1 苏州大学电子信息学院,江苏 苏州 215006
2 香港理工大学电子及资讯工程学系,香港 999077
3 中山大学电子与信息工程学院,广东 广州 510275
针对跨海光通信系统,海岸两侧供电架构导致的能效问题是限制其容量的主要因素。多根单模光纤(M-SMF)复用是目前阶段提高通信海缆容量的主要解决方案。然而,海缆中可容纳的光纤数量往往受限于其机械特性和下缆难度,可容纳光纤数量目前通常限制在32以下。因此,高复用密度的空分复用技术有望在海缆通信领域中展现其优势。对基于多芯光纤(MCF)海缆的能效公式进行了理论推导,对比了MCF海缆与M-SMF海缆的能效特性,并分析多芯耦合器插损、芯间串扰等边际参数对系统总体能效的影响。结果证明:采用4芯光纤在跨大西洋海缆和跨太平洋海缆中的最优光纤数目分别为86和14;采用7芯光纤在跨大西洋海缆和跨太平洋海缆中的最优光纤数目分别为50和8。在海缆最大容纳光纤数目(32)情况下:4芯光纤在跨大西洋场景和跨太平洋场景中相比M-SMF海缆可以提升能效至2.50倍和1.13倍;7芯光纤在跨大西洋场景和跨太平洋场景中相比M-SMF海缆可以提升能效至3.20倍和1.13倍。
光通信 光纤特征 光纤表征 光复用 光学学报
2022, 42(15): 1506005
1 北京邮电大学电子工程学院信息光子学与光通信国家重点实验室,北京 100876
2 北京邮电大学天地互联与融合北京市重点实验室,北京 100876
为了降低少模光纤中的模间串扰,提出了一种新型双耦合环辅助的少模光纤结构设计。首先用COMSOL仿真软件对6-LP光纤结构进行建模,并分析了影响模式间耦合的主要因素,然后对双耦合环结构的5个参数进行仿真分析。结果表明,在6-LP少模光纤中,LP21模和LP02模的有效折射率最接近,其差值是影响串扰的主要因素;该结构中LP21模和LP02模的最小模间折射率差为1.5×10-3,是同等条件下传统阶跃结构的1.88倍,少模光纤中的模间串扰问题得到有效缓解。
光通信 模分复用 少模光纤 双耦合环结构 光纤特性
西安医学院医学技术学院物理教研室,陕西 西安 710021
为进一步提高掺铥双包层光纤(DCF)激光器的输出功率,从提高DCF对泵浦光的吸收效率出发,数值模拟了具有不同纤芯直径和内包层形状的DCF的泵浦吸收特性。模拟结果表明,对于具有不同纤芯直径的新型内包层DCF,随着反射次数的增加,其泵浦吸收效率趋于100%;对于具有不同内包层形状的DCF,新型内包层DCF的泵浦吸收效率最高。实验中,选择正六边形内包层和新型内包层掺铥DCF为工作物质,两种掺铥DCF激光器的输出功率分别为13.2 W和14.8 W,斜率效率分别为31%和35%。新型内包层掺铥DCF激光器的输出功率比正六边形内包层掺铥DCF激光器提高了12.1%,这表明新型内包层DCF更有利于实现高效的泵浦吸收。
光纤光学 光纤性质 新型内包层 掺铥光纤 吸收效率 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(17): 1706009

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonic Technology Laboratory, College of Electronics and Optical Engineering & College of Microelectronics, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210023, China
2 Optical Communications Laboratory, Ocean College, Zhejiang University, Zhoushan 316021, China
3 Aston Institute of Photonic Technologies, Aston University, Birmingham B4 7ET, UK
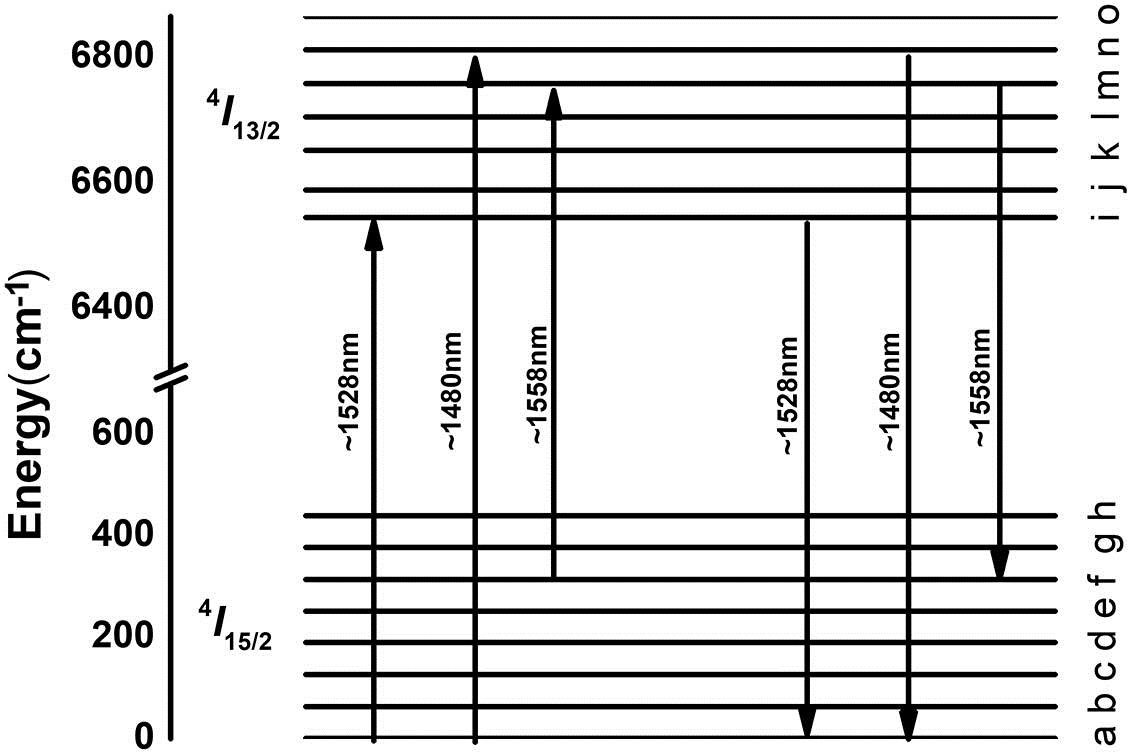
The spectral characteristics and sensitivities of a tapered two-mode fiber sandwiched between two single-mode fibers are systematically investigated. Theoretical calculations reveal that a dispersion turning point (DTP) appears when the group effective refractive index (RI) difference between the fundamental mode and the higher-order mode equals zero; as a result, ultrahigh RI sensitivities can be achieved. Furthermore, the location of the DTP is strongly dependent on the tapering condition. Then, we experimentally demonstrate