Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Beijing Engineering Research Center of Mixed Reality and Advanced Display, School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Key Laboratory of Photoelectronic Imaging Technology and System (Beijing Institute of Technology), Ministry of Education, Beijing 100081, China
3 Department of Hand Surgery, Beijing Ji Shui Tan Hospital, Beijing 100035, China
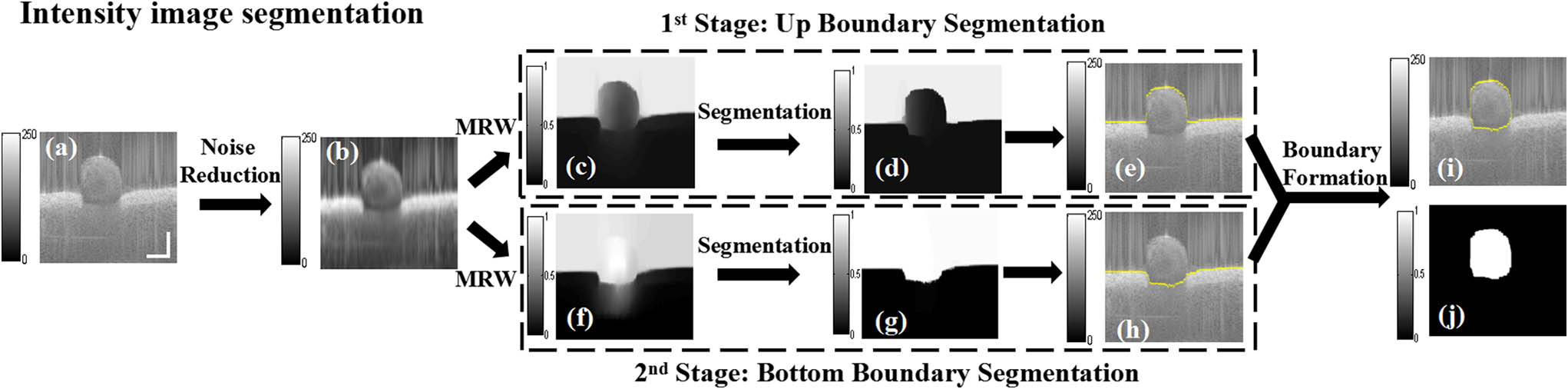
Vascular Doppler optical coherence tomography (DOCT) images with weak boundaries are usually difficult for most algorithms to segment. We propose a modified random walk (MRW) algorithm with a novel regularization for the segmentation of DOCT vessel images. Based on MRW, we perform automatic boundary detection of the vascular wall from intensity images and boundary extraction of the blood flowing region from Doppler phase images. Dice, sensitivity, and specificity coefficients were adopted to verify the segmentation performance. The experimental study on DOCT images of the mouse femoral artery showed the effectiveness of our proposed method, yielding three-dimensional visualization and quantitative evaluation of the vessel.
100.3008 Image recognition, algorithms and filters 170.4500 Optical coherence tomography Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(5): 051001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Mechanical Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China
2 Faculty of Science, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China
We present a simple method for the subsurface imaging of a nucleated cell, which is realized by measuring the difference in wrapped phase between a nucleated cell and its enucleated cell model. The latter one called as the reference phase can be simulated according to the axial thickness and the cytoplasmic refractive index. We illustrate the proposed method with theoretical analysis and numerical simulation of a binucleated cell, and prove its validity on real biological cells by imaging the HeLa cell based on its experimental phase. It shows that this method is suitable for imaging of relatively simple nucleated cells.
100.3008 Image recognition, algorithms and filters 120.5050 Phase measurement 170.0180 Microscopy 170.1530 Cell analysis Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(s1): S11001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 South China Sea Marine Prediction Center, State Oceanic Administration, Guangzhou 510301, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Oceanography in the Tropics, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
Hyperspectral optimization process exemplar, a&bb-based K model, and a water column correction model are used to process the hyperspectral data for detecting the subtle spectral difference of coral reefs. The water column correction model only tracks those effective photons by fully considering the geometrical distribution of the light field. The adaptivity of the parameters and models to the in situ data collected in Sanya Bay is evaluated. The modeled and uncorrected spectra are examined separately to reflect the coral reflectance, and the coefficients of determination for the relationships drops from 0.90 to 0.05. The retrieved bottom reflectance for 70 corals (Acropora, Porites) exhibited the classic chlorophyll features. The reflectance at 700 nm collected in Sanya Bay is relatively lower than the results conducted by other researchers. Peak ratio index and derivative analysis are utilized and are proved to be effective for coral reef classification and coral healthy assessment.
