaneously amplified, the average modal gain is about 15 dB, and differential modal gain is about 2.5 dB for the signal at 1550 nm.
060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.4230 Multiplexing 060.2410 Fibers, erbium 140.4480 Optical amplifiers Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 100604





