1 中国科学院精密测量科学与技术创新研究院波谱与原子分子物理国家重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430071
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
超稳激光是精密测量领域的关键工具,其频率稳定度很大程度上取决于频率锁定稳定度。笔者理论研究了干涉效应对锁频误差信号的影响,并通过实验研究了降低干涉效应的方法,以提高激光的频率锁定稳定度。经过优化后,锁频系统的锁定稳定度相对于参考腔线宽达到了。在参考腔线宽为21 kHz(精细度为7.5万)的情况下,将1.5 μm激光的频率稳定度锁定到水平,接近10 cm参考腔的热噪声极限。本文所提降低干涉效应的方法是研制稳定度高达水平的超稳激光器的重要参考。
激光器 激光稳定 Pound‒Drever‒Hall稳频 干涉效应 超稳腔 超稳激光
光学 精密工程
2023, 31(11): 1607
1 江苏理工学院, 江苏 常州 213001
2 锐光凯奇(镇江)光电科技有限公司, 江苏 镇江 212004
为了提高激光光斑中心的定位精度, 实现激光稳定输出的功能, 提出了基于四象限探测器的激光稳定集成化系统。首先, 根据四象限探测器的工作原理, 对四象限探测器上光斑的中心位置和偏差量进行理论计算和分析, 然后融合计算机信号处理技术和控制技术对四象限探测器信号进行闭环控制, 并将四象限探测器和光学元器件集成在多轴笼式结构中, 完成了激光稳定集成化系统设计。多次实验数据结果表明: 该系统能100%完成对光斑中心的定位, 稳定性达到94.74%, 3次实验误差的差值最大为2.422 μm。
集成化 激光稳定集成化系统 四象限探测器 中心定位 integration, laser stabilization integrated system

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA, USA
2 University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA
Controlling the delivery of multi-terawatt and petawatt laser pulses to final focus, both in position and angle, is critical to many laser applications such as optical guiding, laser–plasma acceleration, and laser-produced secondary radiation. We present an online, non-destructive laser diagnostic, capable of measuring the transverse position and pointing angle at focus. The diagnostic is based on a unique double-surface-coated wedged-mirror design for the final steering optic in the laser line, producing a witness beam highly correlated with the main beam. By propagating low-power kilohertz pulses to focus, we observed spectra of focus position and pointing angle fluctuations dominated by frequencies below 70 Hz. The setup was also used to characterize the excellent position and pointing angle correlation of the 1 Hz high-power laser pulses to this low-power kilohertz pulse train, opening a promising path to fast non-perturbative feedback concepts even on few-hertz-class high-power laser systems.
high-power lasers laser diagnostics laser stabilization High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2021, 9(2): 02000e25
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所空间激光传输与探测技术重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学材料与光电研究中心, 北京 100049
将保偏全光纤环形谐振腔作为转移腔,实现了1550 nm参考激光器到1572 nm从激光器的频率稳定度转移,并研究了温度对光纤谐振腔长期稳定性的影响。理论和实验表明,仅通过压电陶瓷调谐腔长不能很好地实现频率稳定度转移。因此,提出用压电陶瓷快反馈和温控实现环形腔的稳定度转移,可使从激光器的频率稳定度在积分时间为1 s时的阿伦方差为2×10 -12,在积分时间为1000 s时的阿伦方差为5×10 -12。
激光光学 激光稳定性 频率稳定度 保偏全光纤环形谐振腔 转移腔 温度
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2 Key Laboratory of Time and Frequency Primary Standards, National Time Service Center, Xi’an 710600, China
3 AVIC Xi’an Flight Automatic Control Research Institute, Xi’an 710065, China
We demonstrate two ultra-stable laser systems at 1064 nm by independently stabilizing two 10-cm-long Fabry–Pérot cavities. The reference cavities are on a cubic spacer, which is rigidly mounted for both low sensitivity to environmental vibration and ability for transportation. By comparing against an independent ultra-stable laser at 578 nm via an optical frequency comb, the 1064 nm lasers are measured to have frequency instabilities of 6 × 10?16 at 1 s averaging time.