100.3005 Image recognition devices 100.3008 Image recognition, algorithms and filters 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s2): S21001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Noise reduction is one of the most important concerns in electronic speckle pattern interferometry (ESPI). According to partial differential equation (PDE) filtering theory, we present an anisotropic PDE noise-reduction model based on fringe structure information for interferometric fringe patterns. This model is based on coherence diffusion and Perona-Malik (P-M) diffusion. The former can protect the structure information offringe pattern, while the latter can effectively filter off the noise inside the fringes. The proposed model generated by the two diffusion methods helps to obtain good effects of denoising and fidelity. ESPI fringes and the phase pattern are tested. Experimental results validate the performance of the proposed filtering model.
110.6150 Speckle imaging 030.6140 Speckle 100.3008 Image recognition, algorithms and filters Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(10): 101101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Stripe motion artifacts caused by phase fluctuation in phase-resolved optical coherence tomography (OCT) result in the quality degradation of the image ofin vivo blood flow of human eye. In order to suppress the stripe motion artifacts, we design a kind of frequency rejection filter aimed at the frequency spectrum characteristics of the image. Blood flow images of human eye acquired by our research group and another group are filtered to show the performance of the proposed method. Experimental results indicate that the stripe motion artifacts in the projection images are rejected significantly with minimal loss of signal information. The proposed filter can also be used in other imaging systems with similar stripe noise.
170.5755 Retina scanning 170.4500 Optical coherence tomography 100.3008 Image recognition, algorithms and filters Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(3): 031701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
This letter presents a correlation tracking algorithm based on edge detection, in allusion to the phenomenon that the target is susceptible to interference in long-wave infrared image. Firstly, the collected imageis processed by median filtering to remove the defects in the detector. Then thegradient information of the background is filtered out by edge detection method. Secondly, to enhance the edge information, the image is dealt with mathematical morphology (MM). And finally, the correlation matching method is done to acquire the miss-distance information of the target in the image. Through theoretical simulation and practical verification, it is proved that the algorithm has a better effect on inhibiting most of the background information, protecting the target's information effectively, enlarging the weight of the target's information in the correlation operation and improving stability of the detector.
100.4999 Pattern recognition, target tracking 100.3008 Image recognition, algorithms and filters 100.2000 Digital image processing Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(s2): S21005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
A new approach is proposed to extract the rectangular building footprints from single high-resolution synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image by combining region-based information with edge-based information. We build multiscale autoregressive (MAR) model and likelihood rate classifier for SAR image to extract region information. Edge information is extracted from SAR image by using constant false alarm rate edge detector. We propose a new optimization criterion which fuses the previous extracted region information and edge information to obtain the final building footprints. The experimental result shows that the proposed method can extract the building footprints effectively.
100.0100 Image processing 100.3008 Image recognition, algorithms and filters Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(s2): S21001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Integer wavelet transform (IWT) could offer the lower computational complexity and the less storage spending for image compression than the discrete wavelet transform (DWT). But the most coefficients of the IWT image have smaller dynamic change ranges than discrete wavelet transform. In this letter, an efficient and low-complerity coding algorithm called embedded optimal coefficient scaling (EOCS) is proposed. It optimizes the distribution of the wavelet coefficients in every threshold plane and provides an efficient embedded quadtree-partitioning scheme to encode the image. Experimental results show that the presented method cannot provide peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) performance up about 2–6 dB better than set partitioning in hierarohical trees (SPIHT) without the OCSF scheme, but also support both efficiently lossy and lossless compression in single bitstream.
100.2000 Digital image processing 100.3008 Image recognition, algorithms and filters 280.0280 Remote sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(s1): S11010
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We illustrate an approach to statistical model and sequential hypothesis designed to the automatic target recognition (ATR) problem for active imaging LADAR. The key to this approach is using multihypothesis sequential tests to reduce the number of target hypotheses under consideration as more observed data are processed. The approach is potentially useful when sensor data are plentiful but computation time and processing capability are constrained. We experimentally demonstrate that the proposed recognition approach can resolve the military ground vehicle recognition problem of active imaging LADAR with a high recognition rate.
100.3008 Image recognition, algorithms and filters 280.3640 Lidar Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(s1): S11002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The curved surface projection model in fisheye image correction algorithm is presented. To analyze the causes of distortion in existing models, we establish an ideal surface projection model and compare its surface with the surfaces of existing models. Subsequently, feature points are obtained on the ideal surface according to the relationship of coordinates of fish-eye image points and their ideal three-dimentional (3D) points. Finally, the least square method is used to obtain a quadric surface and presents a quadric surface projection model. The experiment shows that the corrected image of the new model is more similar to the actual scene than the corrected images of previous models.
100.3008 Image recognition, algorithms and filters 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(1): 011002