high sensitivities of the RI sensor with the waist diameter of ~4 μm by means of immersing it in a flow cell filled with glycerol solution. In further tracking of the resonant wavelength shift around the DTP, it is found that the proposed RI sensor exhibits a sensitivity of 1.81 × 104 nm/RIU and a limit of detection down up to 3.29 × 10 5 RIU in a liquid glycerol solution.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.2400 Fiber properties Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(11): 110604
1 厦门大学电子科学与技术学院光波技术研究所, 福建 厦门 361005
2 山东大学海洋研究院, 山东 青岛 266237
介绍了一种特殊设计的少模光纤及由少模光纤构成的单模光纤-少模光纤-单模光纤(SFS)传感结构。在对轴激发条件下,少模光纤芯子中仅有基模LP01和第一圆对称高阶模LP02传输,且SFS结构的传输光谱在工作波长范围内有一个特征波长。在特征波长附近相邻两个干涉峰间的波长间距达到最大,且在特征波长处干涉仪的输出光强不随波长变化,这使得特征波长在光谱中唯一且容易识别。理论和实验研究了SFS结构传输光谱的特征波长及其两边干涉条纹随轴向应变、温度、弯曲、液体折射率的传感特性,并将SFS结构用于轴向应变、温度、弯曲、位移、外界折射率和相对湿度的大范围、高灵敏度、多参量同时检测,为解决常规干涉仪存在的测量范围小、输出多值性等问题提供解决方案。
光纤光学 光纤特性 少模光纤 特征波长 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(17): 170620
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Using a heavily erbium-doped aluminosilicate fiber prepared by the sol-gel method combined with high temperature sintering, the temperature dependence of the spectrum around the 1.55 nm band and single-mode fiber laser properties were investigated, respectively. The absorption cross section increases 29.2% at ~1558 nm with the temperature increasing from 20°C to 140°C, while the emission cross section slightly increases 4.3%. In addition, the laser slope of the heavily erbium-doped aluminosilicate fiber at 1558 nm decreases 4.4% from 10.8% to 6.4% with the temperature increasing from 18°C to 440°C. Meanwhile, an experiment lasting 3 h proves that the fiber laser has excellent stability below 440°C.
140.3500 Lasers, erbium 060.2400 Fiber properties 120.6810 Thermal effects 140.3425 Laser stabilization Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 101401

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Next Generation Internet Access National Engineering Laboratory (NGIA), School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 1037 Luoyu Road, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Institute of Physics and Applied Physics, Yonsei University, Seoul 120-749, South Korea