laser stabilization Fabry-Pérot cavity linewidth Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(3): 030201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
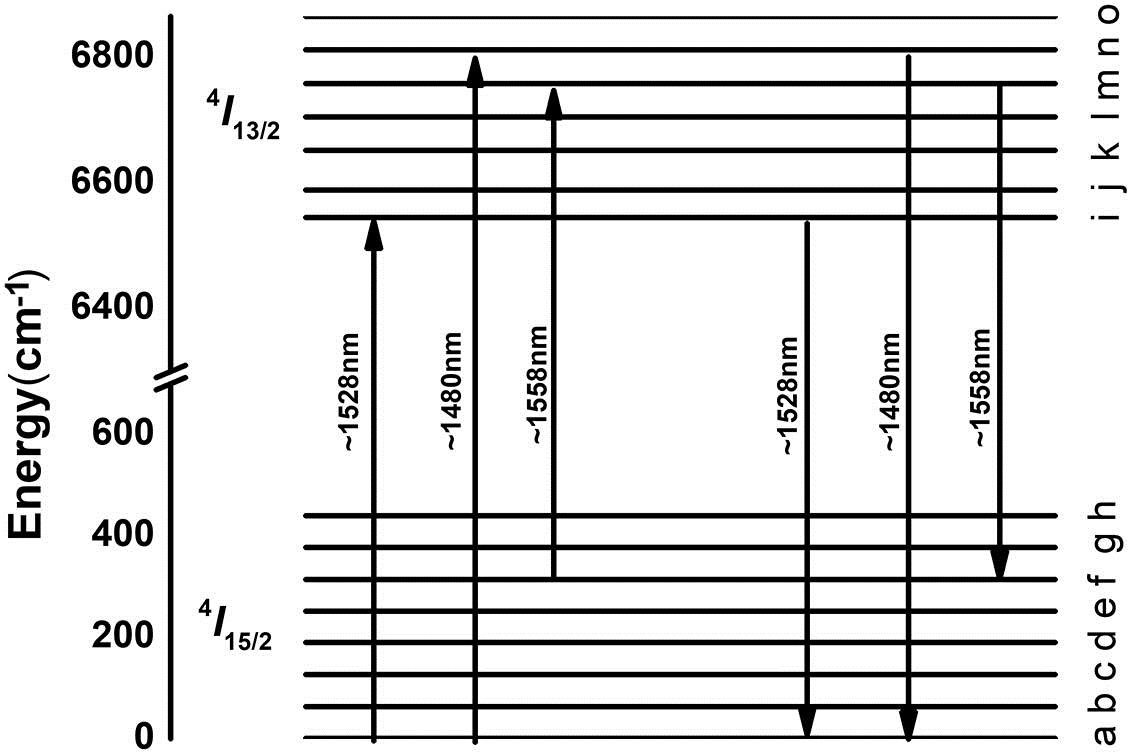
Using a heavily erbium-doped aluminosilicate fiber prepared by the sol-gel method combined with high temperature sintering, the temperature dependence of the spectrum around the 1.55 nm band and single-mode fiber laser properties were investigated, respectively. The absorption cross section increases 29.2% at ~1558 nm with the temperature increasing from 20°C to 140°C, while the emission cross section slightly increases 4.3%. In addition, the laser slope of the heavily erbium-doped aluminosilicate fiber at 1558 nm decreases 4.4% from 10.8% to 6.4% with the temperature increasing from 18°C to 440°C. Meanwhile, an experiment lasting 3 h proves that the fiber laser has excellent stability below 440°C.
140.3500 Lasers, erbium 060.2400 Fiber properties 120.6810 Thermal effects 140.3425 Laser stabilization Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 101401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Excess frequency noise induced by mechanical vibration is the dominant noise source at low Fourier frequencies in fiber-delay-line stabilized lasers. To resolve this problem, a double-winding fiber spool is designed and implemented that has ultralow acceleration sensitivity in all spatial directions. By carefully choosing the optimal geometry parameters of the fiber spool, we achieve acceleration sensitivity of 8 × 10 11/g and 3 × 10 11/g (g denotes the gravitational acceleration) in axial and radial directions, respectively.
140.3425 Laser stabilization 120.7280 Vibration analysis 060.2310 Fiber optics Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 081403
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
We demonstrate the frequency stabilization of a 1.55 μm erbium-doped fiber laser by locking it to a 5-km-long optical fiber delay line (FDL). The stabilized laser is characterized via comparison with a second identical laser system. We obtain a fractional frequency stability of better than 3 × 10 15 over time scales of 1–10 s and a laser linewidth of 0.2 Hz, which is the narrowest linewidth of an FDL-stabilized laser observed to date.
140.3425 Laser stabilization 060.2310 Fiber optics 060.2840 Heterodyne Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(7): 071407
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Division of Time and Frequency Metrology, National Institute of Metrology, Beijing 100029, China
2 Department of Precision Instrument, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
A clock laser based on a 30-cm-long ultrahigh finesse optical cavity was developed to improve the frequency stability of the Sr optical lattice clock at the National Institute of Metrology. Using this clock laser to probe the spin-polarized Sr87 atoms, a Rabi transition linewidth of 1.8 Hz was obtained with 500 ms interrogation time. Two independent digital servos are used to alternatively lock the clock laser to the S01 (mF=+9/2)→P03 (mF=+9/2) transition. The Allan deviation shows that the short-term frequency stability is better than 3.2×10 16 and averages down followed by 1.8×10 15/τ.
140.3425 Laser stabilization Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 051402