3 School of EEE, Nanyang Technological University, 50 Nanyang Avenue, Singapore 639798, Singapore
We propose a novel waveguide design of a polarization-maintaining few mode fiber (PM-FMF) supporting ≥10 non-degenerate modes, utilizing a central circular air hole and a circumjacent elliptical-ring core. The structure endows a new degree of freedom to adjust the birefringence of all the guided modes, including the fundamental polarization mode. Numerical simulations demonstrate that, by optimizing the air hole and elliptical-ring core, a PM-FMF supporting 10 distinctive polarization modes has been achieved, and the effective index difference Δneff between the adjacent guided modes could be kept larger than 1.32×10 4 over the whole C+L band. The proposed fiber structure can be flexibly tailored to support an even larger number of modes in PM-FMF (14-mode PM-FMF has been demonstrated as an example), which can be readily applicable to a scalable mode division multiplexing system.
Fibers, polarization-maintaining Fiber properties Fiber design and fabrication Fiber optics communications Photonics Research
2017, 5(3): 03000261

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Electrical Engineering Department, King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Dhahran 31261, Saudi Arabia
To design a compact erbium-doped fiber laser, a high-concentration erbium-doped fiber (EDF) is needed. However, increasing the erbium ion (Er3+) concentration can reduce the EDF performance via the Er3+-Er3+ interaction. In this Letter, we investigate the Er3+-Er3+ interaction effect by designing a tunable erbium-doped fiber-ring laser (EDFRL). This is the first time (to the best of our knowledge) that someone has considered different numbers of ions per cluster and simulated the EDFRL output power degradation due to ion–ion interaction. If the number of ions in the cluster is increased, the lasing output power will decrease accordingly. The most dominant effect is seen in the 1530 nm wavelength region, where the EDF shows a higher signal absorption compared to the other wavelength region. Moreover, a comparison has been done for lasing performance analysis with different dopant ion concentrations. The comparison results show that a higher dopant concentration is advantageous for longer-wavelength lasing.
060.2290 Fiber materials 060.2320 Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators 060.2400 Fiber properties 060.2410 Fibers, erbium 060.3510 Lasers, fiber Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(1): 010601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Specialty Fiber Optics and Optical Access Networks, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China
2 Laboratory for Microstructures, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
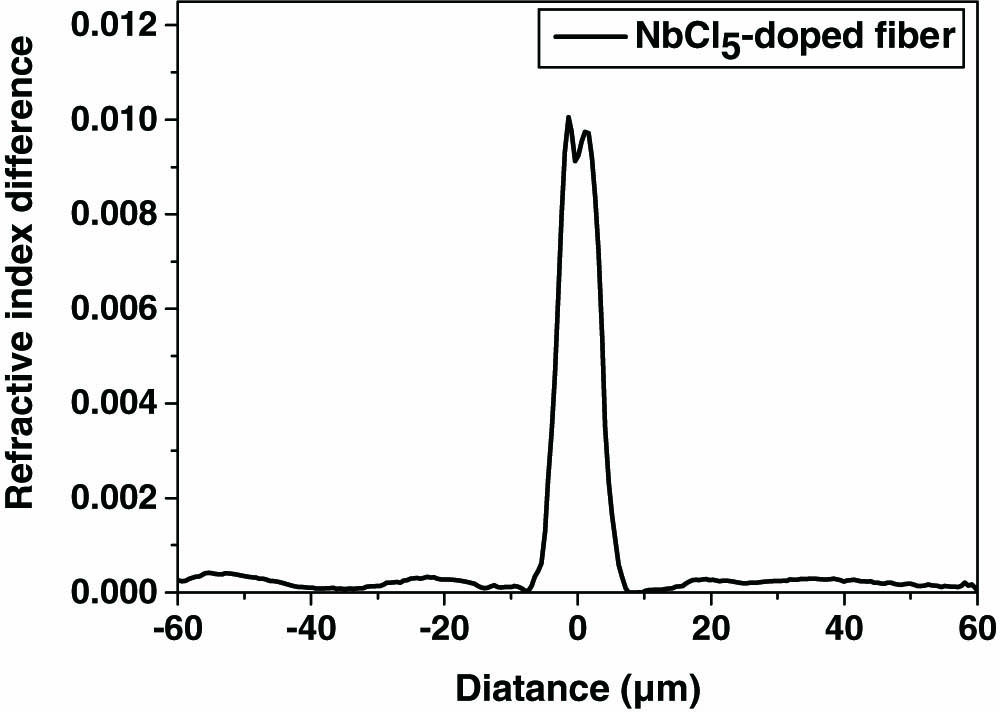
Two kinds of Nb-doped silica fibers, an NbCl5-doped fiber and an Nb2O5-doped fiber, are fabricated and characterized in this Letter. First, the refractive index profiles of both fibers are obtained, and then their Raman spectra are measured with 785 nm exciting light. The Nb-doped fibers’ Raman spectra are compared with a conventional GeO2-doped single-mode silica fiber that is prepared with the same method and under the same conditions. As a result, the Raman gain coefficients of the Nb-doped silica fiber core are obtained. The experimental results show that Nb2O5 doping can enhance the Raman scattering intensity of the optical fibers.
060.2270 Fiber characterization 290.5860 Scattering, Raman 060.2400 Fiber properties 060.2290 Fiber materials Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(10): 100602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Lab of All Optical Network & Advanced Telecommunication Network of EMC, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
2 Institute of Lightwave Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
We present a single-mode multilayer-core fiber with a large mode area (LMA) and a low bending loss in this Letter. A low equivalent core-cladding refractive index difference is achieved by exploiting the multilayer structure. The multilayer structure has a better bending performance than a traditional step-index core and this structure also contributes to realizing different curved refractive index profiles that have a better bending performance. An index trench is also introduced to dramatically reduce the bending loss. The experimental results show that, at a wavelength of 1550 nm, the mode area of the fabricated fiber is about 215.5 μm2 and the bending loss is 0.58 dB/turn at a 10 mm bending radius. The LMA and excellent bending performance can be obtained simultaneously with the proposed fiber.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2310 Fiber optics 060.2400 Fiber properties 060.2430 Fibers, single-mode Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 120601





